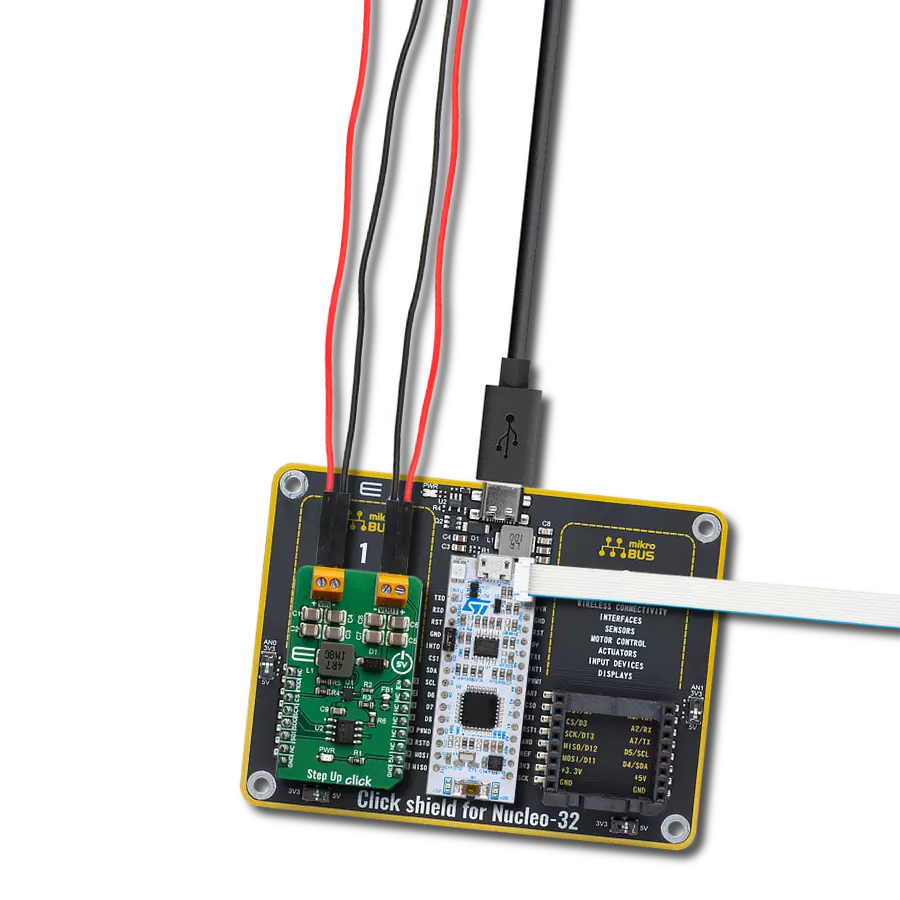
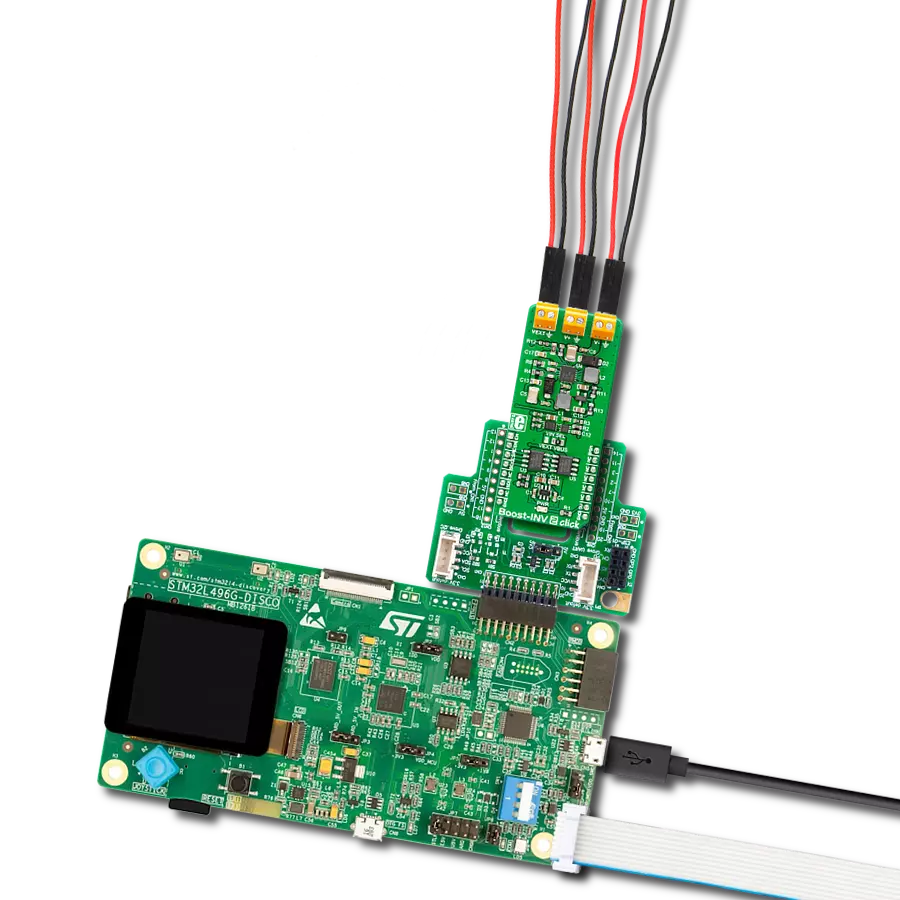
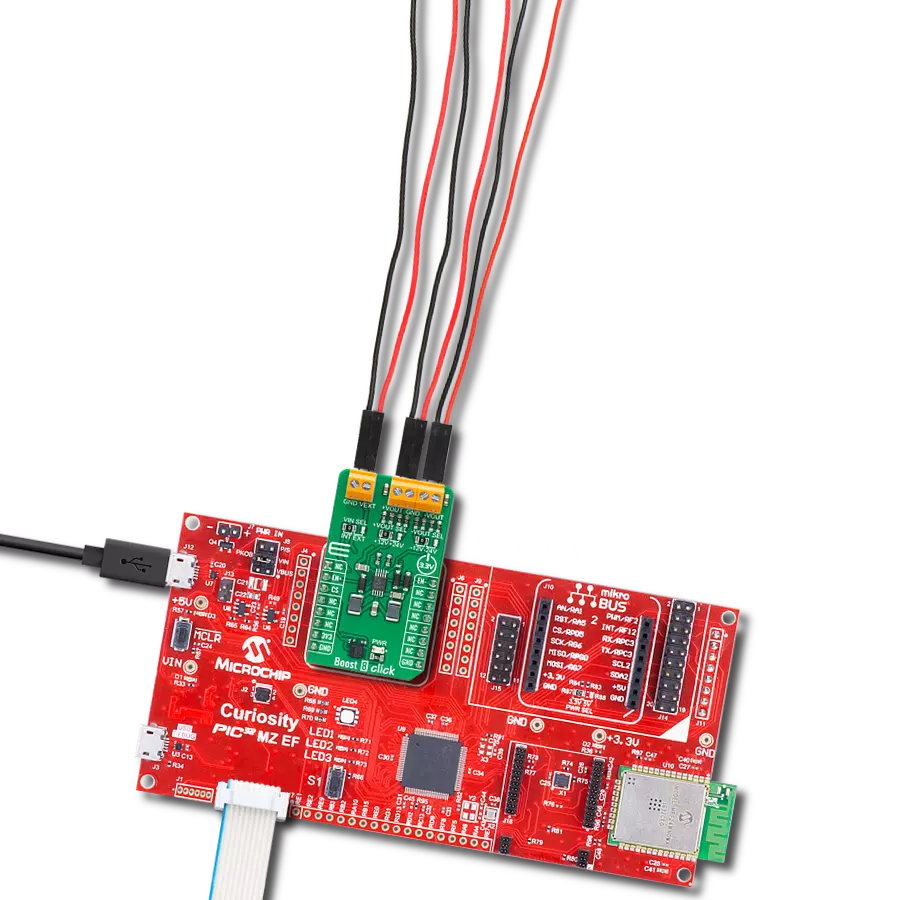
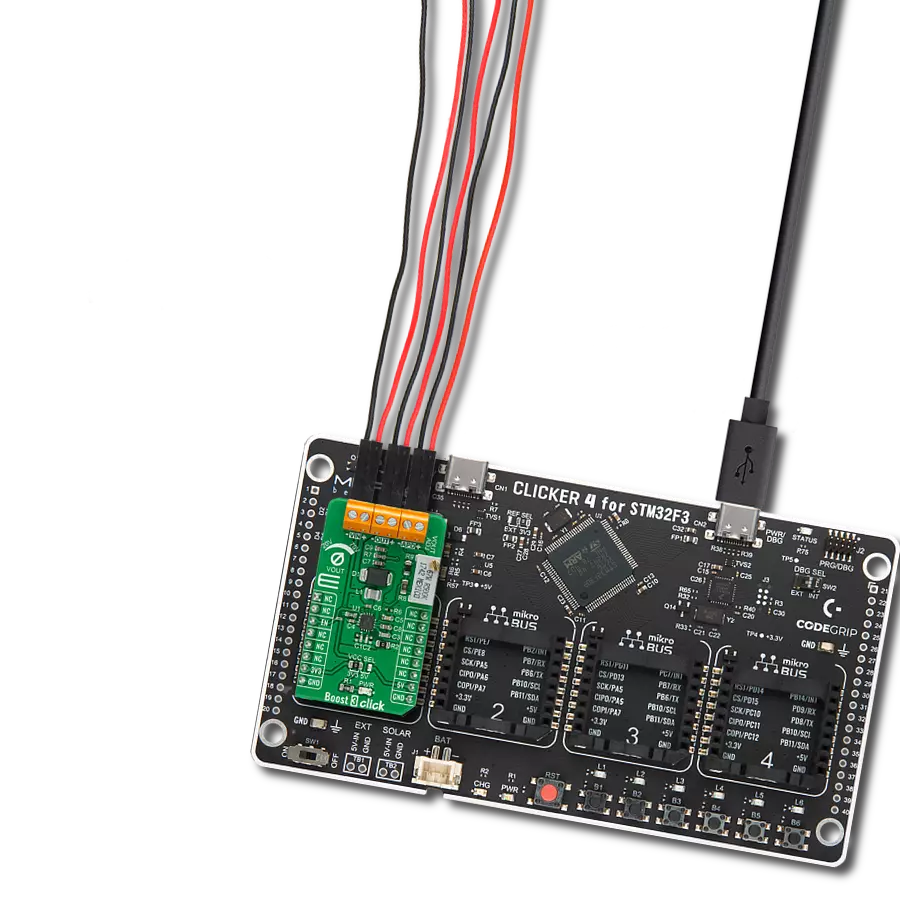
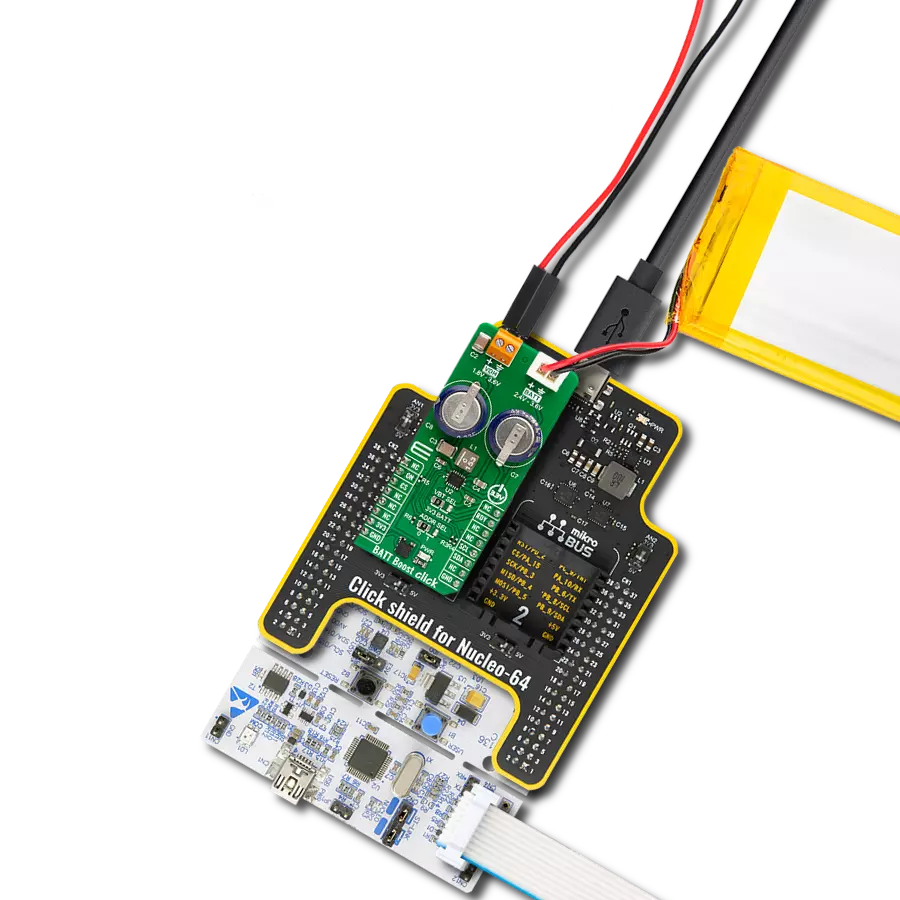
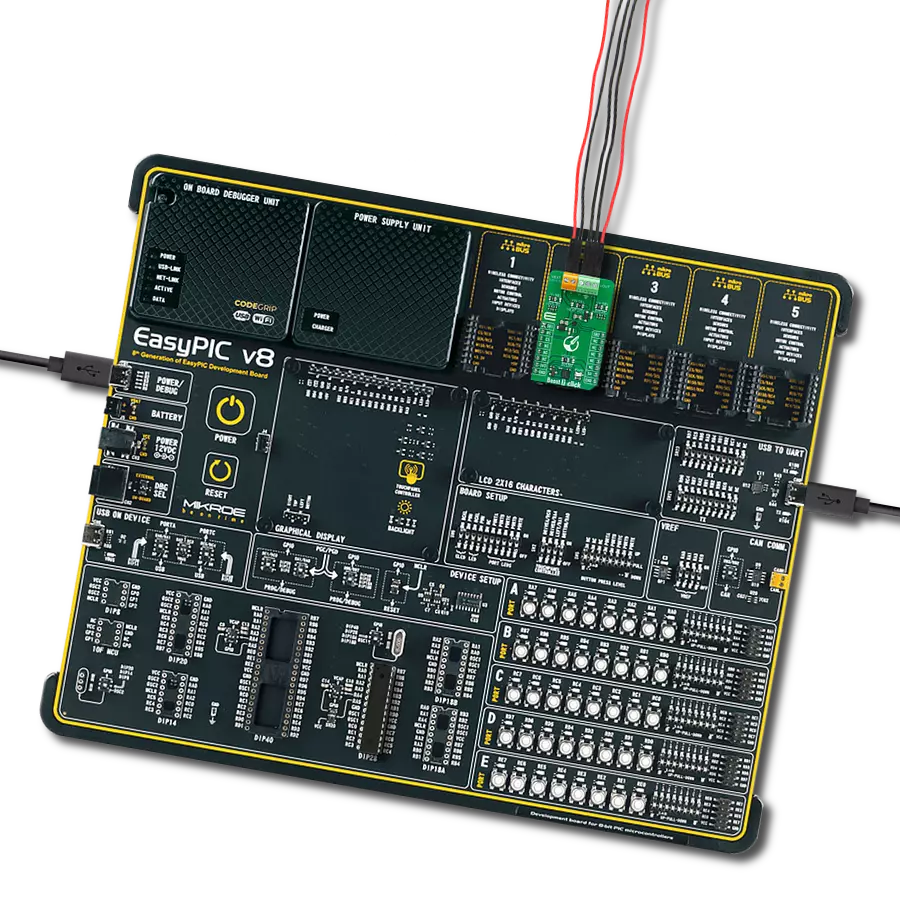
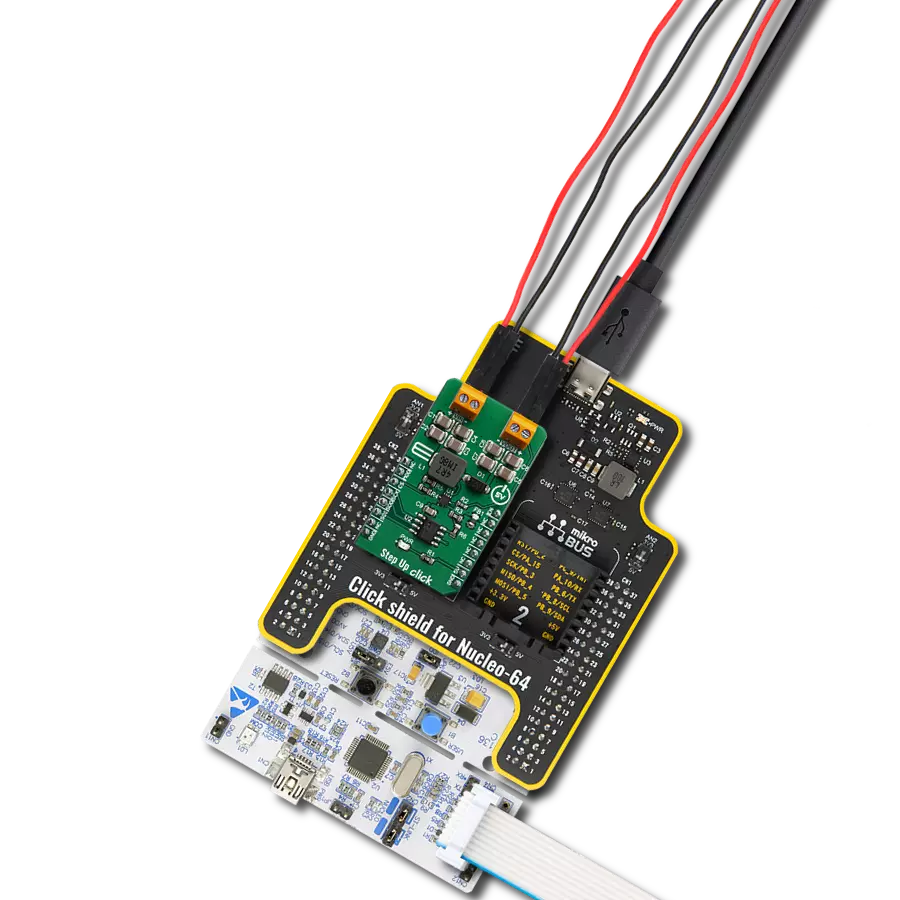
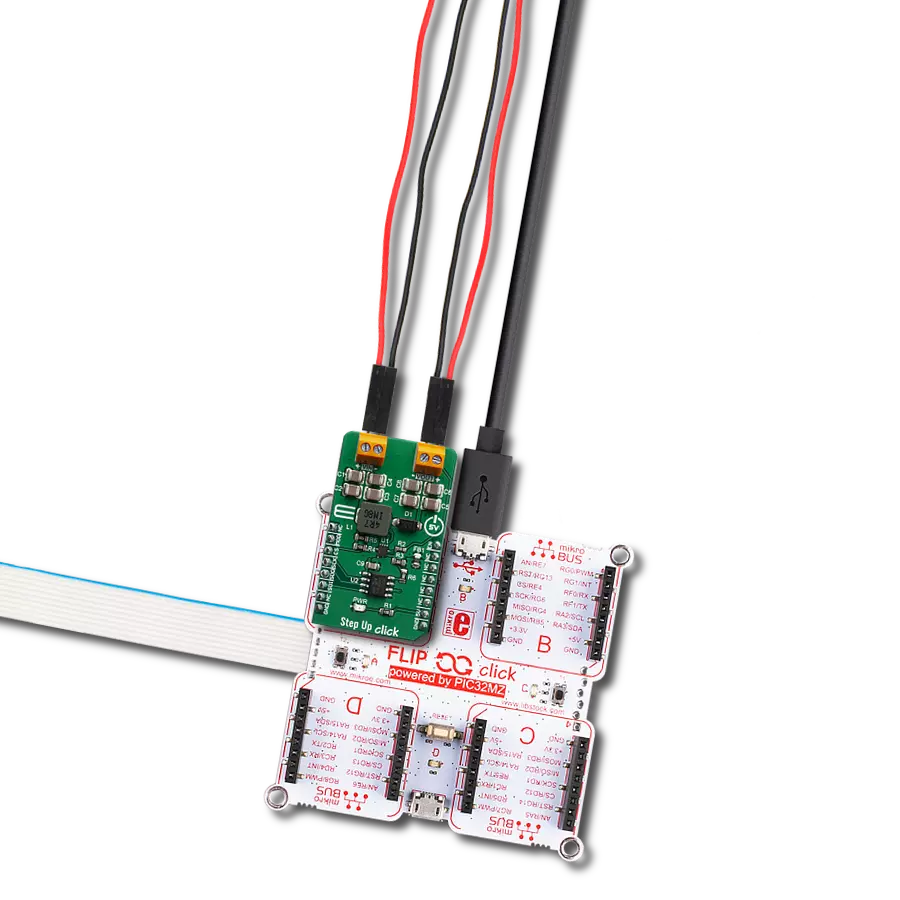
Create a boost (step-up) DC-DC converter with extremely high efficiency and low input voltage aimed at the low-power IoT market, battery-powered sensors, and other devices
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
Nano Power Click is based on the MAX17222, a nano power synchronous boost converter with True Shutdown™ technology, from Analog Devices. The device operates in several modes, allowing optimal utilization of the available power. The device will automatically switch to a different working mode depending on the connected load, providing optimal conditions for a given situation. The MAX17222 uses the pulse frequency modulation control (PFM) topology, which allows high efficiency over a wide range of output currents. The PFM control allows continuous and discontinuous (CCM and DCM) switching modes. Operation of the MAX17222 changes with the connected load, as mentioned above. When the load is very light, the device operates in the Ultra Low Power Mode (ULPM), and the switching is performed in discontinuous mode (DCM). The ULPM is typically used when the device connected at the output is in standby or power-down mode, draining a low current. As the current requirement increases, the MAX17222 device switches to the Low Power mode and further to the High Power mode (LPM and HPM). These modes result in cleaner output and less ripple than the ULPM
mode. When working in HPM, the continuous switching mode (CCM) is used (with no pulses being skipped), providing low noise, ripple-free output voltage, which is suitable for various sensor measurements, A/D conversions, wireless communication, and other noise and ripple-sensitive applications. The EN pin of the MAX17222 is used to enable this device. When a transition from LOW to HIGH logic state appears at this pin (rising edge), it will activate the IC, and regulated 5V will appear at the output (providing the proper input voltage is present). This pin is routed to the mikroBUS™ CS pin, labeled EN. The device will remain enabled, even if the input voltage drops to 0.4V, thanks to the internal ETP section of the MAX17222 IC. Holding the EN pin to a HIGH logic state once the conversion is started results in slightly increased power consumption. The Power LED indicator is connected to the 5V rail of the mikroBUS™ and does not affect the power consumption on the connected external power supply. The power consumption calculations in the datasheet remain true and are not affected by any external components of this Click board™. The Power LED indicates the presence of the
mikroBUS™ voltage, signaling that the EN pin can be controlled via the host MCU. The external power supply can be connected to the input terminals between the VIN and GND, ranging from 0.95V up to 5.5V. However, for an optimal operation of the Nanopower click, the input voltage should be lower than the output voltage. The Nanopower click allows a maximum peak current of 500mA before the current limit protection activates. The output voltage is fixed at 5V by a single resistor, connected between the SEL pin of the IC and GND. This resistor is 0 Ω, and it is basically - an SMD jumper. Using other values (listed in the datasheet of the MAX17222 IC) makes it possible to change the output voltage to a value different than 5V. Please consult the datasheet to select the resistor for the given output voltage properly. The control of the Nanopower click is extremely simple, and it is reduced to controlling a single pin. However, provided library offers functions that simplify and speed up application development even more. The included example application demonstrates their use. This application can be used as a reference for custom projects.
Features overview
Development board
Nucleo-64 with STM32F091RC MCU offers a cost-effective and adaptable platform for developers to explore new ideas and prototype their designs. This board harnesses the versatility of the STM32 microcontroller, enabling users to select the optimal balance of performance and power consumption for their projects. It accommodates the STM32 microcontroller in the LQFP64 package and includes essential components such as a user LED, which doubles as an ARDUINO® signal, alongside user and reset push-buttons, and a 32.768kHz crystal oscillator for precise timing operations. Designed with expansion and flexibility in mind, the Nucleo-64 board features an ARDUINO® Uno V3 expansion connector and ST morpho extension pin
headers, granting complete access to the STM32's I/Os for comprehensive project integration. Power supply options are adaptable, supporting ST-LINK USB VBUS or external power sources, ensuring adaptability in various development environments. The board also has an on-board ST-LINK debugger/programmer with USB re-enumeration capability, simplifying the programming and debugging process. Moreover, the board is designed to simplify advanced development with its external SMPS for efficient Vcore logic supply, support for USB Device full speed or USB SNK/UFP full speed, and built-in cryptographic features, enhancing both the power efficiency and security of projects. Additional connectivity is
provided through dedicated connectors for external SMPS experimentation, a USB connector for the ST-LINK, and a MIPI® debug connector, expanding the possibilities for hardware interfacing and experimentation. Developers will find extensive support through comprehensive free software libraries and examples, courtesy of the STM32Cube MCU Package. This, combined with compatibility with a wide array of Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), including IAR Embedded Workbench®, MDK-ARM, and STM32CubeIDE, ensures a smooth and efficient development experience, allowing users to fully leverage the capabilities of the Nucleo-64 board in their projects.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M0
MCU Memory (KB)
256
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
64
RAM (Bytes)
32768
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Nucleo-64 comes equipped with two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the STM32 Nucleo-64 board with no effort. This way, Mikroe allows its users to add any functionality from our ever-growing range of Click boards™, such as WiFi, GSM, GPS, Bluetooth, ZigBee, environmental sensors, LEDs, speech recognition, motor control, movement sensors, and many more. More than 1537 Click boards™, which can be stacked and integrated, are at your disposal. The STM32 Nucleo-64 boards are based on the microcontrollers in 64-pin packages, a 32-bit MCU with an ARM Cortex M4 processor operating at 84MHz, 512Kb Flash, and 96KB SRAM, divided into two regions where the top section represents the ST-Link/V2 debugger and programmer while the bottom section of the board is an actual development board. These boards are controlled and powered conveniently through a USB connection to program and efficiently debug the Nucleo-64 board out of the box, with an additional USB cable connected to the USB mini port on the board. Most of the STM32 microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the STM32 Nucleo-64 board with our Click Shield for Nucleo-64, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Nano Power Click driver.
Key functions:
nanopw_enable_device- This function enables and disables the device
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Nano Power Click example
*
* # Description
* This aplication performs control of the device's voltage.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes GPIO driver.
*
* ## Application Task
* Turns device on for 5 seconds and than turns device off for 10 seconds,
* then the output voltage starts to fall.
* When input voltage rises from 0.8V to 5.5V,
* the output voltage rises from 5.1V to 5.25V.
* When input voltage is less than 0.8V, the output voltage is less than 5V.
*
*
* \author Petar Suknjaja
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "nanopower.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static nanopower_t nanopower;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
nanopower_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info(&logger, "---- Application Init ----");
// Click initialization.
nanopower_cfg_setup( &cfg );
NANOPOWER_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
nanopower_init( &nanopower, &cfg );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
log_printf(&logger,"Device enabled\r\n");
nanopw_enable_device( &nanopower, NANOPW_ENABLE_DEVICE );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf(&logger,"Device disabled\r\n");
nanopw_enable_device( &nanopower, NANOPW_DISABLE_DEVICE );
// 10 seconds delay
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Boost