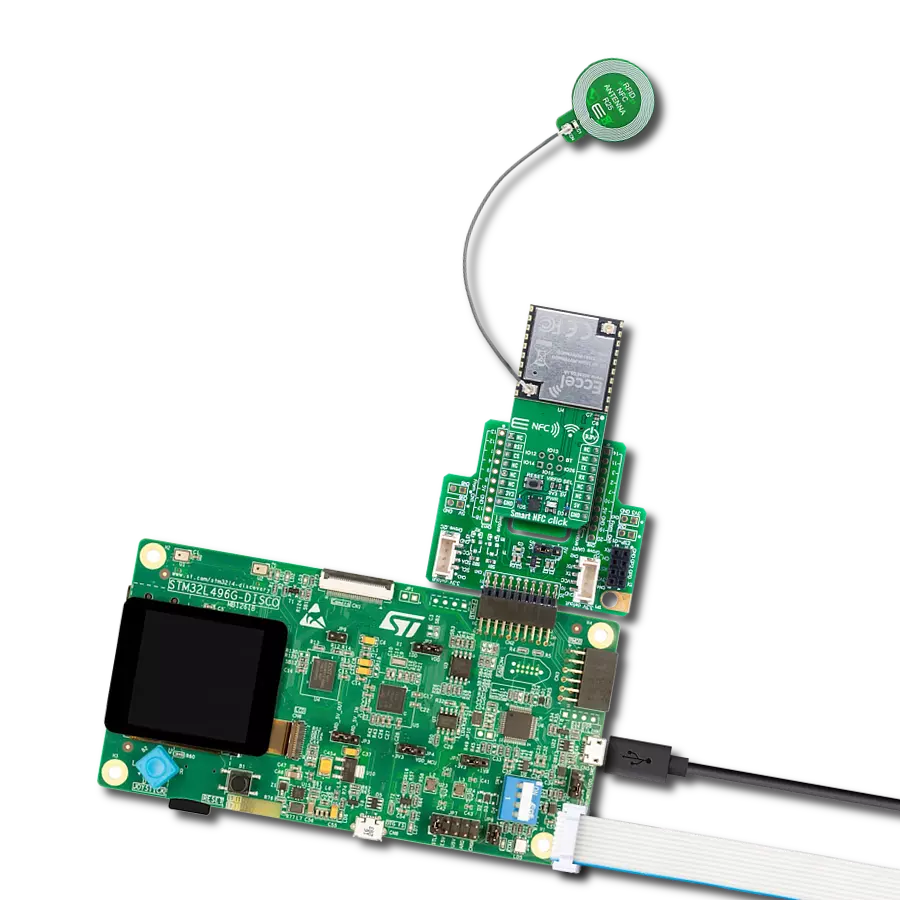
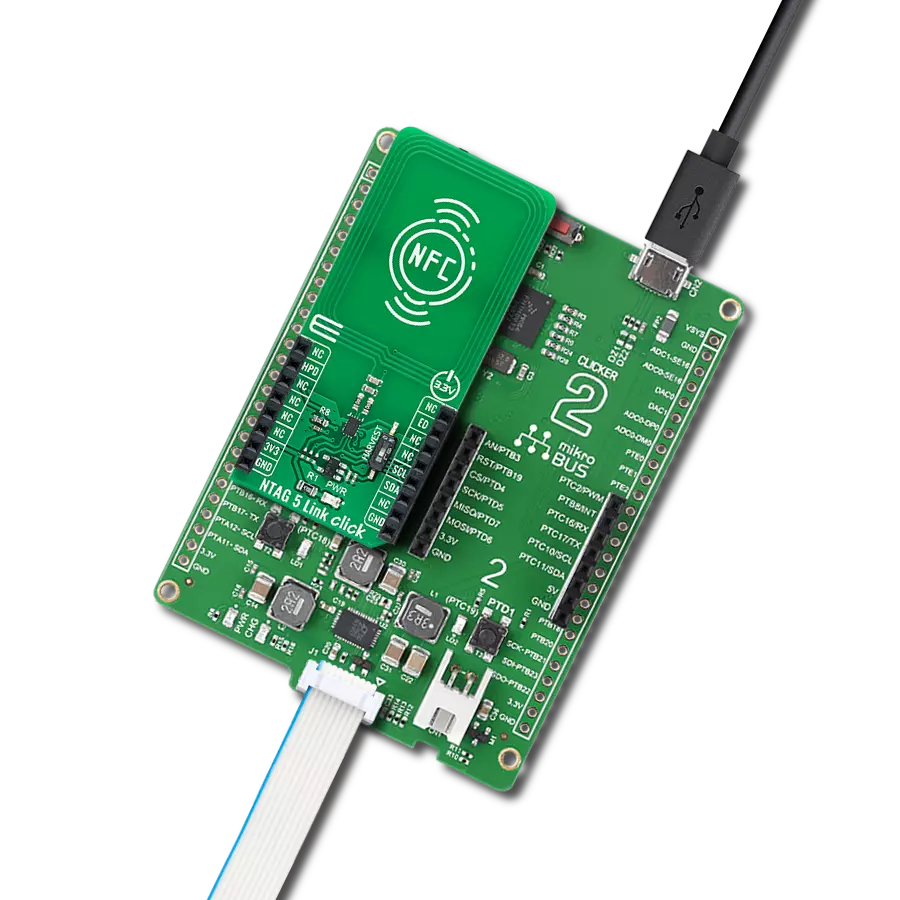
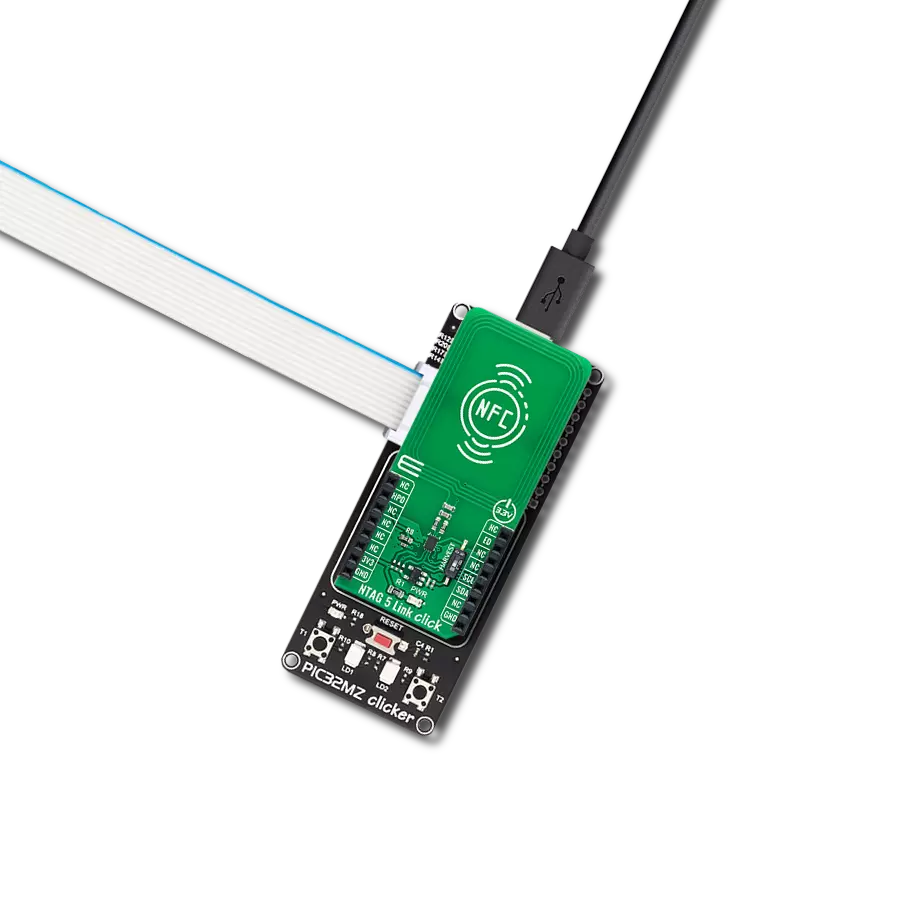
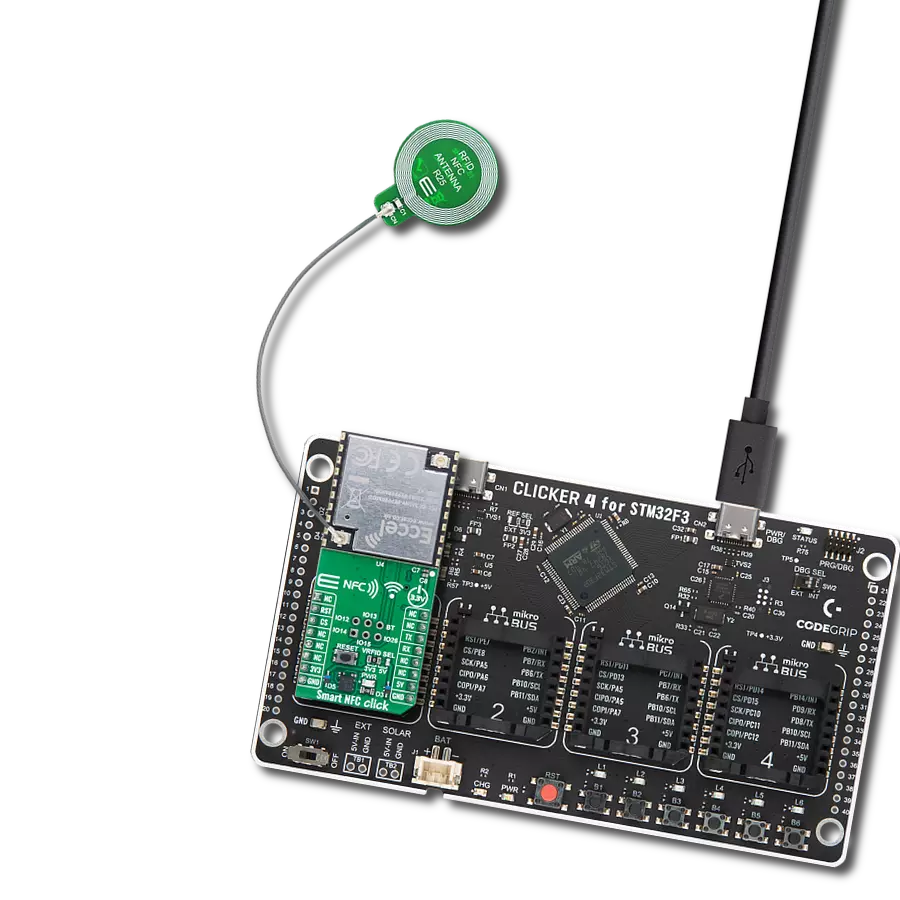
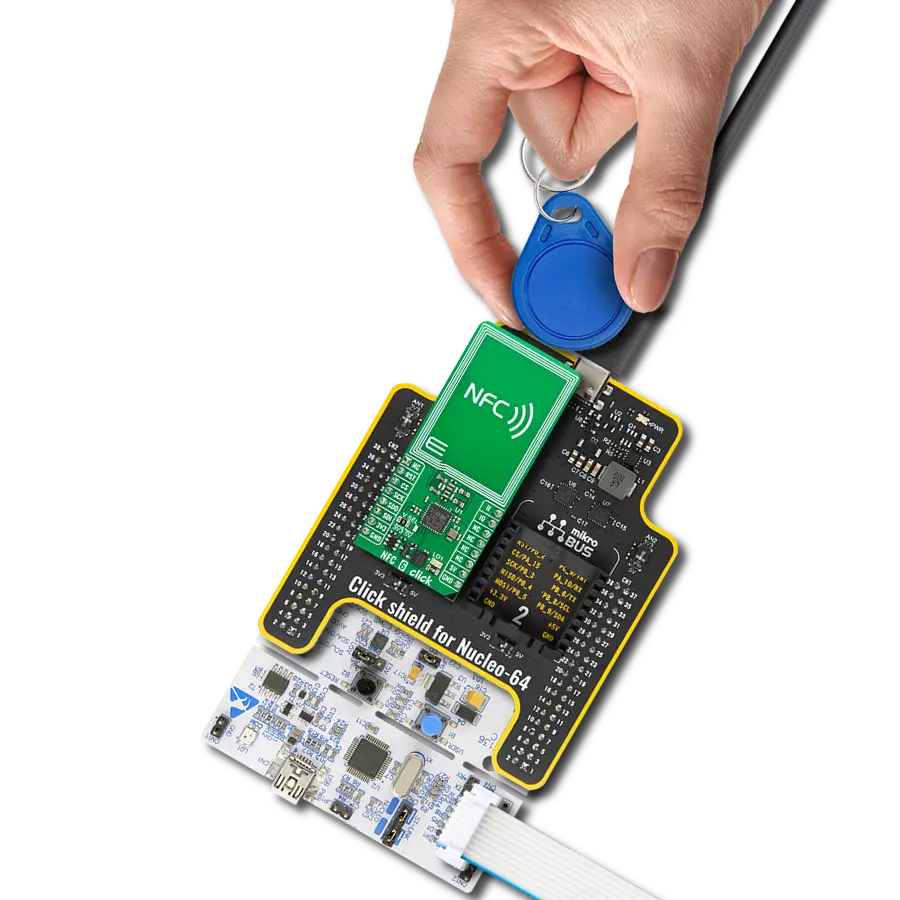
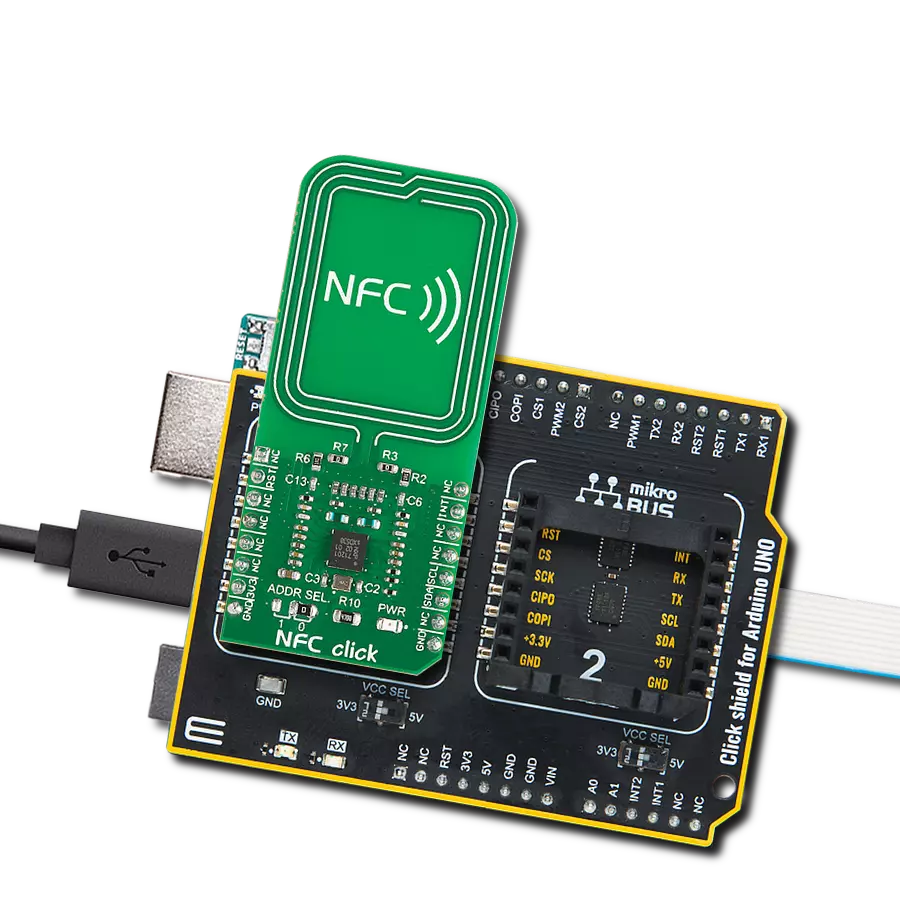
High-sensitivity NFC functionality with low power requirements, ideal for mobile devices and smart home gateways
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
NFC 7 Click is based on the PN7160, a Near Field Communication (NFC) controller from NXP. This versatile NFC solution is designed to comply with NFC Forum and NCI 2.0 standards, offering robust integration for a wide range of NFC-enabled applications. This version of NFC 7 Click communicates with the host MCU exclusively through an SPI interface (PN7160B1HN/C100E) and provides an optimized architecture for low-power consumption. The PN7160 features multiple power-saving modes, including a Hard Power-Down state, a firmware-activated Standby state, and a low-power polling loop for automatic device discovery to ensure efficient energy use across various operating scenarios. NFC 7 Click is particularly well-suited for portable and low-power applications where reliable NFC functionality is essential, including mobile devices, wearable technology, personal digital assistants, consumer electronics, and smart home gateways. At its core, the PN7160 incorporates a new generation RF contactless front-end, supporting transmission modes compliant with NFCIP-1 and NFCIP-2, as well as ISO/IEC 14443, ISO/IEC 15693, MIFARE,
and FeliCa standards. This advanced design significantly enhances performance by delivering higher sensitivity and active load modulation capabilities. These improvements allow NFC 7 Click to maintain reliable communication even with small antenna designs, such as the one integrated into this board. The PN7160 introduces Enhanced Dynamic Load Modulation Amplitude (DLMA), which adapts the modulation amplitude dynamically based on external field strength. This feature extends communication distances in card emulation mode, ensuring independent phase adjustments for Type A, B, and F communication with 5° precision. Additionally, dynamic power control enables the board to operate at maximum power in reader mode without surpassing standard-defined limits, even at zero distance. In standalone card functionality, the PN7160 can operate autonomously once configured by the host MCU, allowing Passive Integrated Circuit Card (PICC) features to function without requiring the host to remain powered on. This makes NFC 7 Click an ideal solution for energy-efficient and always-on NFC applications. As mentioned, NFC 7 Click uses
a standard SPI communication protocol, allowing the host MCU to control the PN7160 with clock frequencies up to 7MHz. At the back of the board features a set of resistors that need to be populated depending on the board version; in this case, only the resistors in the SPI positions are populated, as required for SPI functionality. Besides the interface pins, NFC 7 Click incorporates the VEN pin, which places the device into Hard Power-Down mode to conserve energy when not in use. It also uses the IRQ pin to handle interrupt requests, providing a mechanism for the host MCU to respond promptly to events such as tag detection, completed operations, or errors, enhancing the overall responsiveness and efficiency of NFC-based applications. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
6LoWPAN Clicker is a compact starter development board that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It comes with an onboard 32-bit PIC microcontroller, the PIC32MX470F512H from Microchip, a USB connector, LED indicators, buttons, a mikroProg connector, and a header for interfacing with external electronics. Along with this microcontroller, the board also contains a 2.4GHz ISM band transceiver, allowing you to add wireless communication to your target application. Its compact design provides a fluid and immersive working experience, allowing access anywhere
and under any circumstances. Each part of the 6LoWPAN Clicker development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the possibility of choosing the 6LoWPAN Clicker programming method, using USB HID mikroBootloader, or through an external mikroProg connector for PIC, dsPIC, or PIC32 programmer, the Clicker board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development kit. The USB Micro-B connection can provide up to 500mA of current for the Clicker board, which is more than enough to operate all onboard and additional modules, or it can power
over two standard AA batteries. All communication methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board, including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, reset button, and several buttons and LED indicators. 6LoWPAN Clicker is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem, allowing you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
512
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
64
RAM (Bytes)
131072
You complete me!
Accessories
RFID tag operating at 13.56MHz adheres to the ISO14443-A standard, ensuring high-frequency communication. This proximity card technology, often exemplified by MIFARE cards, facilitates secure and contactless interactions in applications like access control, public transport, and payment systems. The ISO14443-A standard defines the communication protocol, incorporating anti-collision mechanisms for simultaneous card handling. These RFID tags possess variable memory capacities, ranging from a few bytes to kilobytes, catering to diverse application needs. Ensuring data security, the standard integrates features such as encryption and authentication. These tags, exemplified by MIFARE technology, are widely used for their efficiency and are vital in enhancing convenience and security in diverse identification and access scenarios.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
NFC 7 Click - SPI demo application is developed using the NECTO Studio, ensuring compatibility with mikroSDK's open-source libraries and tools. Designed for plug-and-play implementation and testing, the demo is fully compatible with all development, starter, and mikromedia boards featuring a mikroBUS™ socket.
Example Description
This example demonstrates the use of NFC 7 SPI Click board by handling the detection and processing of various NFC technologies and protocols, and ensuring the application can respond to different NFC card types (A,B,F,V).
Key functions:
nfc7spi_cfg_setup- Config Object Initialization function.nfc7spi_init- Initialization function.nfc7spi_default_cfg- Click Default Configuration function.nfc7spi_wait_discovery- This function waits until remote NFC device is discovered.nfc7spi_presence_check- This function waits until the discovered target device is removed.nfc7spi_stop_discovery- This function stops the RF discovery process.
Application Init
Initializes the driver and logger, performs the Click default configuration and reads the device firmware version.
Application Task
Waits for an NFC device to be discovered, checks if it supports a known NFC technology, and then handles the device based on its protocol. The application continues processing the device (reading and writing information) and waits until the card is removed. Once the card is removed, the discovery process is restarted to detect a new NFC device.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief NFC 7 SPI Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of NFC 7 SPI Click board by handling the detection
* and processing of various NFC technologies and protocols, and ensuring the application
* can respond to different NFC card types (A,B,F,V).
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and logger, performs the Click default configuration and
* reads the device firmware version.
*
* ## Application Task
* Waits for an NFC device to be discovered, checks if it supports a known NFC technology,
* and then handles the device based on its protocol. The application continues processing
* the device (reading and writing information) and waits until the card is removed.
* Once the card is removed, the discovery process is restarted to detect a new NFC device.
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "nfc7spi.h"
static nfc7spi_t nfc7spi;
static log_t logger;
/**
* @brief NFC 7 SPI handle ISO14443-3A function.
* @details This function handles discovered ISO14443-3A / Type 2 Tag (T2T) card by performing
* read/write data to memory block 32.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #nfc7spi_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return None.
* @note None.
*/
static void nfc7spi_handle_iso14443_3a ( nfc7spi_t *ctx );
/**
* @brief NFC 7 SPI handle ISO14443-4 function.
* @details This function handles discovered ISO14443-4 (ISO-DEP) card by selecting the PPSE
* (Paypass Payment System Environment) application.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #nfc7spi_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return None.
* @note None.
*/
static void nfc7spi_handle_iso14443_4 ( nfc7spi_t *ctx );
/**
* @brief NFC 7 SPI handle ISO15693 function.
* @details This function handles discovered ISO15693 card by performing read/write data
* to memory block 32.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #nfc7spi_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return None.
* @note None.
*/
static void nfc7spi_handle_iso15693 ( nfc7spi_t *ctx );
/**
* @brief NFC 7 SPI handle mifare function.
* @details This function handles discovered MIFARE card by performing read/write data
* to memory block 32.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #nfc7spi_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return None.
* @note None.
*/
static void nfc7spi_handle_mifare ( nfc7spi_t *ctx );
/**
* @brief NFC 7 SPI display card info function.
* @details This function parses and displays the discovered card info on the USB UART.
* @param[in] rf_intf : Discovered NFC remote device properties.
* @return None.
* @note None.
*/
static void nfc7spi_display_card_info ( nfc7spi_rf_intf_t rf_intf );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
nfc7spi_cfg_t nfc7spi_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
nfc7spi_cfg_setup( &nfc7spi_cfg );
NFC7SPI_MAP_MIKROBUS( nfc7spi_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( SPI_MASTER_ERROR == nfc7spi_init( &nfc7spi, &nfc7spi_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
if ( NFC7SPI_ERROR == nfc7spi_default_cfg ( &nfc7spi ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Default configuration." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_printf( &logger, " FW version: %.2X.%.2X.%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) nfc7spi.fw_version[ 0 ],
( uint16_t ) nfc7spi.fw_version[ 1 ],
( uint16_t ) nfc7spi.fw_version[ 2 ] );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
nfc7spi_rf_intf_t rf_intf;
log_printf( &logger, " WAITING FOR DEVICE DISCOVERY\r\n\n" );
if ( NFC7SPI_OK == nfc7spi_wait_discovery ( &nfc7spi, &rf_intf ) )
{
if ( ( NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_TECH_PASSIVE_POLL_NFC_A == rf_intf.mode_tech ) ||
( NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_TECH_PASSIVE_POLL_NFC_B == rf_intf.mode_tech ) ||
( NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_TECH_PASSIVE_POLL_NFC_F == rf_intf.mode_tech ) ||
( NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_TECH_PASSIVE_POLL_15693 == rf_intf.mode_tech ) )
{
for ( ; ; )
{
nfc7spi_display_card_info ( rf_intf );
switch ( rf_intf.protocol )
{
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_PROT_T2T:
{
nfc7spi_handle_iso14443_3a ( &nfc7spi );
break;
}
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_PROT_ISODEP:
{
nfc7spi_handle_iso14443_4 ( &nfc7spi );
break;
}
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_PROT_T5T:
{
nfc7spi_handle_iso15693 ( &nfc7spi );
break;
}
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_PROT_MIFARE:
{
nfc7spi_handle_mifare ( &nfc7spi );
break;
}
default:
{
break;
}
}
if ( !rf_intf.more_tags )
{
break;
}
nfc7spi_reader_act_next ( &nfc7spi, &rf_intf );
}
nfc7spi_presence_check ( &nfc7spi, &rf_intf );
log_printf ( &logger, " - CARD REMOVED\r\n\n" );
nfc7spi_stop_discovery ( &nfc7spi );
while ( NFC7SPI_OK != nfc7spi_start_discovery ( &nfc7spi ) );
}
else
{
log_printf ( &logger, " - WRONG DISCOVERY\r\n\n" );
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static void nfc7spi_handle_iso14443_3a ( nfc7spi_t *ctx )
{
#define BLK_NB_ISO14443_3A 32
#define DATA_WRITE_ISO14443_3A 0x11, 0x22, 0x33, 0x44
uint8_t rd_block[ ] = { NFC7SPI_T2T_CMD_READ, BLK_NB_ISO14443_3A };
uint8_t wr_block[ ] = { NFC7SPI_T2T_CMD_WRITE, BLK_NB_ISO14443_3A, DATA_WRITE_ISO14443_3A };
err_t error_flag = NFC7SPI_OK;
// Read block
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = sizeof ( rd_block );
memcpy ( ctx->pkt_data.payload, rd_block, ctx->pkt_data.payload_len );
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) ||
( NFC7SPI_NCI_STAT_OK != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u failed with error %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 1 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u: ", ( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 1 ] );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < 4; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
// Write block
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = sizeof ( wr_block );
memcpy ( ctx->pkt_data.payload, wr_block, ctx->pkt_data.payload_len );
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) || ( NFC7SPI_T2T_ACK != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ 0 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Write block %u failed with error %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) wr_block[ 1 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Block %u written\r\n", ( uint16_t ) wr_block[ 1 ] );
// Read back block
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = sizeof ( rd_block );
memcpy ( ctx->pkt_data.payload, rd_block, ctx->pkt_data.payload_len );
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) ||
( NFC7SPI_NCI_STAT_OK != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u failed with error %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 1 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u: ", ( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 1 ] );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < 4; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
}
static void nfc7spi_handle_iso14443_4 ( nfc7spi_t *ctx )
{
err_t error_flag = NFC7SPI_OK;
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = strlen ( NFC7SPI_T4T_PPSE_APDU ) + 6;
ctx->pkt_data.payload[ 0 ] = NFC7SPI_T4T_CLA_NO_SECURE;
ctx->pkt_data.payload[ 1 ] = NFC7SPI_T4T_INS_SELECT;
ctx->pkt_data.payload[ 2 ] = NFC7SPI_T4T_P1_SELECT_BY_NAME;
ctx->pkt_data.payload[ 3 ] = NFC7SPI_T4T_P2_ONLY_OCCURANCE;
ctx->pkt_data.payload[ 4 ] = strlen ( NFC7SPI_T4T_PPSE_APDU );
memcpy ( &ctx->pkt_data.payload[ 5 ], NFC7SPI_T4T_PPSE_APDU, strlen ( NFC7SPI_T4T_PPSE_APDU ) );
ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] = NFC7SPI_T4T_LE_RSP_MAY_PRESENT;
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) ||
( NFC7SPI_T4T_RSP_COMPLETE_1 != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 2 ] ) ||
( NFC7SPI_T4T_RSP_COMPLETE_2 != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Select PPSE failed with error %.2X %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 2 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Select PPSE Application succeed\r\n" );
}
static void nfc7spi_handle_iso15693 ( nfc7spi_t *ctx )
{
#define BLK_NB_ISO15693 32
#define DATA_WRITE_ISO15693 0x11, 0x22, 0x33, 0x44
uint8_t rd_block[ ] = { NFC7SPI_ISO15693_FLAG_DR_HIGH, NFC7SPI_ISO15693_CMD_READ_SINGLE, BLK_NB_ISO15693 };
uint8_t wr_block[ ] = { NFC7SPI_ISO15693_FLAG_DR_HIGH, NFC7SPI_ISO15693_CMD_WRITE_SINGLE,
BLK_NB_ISO15693, DATA_WRITE_ISO15693 };
err_t error_flag = NFC7SPI_OK;
// Read
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = sizeof ( rd_block );
memcpy ( ctx->pkt_data.payload, rd_block, ctx->pkt_data.payload_len );
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) ||
( NFC7SPI_ISO15693_RSP_OK != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u failed with error %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 2 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u: ", ( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 2 ] );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < ( ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 2 ); cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ cnt + 1 ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
// Write
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = sizeof ( wr_block );
memcpy ( ctx->pkt_data.payload, wr_block, ctx->pkt_data.payload_len );
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) ||
( NFC7SPI_ISO15693_RSP_OK != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Write block %u failed with error %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) wr_block[ 2 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Block %u written\r\n", ( uint16_t ) wr_block[ 2 ] );
// Read back
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = sizeof ( rd_block );
memcpy ( ctx->pkt_data.payload, rd_block, ctx->pkt_data.payload_len );
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) ||
( NFC7SPI_ISO15693_RSP_OK != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u failed with error %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 2 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u: ", ( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 2 ] );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < ( ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 2 ); cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ cnt + 1 ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
}
static void nfc7spi_handle_mifare ( nfc7spi_t *ctx )
{
#define BLK_NB_MFC 32 // Do not use first 4 blocks and sector trailer blocks (7, 11, 15, etc)
#define KEY_MFC 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF
#define DATA_WRITE_MFC 0x00, 0x11, 0x22, 0x33, 0x44, 0x55, 0x66, 0x77, 0x88, 0x99, 0xAA, 0xBB, 0xCC, 0xDD, 0xEE, 0xFF
uint8_t authenticate[ ] = { NFC7SPI_MFC_REQ_AUTHENTICATE, BLK_NB_MFC / 4, NFC7SPI_MFC_KEY_SELECTOR_A_EMB, KEY_MFC };
uint8_t rd_block[ ] = { NFC7SPI_MFC_REQ_XCHG_DATA, NFC7SPI_MFC_CMD_READ, BLK_NB_MFC };
uint8_t wr_part1[ ] = { NFC7SPI_MFC_REQ_XCHG_DATA, NFC7SPI_MFC_CMD_WRITE, BLK_NB_MFC };
uint8_t wr_part2[ ] = { NFC7SPI_MFC_REQ_XCHG_DATA, DATA_WRITE_MFC };
err_t error_flag = NFC7SPI_OK;
if ( ( BLK_NB_MFC < 4 ) || ( 3 == ( BLK_NB_MFC % 4 ) ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Block %u is a sector trailer block\r\n", ( uint16_t ) BLK_NB_MFC );
return;
}
// Authenticate
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = sizeof ( authenticate );
memcpy ( ctx->pkt_data.payload, authenticate, ctx->pkt_data.payload_len );
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) ||
( NFC7SPI_NCI_STAT_OK != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Authenticate sector %u failed with error %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) authenticate[ 1 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Authenticate sector %u succeed\r\n", ( uint16_t ) authenticate[ 1 ] );
// Read block
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = sizeof ( rd_block );
memcpy ( ctx->pkt_data.payload, rd_block, ctx->pkt_data.payload_len );
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) ||
( NFC7SPI_NCI_STAT_OK != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u failed with error %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 2 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u: ", ( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 2 ] );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < ( ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 2 ); cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ cnt + 1 ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
// Write block
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = sizeof ( wr_part1 );
memcpy ( ctx->pkt_data.payload, wr_part1, ctx->pkt_data.payload_len );
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) || ( NFC7SPI_MFC_ACK != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Write block %u failed with error %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) wr_part1[ 2 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = sizeof ( wr_part2 );
memcpy ( ctx->pkt_data.payload, wr_part2, ctx->pkt_data.payload_len );
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) || ( NFC7SPI_MFC_ACK != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Write block %u failed with error %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) wr_part1[ 2 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Block %u written\r\n", ( uint16_t ) wr_part1[ 2 ] );
// Read back
ctx->pkt_data.payload_len = sizeof ( rd_block );
memcpy ( ctx->pkt_data.payload, rd_block, ctx->pkt_data.payload_len );
error_flag = nfc7spi_reader_tag_cmd ( ctx, &ctx->pkt_data );
if ( ( NFC7SPI_OK != error_flag ) ||
( NFC7SPI_NCI_STAT_OK != ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u failed with error %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 2 ],
( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 1 ] );
return;
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Read block %u: ", ( uint16_t ) rd_block[ 2 ] );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < ( ctx->pkt_data.payload_len - 2 ); cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) ctx->pkt_data.payload[ cnt + 1 ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
}
static void nfc7spi_display_card_info ( nfc7spi_rf_intf_t rf_intf )
{
switch ( rf_intf.protocol )
{
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_PROT_T1T:
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_PROT_T2T:
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_PROT_T3T:
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_PROT_ISODEP:
{
log_printf( &logger, " - POLL MODE: Remote T%uT activated\r\n", ( uint16_t ) rf_intf.protocol );
break;
}
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_PROT_T5T:
{
log_printf( &logger, " - POLL MODE: Remote ISO15693 card activated\r\n" );
break;
}
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_PROT_MIFARE:
{
log_printf( &logger, " - POLL MODE: Remote MIFARE card activated\r\n" );
break;
}
default:
{
log_printf( &logger, " - POLL MODE: Undetermined target\r\n" );
return;
}
}
switch ( rf_intf.mode_tech )
{
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_TECH_PASSIVE_POLL_NFC_A:
{
log_printf( &logger, "\tSENS_RES = %.2X %.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) rf_intf.info.nfc_app.sens_res[ 0 ],
( uint16_t ) rf_intf.info.nfc_app.sens_res[ 1 ] );
log_printf( &logger, "\tNFCID = " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < rf_intf.info.nfc_app.nfc_id_len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) rf_intf.info.nfc_app.nfc_id[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
if ( 0 != rf_intf.info.nfc_app.sel_res_len )
{
log_printf( &logger, "\tSEL_RES = %.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) rf_intf.info.nfc_app.sens_res[ 0 ] );
}
break;
}
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_TECH_PASSIVE_POLL_NFC_B:
{
if ( 0 != rf_intf.info.nfc_bpp.sens_res_len )
{
log_printf( &logger, "\tSENS_RES = " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < rf_intf.info.nfc_bpp.sens_res_len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) rf_intf.info.nfc_bpp.sens_res[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
}
break;
}
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_TECH_PASSIVE_POLL_NFC_F:
{
log_printf( &logger, "\tBitrate = %s\r\n", ( char * )
( ( 1 == rf_intf.info.nfc_fpp.bitrate ) ? "212" : "424" ) );
if ( 0 != rf_intf.info.nfc_fpp.sens_res_len )
{
log_printf( &logger, "\tSENS_RES = " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < rf_intf.info.nfc_fpp.sens_res_len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) rf_intf.info.nfc_fpp.sens_res[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
}
break;
}
case NFC7SPI_NCI_RF_TECH_PASSIVE_POLL_15693:
{
log_printf( &logger, "\tID = " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < sizeof ( rf_intf.info.nfc_vpp.id ); cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) rf_intf.info.nfc_vpp.id[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "\tAFI = %.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) rf_intf.info.nfc_vpp.afi );
log_printf( &logger, "\tDSFID = %.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) rf_intf.info.nfc_vpp.dsf_id );
break;
}
default:
{
break;
}
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:RFID/NFC