Designed to enhance user experience, our solution facilitates the seamless integration of conductive materials, allowing them to serve as intuitive input buttons
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
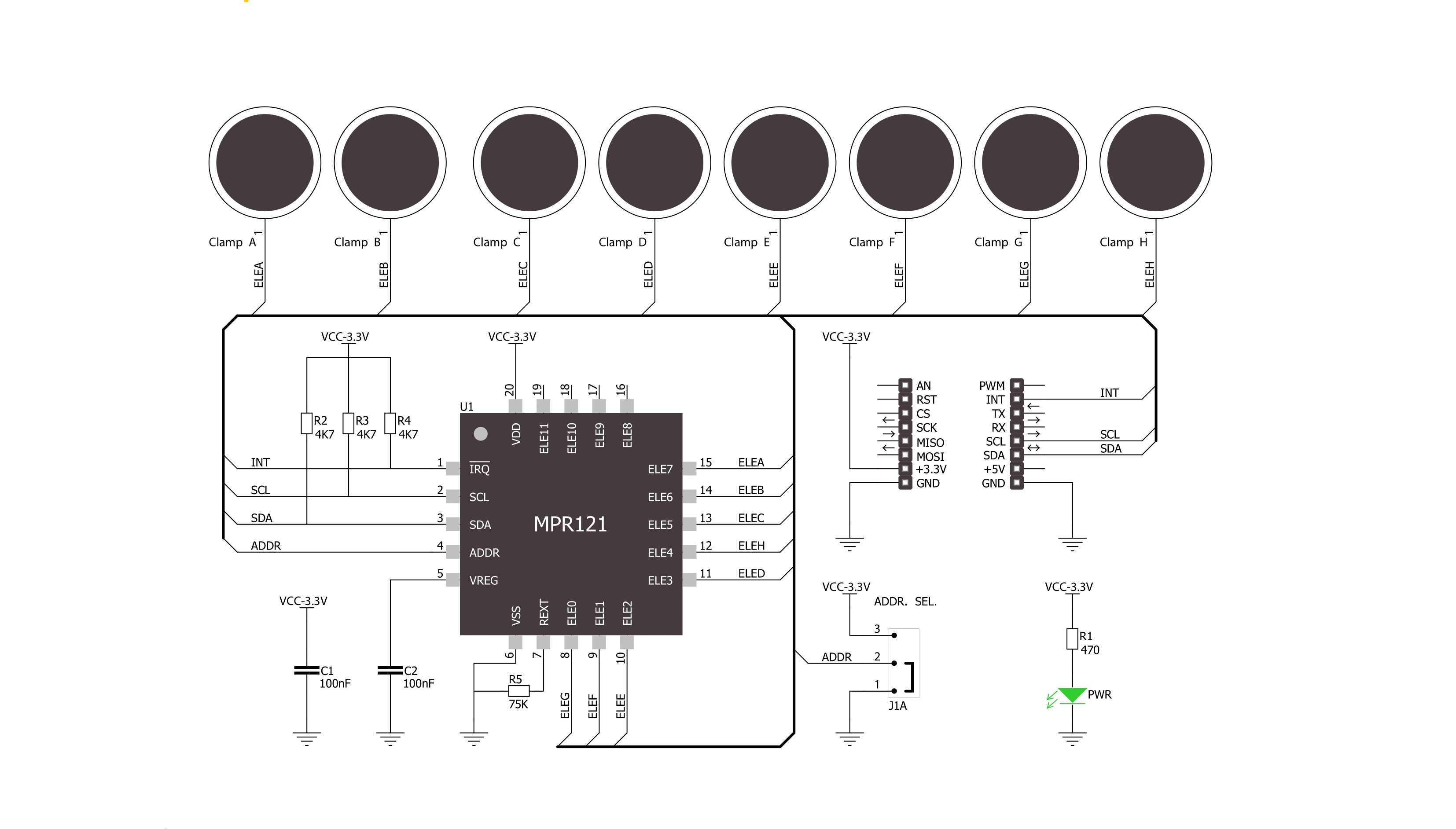
TouchClamp Click is based on the MPR121, a proximity capacitive touch sensor controller from NXP Semiconductors. The MPR121 uses seven electrodes/capacitance sensing inputs, four of which are multifunctional for LED driving (H, C, B, A) and GPIO. One electrode is an extra capacitive button in the middle of the board labeled H. It also features the 8th simulated electrode, which represents the simultaneous charging of all electrodes connected together. The MPR121 has integrated independent autocalibration and autoconfiguration for each electrode input and separate touch and release trip thresholds for each, providing hysteresis and electrode independence. The easiest way to experiment with TouchClamp click is to use wires with alligator clips. Let your imagination roam free when choosing conductive objects such as cans, fruit, jar lids, and more. The MPR121 chip has several features in addition that simplify development and integration. First, it applies three levels of digital filtering to the raw ADC data to remove high and low-frequency noise, ensuring that
the interrupts are properly registered in a broad range of applications. The auto-calibration function, according to the vendor's datasheet, "continually learns the background baseline capacitance of each individual electrode, so the system only has to program the amount of small change from these baselines that represents a touch or release." The auto-configuration uses the given target charge level so the chip can automatically run to get an optimized charge current and charge time setting for each electrode without knowing the specific capacitance value on the electrode input. The capacitance sensing uses a constant DC current capacitance sensing scheme and can measure capacitances ranging from 10pF to over 2000pF, with resolutions up to 0.01pF. The voltage measured on the input sensing node is inversely proportional to the capacitance and is sampled by an internal 10-bit ADC. The touch sensing compares the baseline value with the current immediate electrode data to determine if a touch or a release has occurred, with the ability to set a touch/release threshold.
The proximity sensing acts as the near proximity sensing system, where all electrodes can be summoned together to create a single large electrode, thus covering a much larger area. Touch sensing and proximity sensing can be used at the same time. Among 12 electrodes, eight of them can be used as a GPIO and can be used to drive LEDs or for GPIO. The TouchClamp Click uses an I2C 2-Wire interface to communicate with the host MCU. It also has an ADDR SEL jumper to choose between the two available I2C addresses and can be connected to VDD or VSS (VSS position set by default). In addition, the TouchClamp Click comes with an interrupt INT pin, which is triggered anytime a touch or release is detected. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
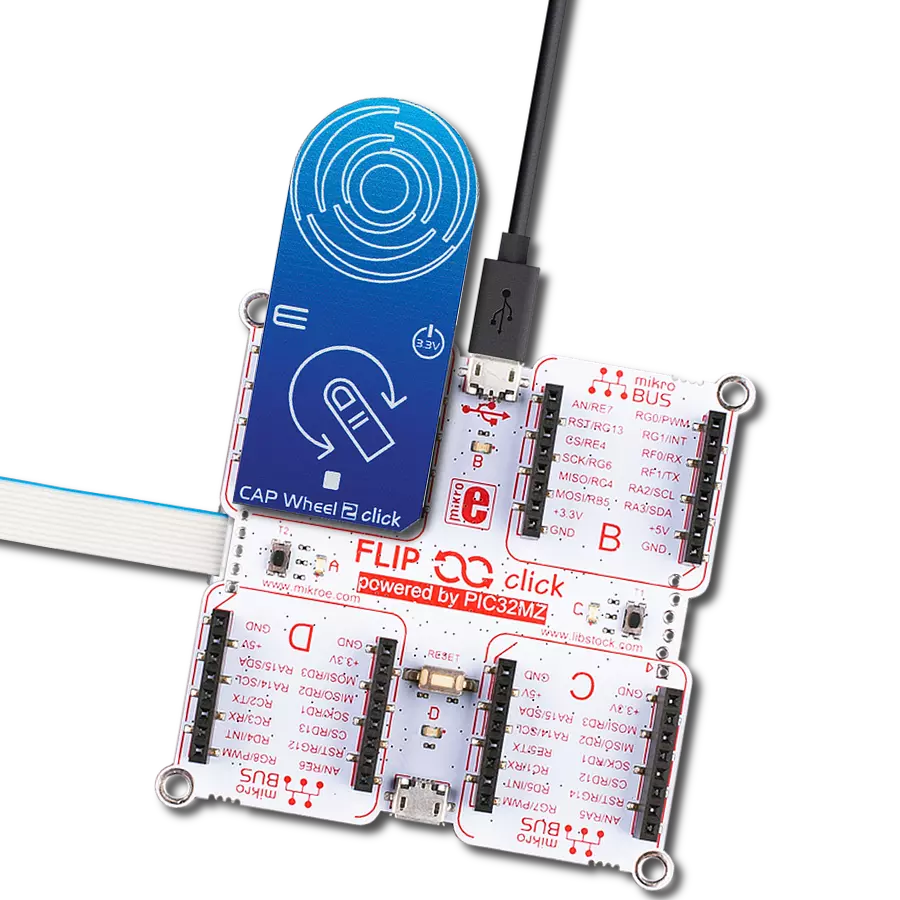
Development board
Flip&Click PIC32MZ is a compact development board designed as a complete solution that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It comes with an onboard 32-bit PIC32MZ microcontroller, the PIC32MZ2048EFH100 from Microchip, four mikroBUS™ sockets for Click board™ connectivity, two USB connectors, LED indicators, buttons, debugger/programmer connectors, and two headers compatible with Arduino-UNO pinout. Thanks to innovative manufacturing technology,
it allows you to build gadgets with unique functionalities and features quickly. Each part of the Flip&Click PIC32MZ development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition, there is the possibility of choosing the Flip&Click PIC32MZ programming method, using the chipKIT bootloader (Arduino-style development environment) or our USB HID bootloader using mikroC, mikroBasic, and mikroPascal for PIC32. This kit includes a clean and regulated power supply block through the USB Type-C (USB-C) connector. All communication
methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board, including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, user-configurable buttons, and LED indicators. Flip&Click PIC32MZ development kit allows you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
2048
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
524288
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for TouchClamp Click driver.
Key functions:
etouchclamp_get_touch_data- Get touch data function
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief TouchClamp Click example
*
* # Description
* This demo-app shows the touch position using TouchClamp Click.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Configuring Clicks and log objects.
* Setting the Click in the default configuration.
*
* ## Application Task
* Detect and dispay touch position when the Click is triggered.
*
* \author Nenad Filipovic
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "touchclamp.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static touchclamp_t touchclamp;
static log_t logger;
uint16_t touch_data;
uint16_t touch_data_old;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
touchclamp_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
touchclamp_cfg_setup( &cfg );
TOUCHCLAMP_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
touchclamp_init( &touchclamp, &cfg );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
touchclamp_soft_reset( &touchclamp );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
touchclamp_default_cfg( &touchclamp );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
touch_data_old = TOUCHCLAMP_NO_TOUCH;
log_printf( &logger, "-------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Touch Clamp Click \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "-------------------\r\n" );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
touch_data = touchclamp_get_touch_data( &touchclamp );
if ( touch_data_old != touch_data )
{
if ( touch_data == TOUCHCLAMP_TOUCH_POSITION_H )
log_printf( &logger, " - - - - - - - H\r\n" );
if ( touch_data == TOUCHCLAMP_TOUCH_POSITION_G )
log_printf( &logger, " - - - - - - G -\r\n" );
if ( touch_data == TOUCHCLAMP_TOUCH_POSITION_F )
log_printf( &logger, " - - - - - F - -\r\n" );
if ( touch_data == TOUCHCLAMP_TOUCH_POSITION_E )
log_printf( &logger, " - - - - E - - -\r\n" );
if ( touch_data == TOUCHCLAMP_TOUCH_POSITION_D )
log_printf( &logger, " - - - D - - - -\r\n" );
if ( touch_data == TOUCHCLAMP_TOUCH_POSITION_C )
log_printf( &logger, " - - C - - - - -\r\n" );
if ( touch_data == TOUCHCLAMP_TOUCH_POSITION_B )
log_printf( &logger, " - B - - - - - -\r\n" );
if ( touch_data == TOUCHCLAMP_TOUCH_POSITION_A )
log_printf( &logger, " A - - - - - - -\r\n" );
touch_data_old = touch_data;
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Capacitive