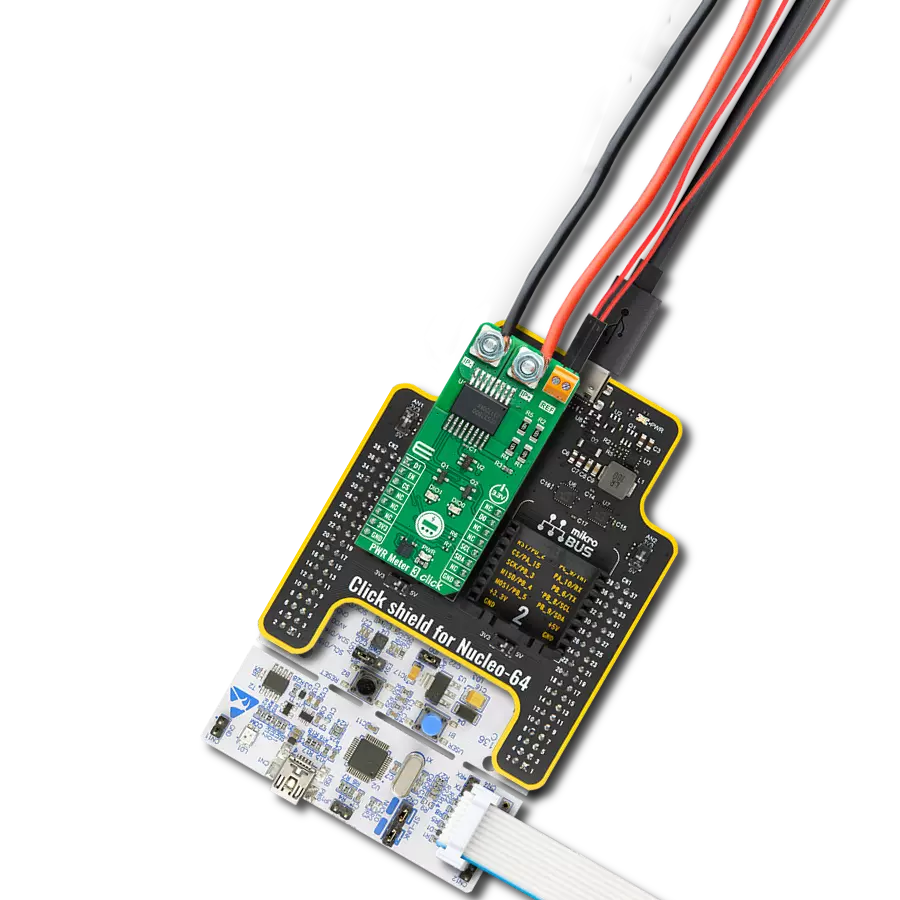
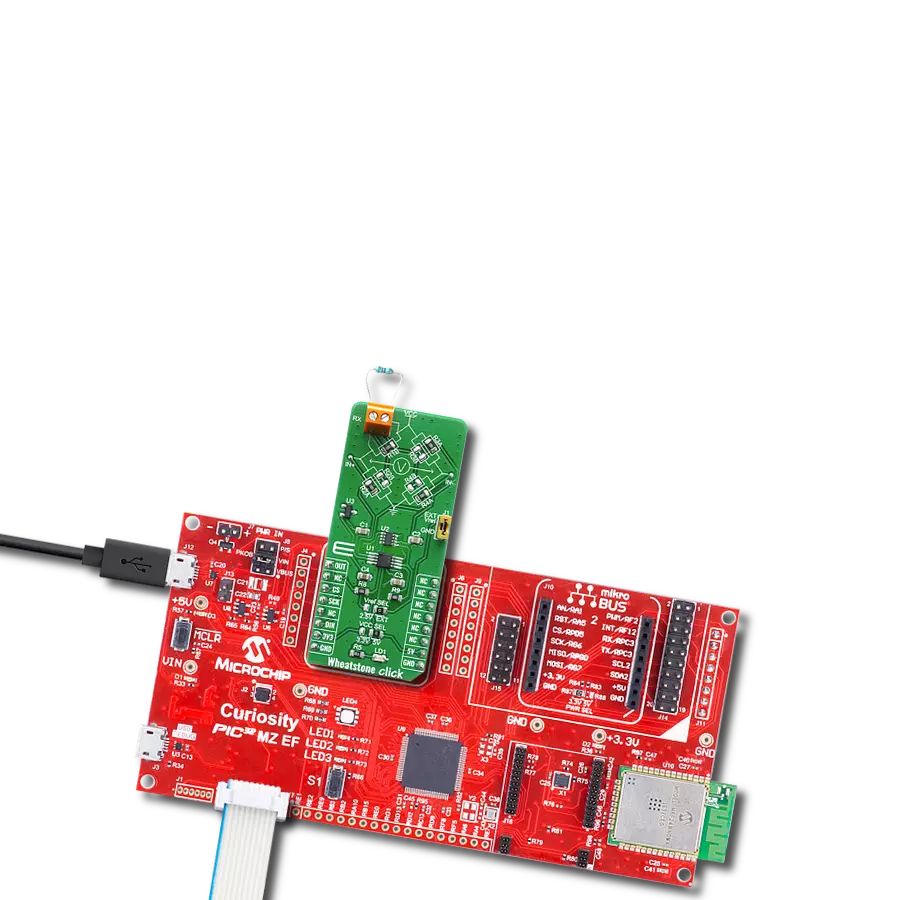
Discover the ultimate tool for precision resistance measurement – our Wheatstone bridge circuit solution is here to empower your journey towards accurate and reliable data.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
Wheatstone Click is based on the MAX4208, an ultra-low offset/drift, precision instrumentation amplifier, from Analog Devices. A Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two branches of a bridge circuit, one branch of which includes the unknown component. The primary benefit of the circuit is its ability to provide extremely accurate measurements, in contrast with a simple voltage divider. The R2, R3, and R4 are resistors of known resistance (1k ohm), while the resistance R1 is brought to the terminal block and therefore it is changeable. With no resistance connected to the terminal block, the bridge on this Click board™ is in balance. At this point, the voltage between the two midpoints (IN- and IN+) will be zero. Therefore the ratio
of the two resistances in the known branch (R1 and R3) is equal to the ratio of the two resistances in the unknown leg (R2 and R4). If the external resistance is connected to the terminal block, bridge is unbalanced, and the voltage on the midpoints is proportional to the external resistor value. Wheatstone click is based around the MAX4208 IC, which is connected to an onboard Wheatstone bridge circuit, in order to precisely measure the resistance of an external element. The mentioned IC uses a spreadspectrum, autozeroing technique that constantly measures and corrects the input offset, eliminating drift over time and temperature and the effect of 1/f noise. This technique achieves less than 20μV offset voltage, allows ground-sensing capability, provides ultra-low CMOS input bias current and increased
common-mode rejection performance. It also provides high-impedance inputs, optimized for small-signal differential voltages (±100mV), which makes it ideal for an application such as wheatstone bridge disbalance measurement. This Click board™ also has TPL0501 onboard - 256-Taps, Single-Channel, Digital Potentiometer With SPI Interface, from texas instruments. It is connected to the MAX4208 in a way that it serves an gain adjust instead of with two external resistors The power supply voltage selection for the logic section is done by moving the SMD jumper labeled as VCC SEL to a desired position: left position to select 3.3V, right position to select 5V. This will allow both 3.3V and 5V MCUs to be interfaced with the Click board™ directly.
Features overview
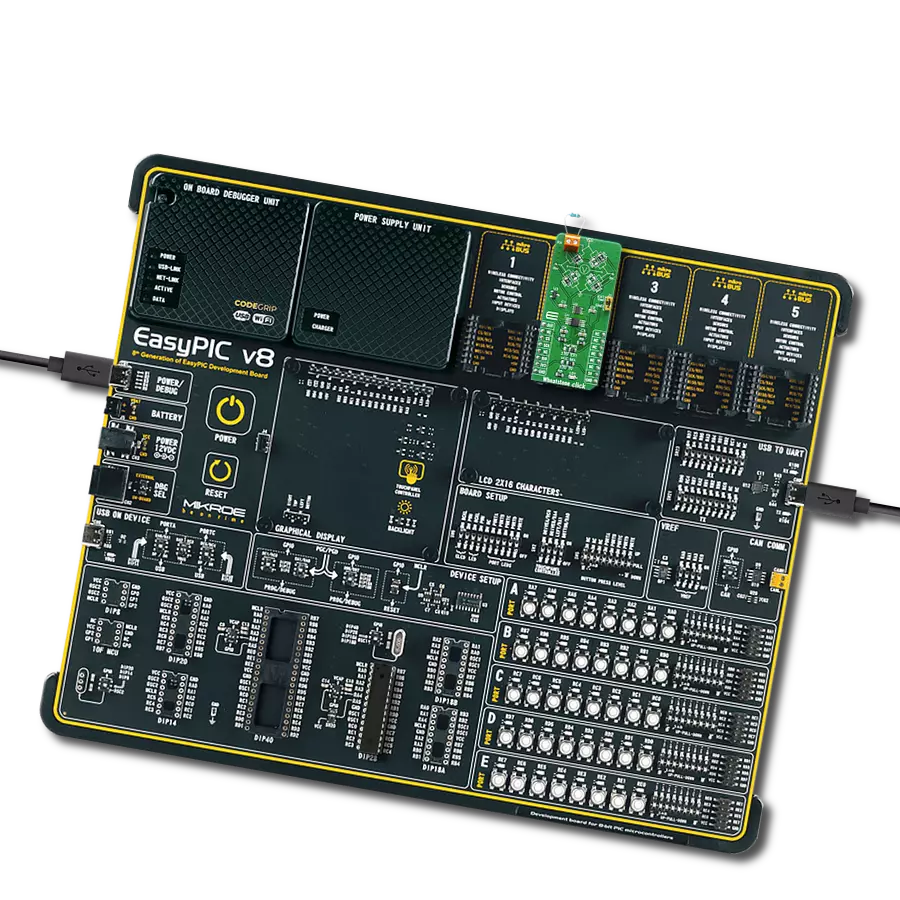
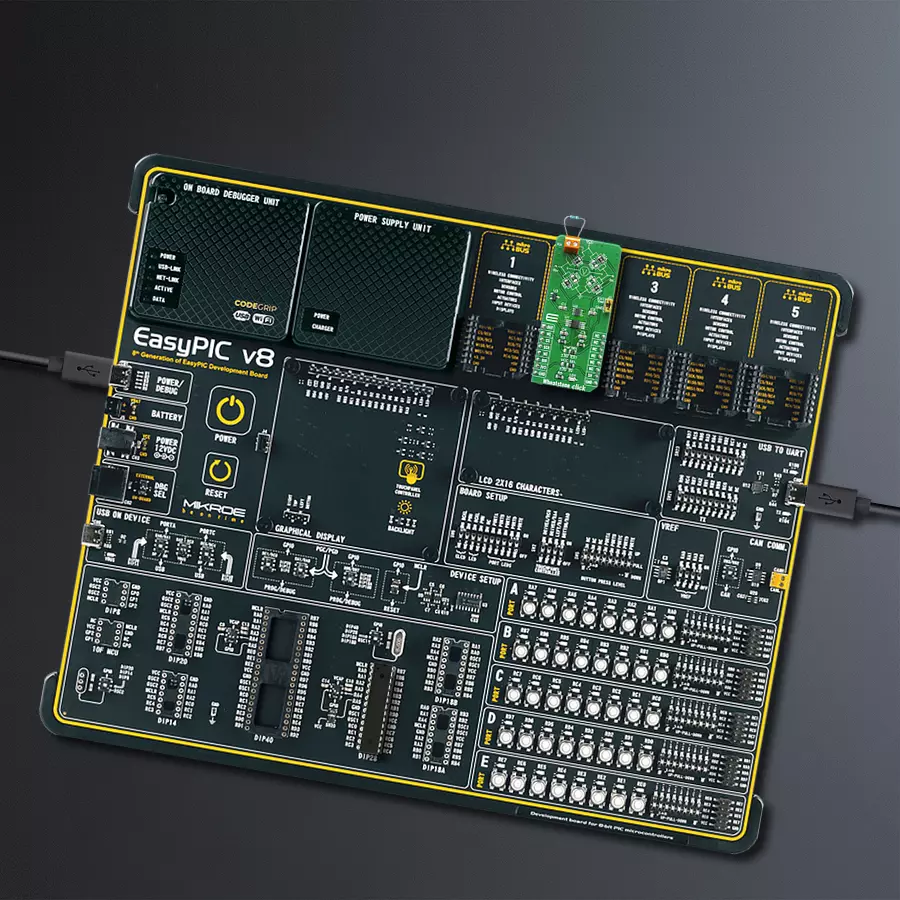
Development board
EasyPIC v8 is a development board specially designed for the needs of rapid development of embedded applications. It supports many high pin count 8-bit PIC microcontrollers from Microchip, regardless of their number of pins, and a broad set of unique functions, such as the first-ever embedded debugger/programmer. The development board is well organized and designed so that the end-user has all the necessary elements, such as switches, buttons, indicators, connectors, and others, in one place. Thanks to innovative manufacturing technology, EasyPIC v8 provides a fluid and immersive working experience, allowing access anywhere and under any
circumstances at any time. Each part of the EasyPIC v8 development board contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the advanced integrated CODEGRIP programmer/debugger module, which offers many valuable programming/debugging options and seamless integration with the Mikroe software environment, the board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development board. It can use a wide range of external power sources, including a battery, an external 12V power supply, and a power source via the USB Type-C (USB-C) connector.
Communication options such as USB-UART, USB DEVICE, and CAN are also included, including the well-established mikroBUS™ standard, two display options (graphical and character-based LCD), and several different DIP sockets. These sockets cover a wide range of 8-bit PIC MCUs, from the smallest PIC MCU devices with only eight up to forty pins. EasyPIC v8 is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem for rapid development. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping and development thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
28
RAM (Bytes)
2048
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Wheatstone Click driver.
Key functions:
wheatstone_set_potentiometer- Set potentiometer ( 0 - 100k )wheatstone_read_an_pin_voltage- This function reads results of AD conversion of the AN pin and converts them to proportional voltage level.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Wheatstone Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of Wheatstone Click board by measuring the input
* resistance.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and logger and sets the default potentiometer (gain) level.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads the AN pin voltage and calculates the input resistance from it.
* All data are being displayed on the USB UART where you can track their changes.
*
* @note
* The following formulas you may find useful:
* AN_PIN(V) = ( ( 1kOhm + R_INPUT(kOhm) ) / ( 1kOhm + 2*R_INPUT(kOhm) ) - 1/2 ) * VCC(V) * GAIN
* VOUT(V) = AN_PIN(V) / GAIN
* R_INPUT(kOhm) = ( VCC(V) * GAIN - 2*AN_PIN(V) ) / ( 4*AN_PIN(V) )
* R_INPUT(kOhm) = ( VCC(V) - 2*VOUT(V) ) / ( 4*VOUT(V) )
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "wheatstone.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static wheatstone_t wheatstone;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
wheatstone_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
wheatstone_cfg_setup( &cfg );
WHEATSTONE_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
wheatstone_init( &wheatstone, &cfg );
wheatstone_set_potentiometer ( &wheatstone, WHEATSTONE_POT_MAX );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
float an_pin_v = 0;
float vout = 0;
float r_kohm = 0;
if ( WHEATSTONE_OK == wheatstone_read_an_pin_voltage ( &wheatstone, &an_pin_v ) )
{
vout = an_pin_v / wheatstone.gain;
if ( 0 != vout )
{
r_kohm = ( WHEATSTONE_VCC_5V - 2 * vout ) / ( 4 * vout );
}
log_printf( &logger, " VCC : %.3f V\r\n", WHEATSTONE_VCC_5V );
log_printf( &logger, " GAIN : %.3f\r\n", wheatstone.gain );
log_printf( &logger, " AN_PIN : %.3f V\r\n", an_pin_v );
log_printf( &logger, " VOUT : %.3f V\r\n", vout );
log_printf( &logger, " R_INPUT : %.3f kOhm\r\n\n", r_kohm );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Measurements