Our LIN transceiver empowers vehicles and industrial systems to efficiently exchange critical data at low speeds, ensuring seamless communication
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
ATA663211 Click is based on the ATA663211, a LIN transceiver from Microchip. It features several protection functionalities, such as over-temperature, short-circuit protection vs. GND and battery, advanced EMC and ESD, and more. The integrated 3.3V onboard LDO voltage regulator is the MCP1804, an LDO regulator with shutdown from Microchip. The combination of a voltage regulator and a bus transceiver makes it possible to develop simple but powerful slave nodes in LIN bus systems. This way, ATA663211 Click can be used as a standalone LIN transceiver without being connected to a mikroBUS™ socket. An onboard LDO (low-dropout regulator) lets it supply power through the VS line screw terminal. This regulated voltage is also available on the +3.3V rail of the mikroBUS™ socket to power up the 3.3V attached host MCU. There are several operating modes for the ATA663211 Click. In Normal mode, the LIN interface is transmitting and receiving. In Sleep mode, the transmission path is disabled, and the LIN transceiver is in low-power mode. The Failsafe mode is automatically switched at system power-up or after a wake-up event. The LIN transceiver
is switched off in this mode, and the inhibit output pin is switched on. For the typical application as a Master node, the ATA663211 requires the LBUS line of the chip to be connected to the VBB of the LIN BUS, achievable via a populated L-PULL jumper. This jumper can be removed in other scenarios, such as the LIN Slave node. The ATA663211 communicates with the MCU using the UART RX and TX signals. Besides communication, these pins also serve to signal the failsafe condition. The undervoltage on the LIN connector can cause the failsafe condition: less than 3.9V will cause the undervoltage condition, signaled by the LOW logic state on the RX pin and the HIGH logic state on the TX pin. A LIN wake-up event from either silent or sleep mode is signaled by the LOW logic state on both the RX and TX pins. This event is received via the LIN bus and is used to switch the ATA663211 click to an active state. On the other hand, Low on TX and HIGH on RX will signal the local wake-up. RX and TX signals are also routed to the header on the edge of the Click board™ so they can be used independently of the mikroBUS™ socket. The inhibit output pin of the LIN transceiver is used
to control the Shutdown input of the MCP1804 LDO; thus, the supply pin of the LIN transceiver itself, as the LDO, supplies the LIN transceiver supply pin with LIN operating voltage. The voltages on this line can be monitored over the INH pin of the mikroBUS™ socket via the resistor divider. To enable the LIN transceiver, there is an EN SEL jumper set to the HI position by default, thus enabling the transceiver. Setting it to the LOW position allows you to control the enable function over the EN pin of the mikroBUS™ socket. In addition, this same pin is routed to the second pair of headers to enable the LIN transceiver externally. The other pin on this header is WKin, a high-voltage input for waking up the device. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
PIC18F47K42 Curiosity Nano evaluation kit is a cutting-edge hardware platform designed to evaluate the PIC18F47K42 microcontroller (MCU). Central to its design is the inclusion of the powerful PIC18F47K42 microcontroller (MCU), offering advanced functionalities and robust performance. Key features of this evaluation kit include a yellow user LED and a responsive mechanical user switch
providing seamless interaction and testing. The provision for a 32.768kHz crystal footprint ensures precision timing capabilities. With an onboard debugger boasting a green power and status LED, programming and debugging become intuitive and efficient. Further enhancing its utility is the Virtual serial port (CDC) and a debug GPIO channel (DGI GPIO), offering extensive connectivity options.
Powered via USB, this kit boasts an adjustable target voltage feature facilitated by the MIC5353 LDO regulator, ensuring stable operation with an output voltage ranging from 2.3V to 5.1V (limited by USB input voltage), with a maximum output current of 500mA, subject to ambient temperature and voltage constraints.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC
MCU Memory (KB)
128
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
40
RAM (Bytes)
8192
You complete me!
Accessories
Curiosity Nano Base for Click boards is a versatile hardware extension platform created to streamline the integration between Curiosity Nano kits and extension boards, tailored explicitly for the mikroBUS™-standardized Click boards and Xplained Pro extension boards. This innovative base board (shield) offers seamless connectivity and expansion possibilities, simplifying experimentation and development. Key features include USB power compatibility from the Curiosity Nano kit, alongside an alternative external power input option for enhanced flexibility. The onboard Li-Ion/LiPo charger and management circuit ensure smooth operation for battery-powered applications, simplifying usage and management. Moreover, the base incorporates a fixed 3.3V PSU dedicated to target and mikroBUS™ power rails, alongside a fixed 5.0V boost converter catering to 5V power rails of mikroBUS™ sockets, providing stable power delivery for various connected devices.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
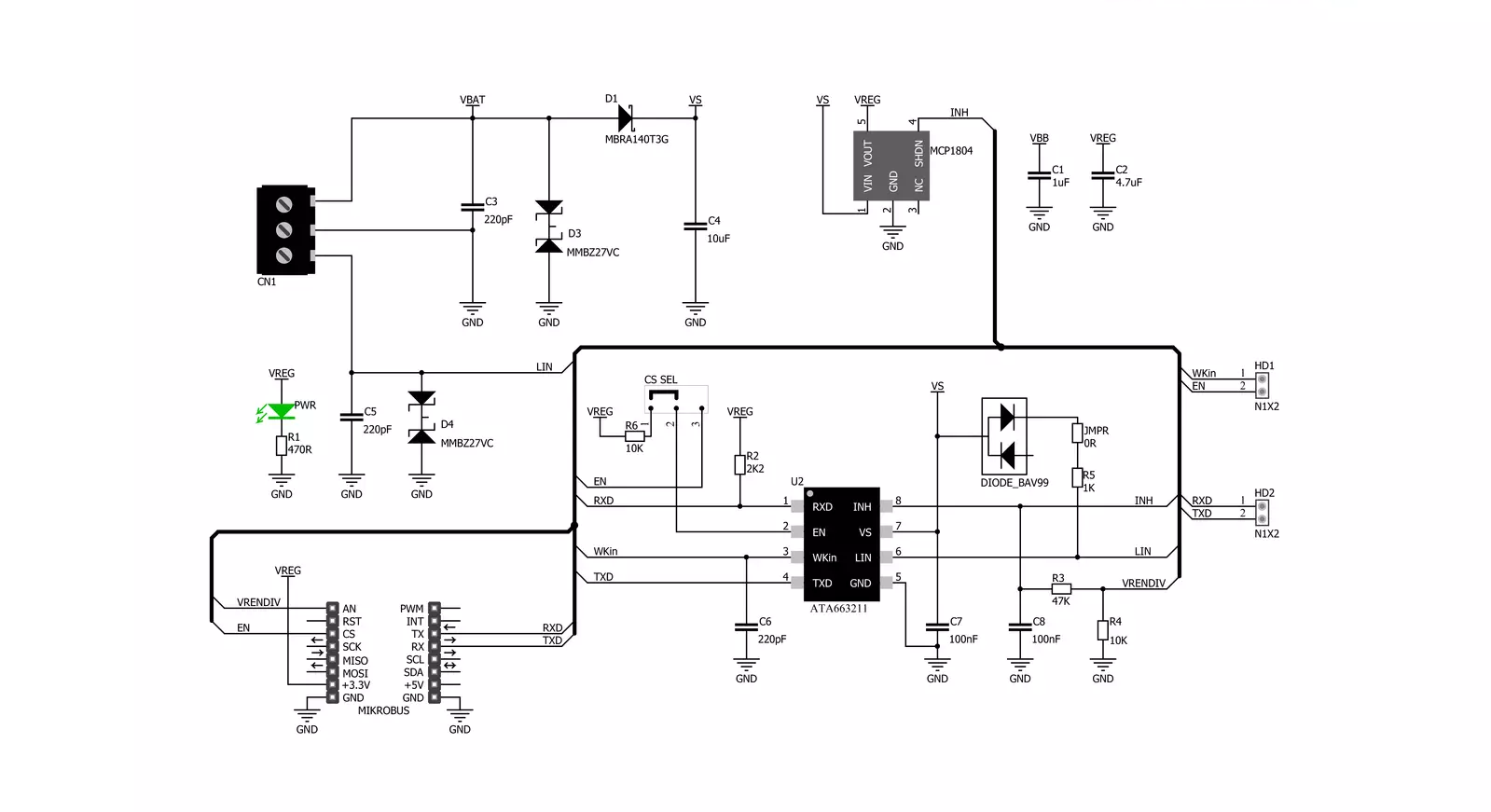
Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
After loading the code example, pressing the "DEBUG" button builds and programs it on the selected setup.
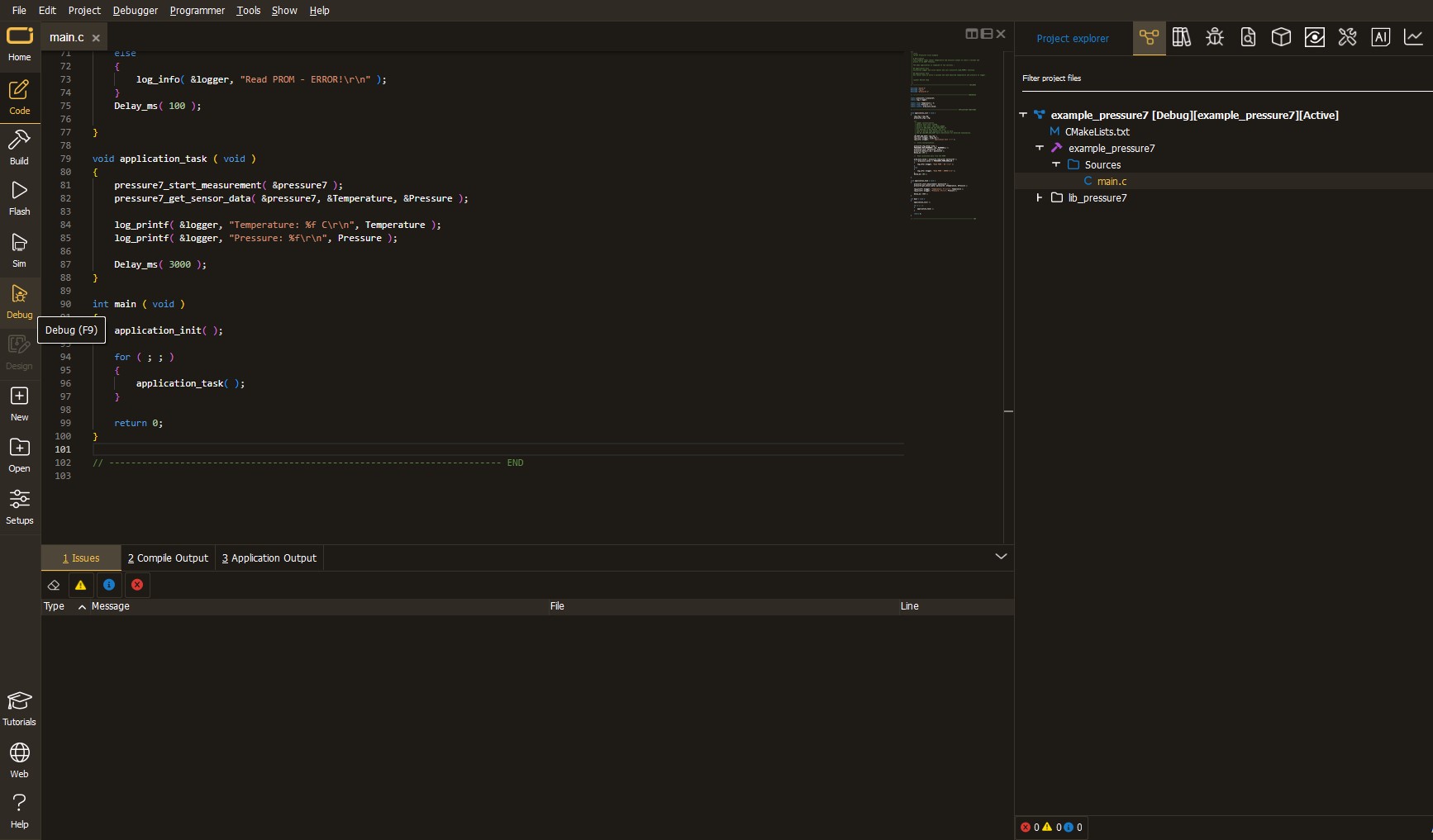
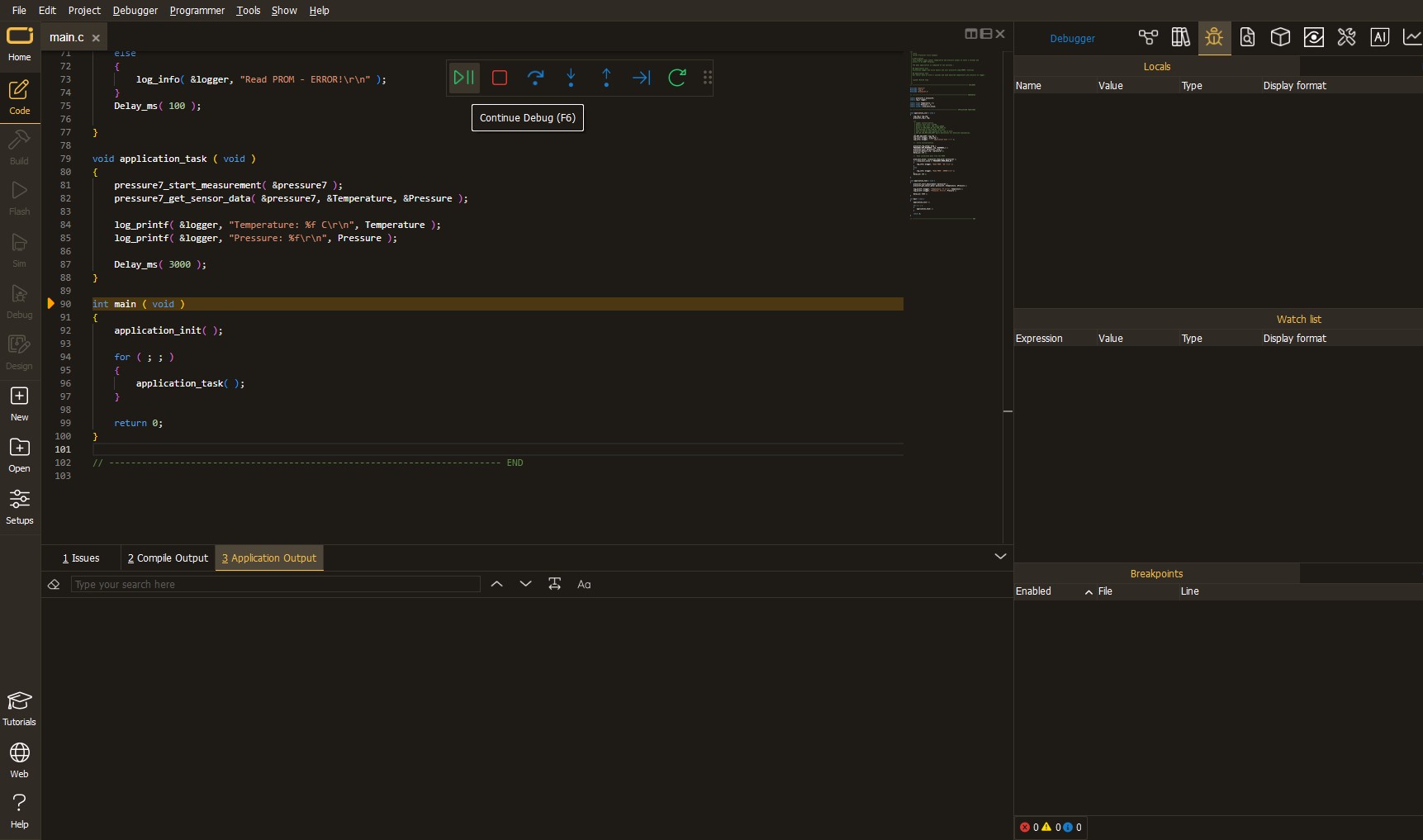
After programming is completed, a header with buttons for various actions available in the IDE appears. By clicking the green "PLAY "button, we start reading the results achieved with Click board™.
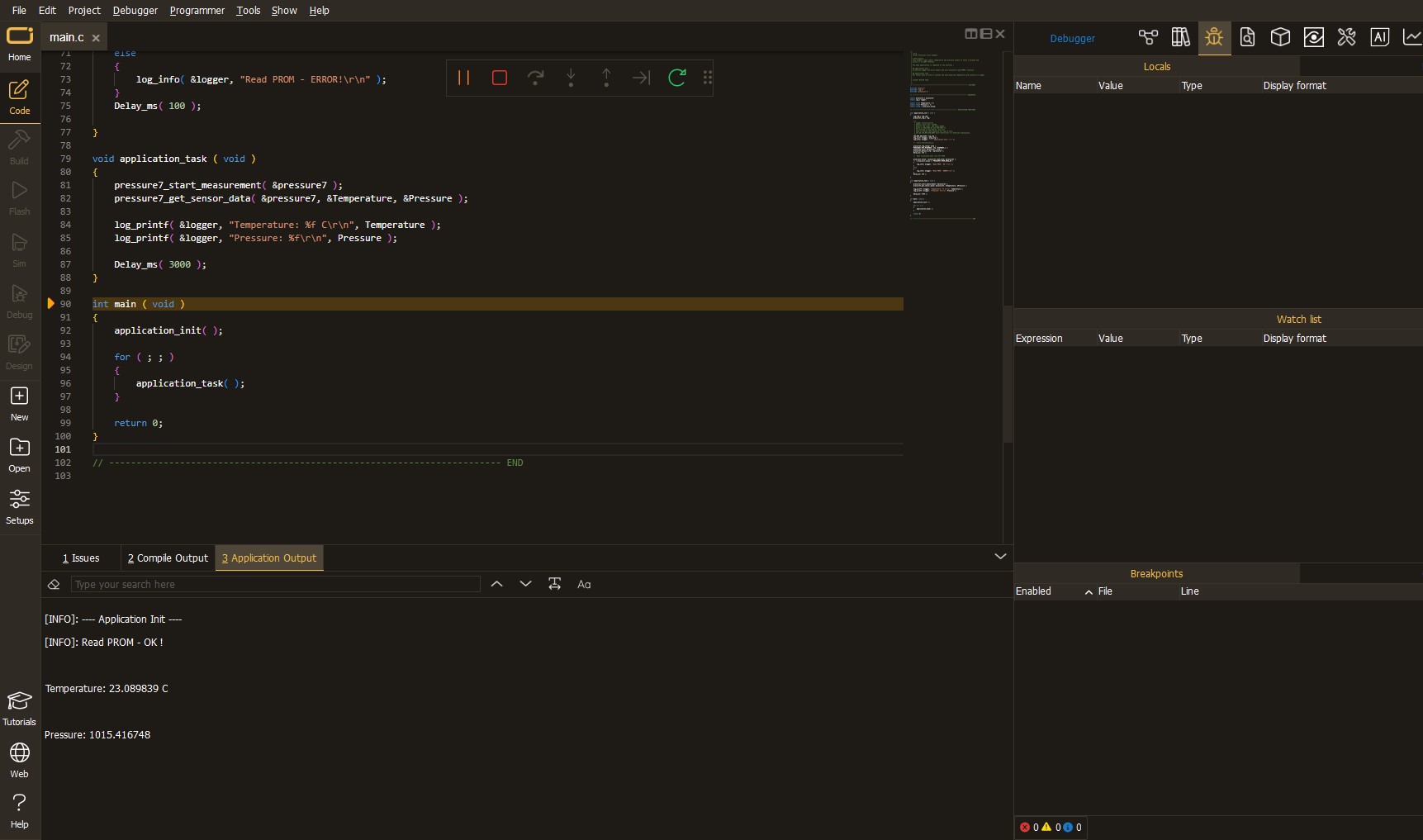
Upon completion of programming, the Application Output tab is automatically opened, where the achieved result can be read. In case of an inability to perform the Debug function, check if a proper connection between the MCU used by the setup and the CODEGRIP programmer has been established. A detailed explanation of the CODEGRIP-board connection can be found in the CODEGRIP User Manual. Please find it in the RESOURCES section.
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for ATA663211 Click driver.
Key functions:
ata663211_generic_write- Generic write functionata663211_generic_read- Generic read function.
Open Source
Code example
This example can be found in NECTO Studio. Feel free to download the code, or you can copy the code below.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Ata663211 Click example
*
* # Description
* This application is for handling low-speed data communication in vehicles and in industrial.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initalizes device and makes an initial log.
*
* ## Application Task
* Checks if new data byte have received in rx buffer (ready for reading), and if ready than reads one byte from rx buffer.
*
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "ata663211.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
//#define DEMO_APP_RECEIVER
#define DEMO_APP_TRANSMITER
static ata663211_t ata663211;
static log_t logger;
static char demo_message[ 9 ] = { 'M', 'i', 'k', 'r', 'o', 'E', 13, 10, 0 };
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
ata663211_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
ata663211_cfg_setup( &cfg );
ATA663211_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
ata663211_init( &ata663211, &cfg );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
char tmp;
// Task implementation.
#ifdef DEMO_APP_RECEIVER
// RECEIVER - UART polling
tmp = ata663211_generic_single_read( &ata663211 );
log_printf( &logger, " %c ", tmp );
#endif
#ifdef DEMO_APP_TRANSMITER
// TRANSMITER - TX each 2 sec
ata663211_generic_multi_write( &ata663211, demo_message, 9 );
Delay_ms( 2000 );
#endif
}
void main ( void )
{
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END

































