Detect the absolute rotor position of brushless motors with ease, allowing for seamless control and optimization of motor performance
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
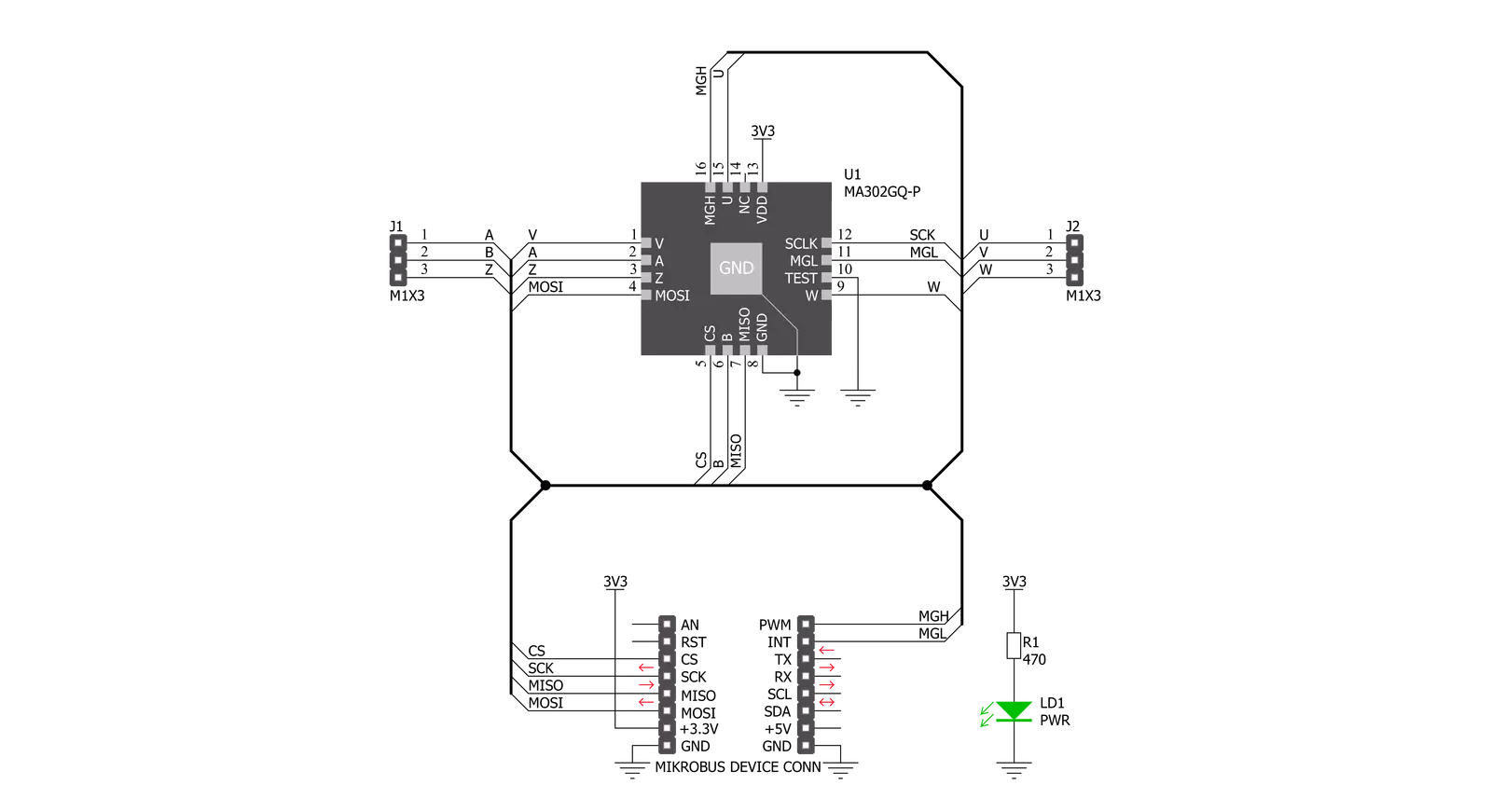
Angle 5 Click is based on the MA302, a 12-bit digital contactless angle sensor with ABZ and UVW incremental outputs from Monolithic Power Systems. This Click board™ can detect the absolute rotor position of a Brushless motor in real-time, even without a target magnet, by measuring the fringe field of the rotor. The sensor must be positioned at the correct place (in this case, below the rotor) to get the maximum value of the rotor magnetic field without being disturbed by other fields. The rotor magnetic field is then measured, and an adequate position was determined from that information. It uses the SPI serial interface for digital angle readout and configuration alongside a programmable magnetic field strength detection function for diagnostic checks. The magnetic field is detected with integrated Hall devices located in the center of the package. The angle is measured using the Spinaxis™ method, based on phase detection,
and generates a sinusoidal signal with a phase that represents the angle of the magnetic field. The angle is then obtained by a time-to-digital converter, which measures the time between the zero-crossing of the sinusoidal signal and the edge of a constant waveform. The time-to-digital represents an output from the front end to the digital conditioning block. This output delivers a digital number proportional to the angle of the magnetic field at the rate of 1MHz in a straightforward and open-loop manner. The Angle 5 Click communicates with MCU using the standard SPI serial interface for angle reading and register programming, which supports SPI Mode 0 and 3 and operates at clock rates up to 25 MHz. It also has the magnetic flags used for indication when the magnetic field at the sensor position is out of range, defined by the lower and upper magnetic field thresholds, routed on the PWM and INT pin of the mikroBUS™ socket labeled as MGH
and MGL. This Click board™ possesses an incremental encoder and block commutation function that uses three output pins each: ABZ and UVW. The ABZ output emulates a 10-bit incremental encoder (such as an optical encoder) providing logic pulses in quadrature, while the UVW output emulates the three Hall switches usually used for the block commutation of a three-phase electric motor. The ABZ and UVW pins of the MA302 are routed on two standard 2.54 mm (0.1 inches) pitch 1x3 header mounted on the Angle 5 Click so an external application can easily access it. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino UNO is a versatile microcontroller board built around the ATmega328P chip. It offers extensive connectivity options for various projects, featuring 14 digital input/output pins, six of which are PWM-capable, along with six analog inputs. Its core components include a 16MHz ceramic resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an
ICSP header, and a reset button, providing everything necessary to power and program the board. The Uno is ready to go, whether connected to a computer via USB or powered by an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. As the first USB Arduino board, it serves as the benchmark for the Arduino platform, with "Uno" symbolizing its status as the
first in a series. This name choice, meaning "one" in Italian, commemorates the launch of Arduino Software (IDE) 1.0. Initially introduced alongside version 1.0 of the Arduino Software (IDE), the Uno has since become the foundational model for subsequent Arduino releases, embodying the platform's evolution.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
28
RAM (Bytes)
2048
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino UNO has two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino UNO board without effort. The Arduino Uno, a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P, provides an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts and build prototypes with the ATmega328P microcontroller from various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (of which six can be used as PWM outputs), six analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator (CSTCE16M0V53-R0), a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and reset button. Most of the ATmega328P microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino UNO board with our Click Shield for Arduino UNO, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
2207V-2500kV BLDC Motor is an outrunner brushless DC motor with a kV rating of 2500 and an M5 shaft diameter. It is an excellent solution for fulfilling many functions initially performed by brushed DC motors or in RC drones, racing cars, and much more.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
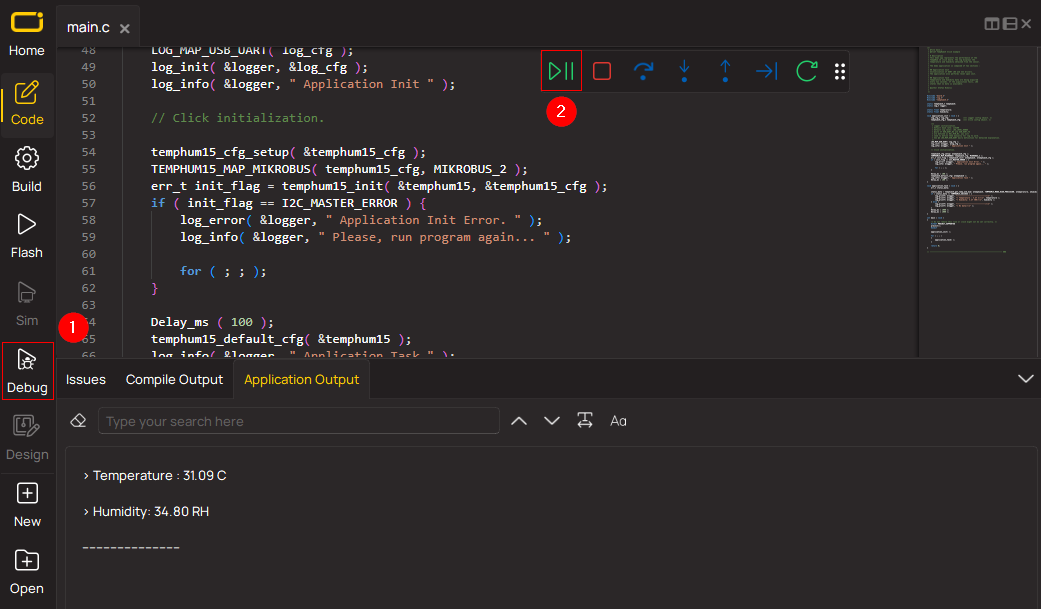
Application Output via Debug Mode
1. Once the code example is loaded, pressing the "DEBUG" button initiates the build process, programs it on the created setup, and enters Debug mode.
2. After the programming is completed, a header with buttons for various actions within the IDE becomes visible. Clicking the green "PLAY" button starts reading the results achieved with the Click board™. The achieved results are displayed in the Application Output tab.
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Angle 5 Click driver.
Key functions:
angle5_read_raw_angle- Use this function to read raw angle dataangle5_read_angle_deg- Use this function to read angle data
Open Source
Code example
This example can be found in NECTO Studio. Feel free to download the code, or you can copy the code below.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Angle5 Click example
*
* # Description
* Angle 5 click is a magnetic rotational sensor.
* It communicates with the target microcontroller over SPI interface.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads the angle position of the magnet and displays the results on the USB UART.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "angle5.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static angle5_t angle5;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
angle5_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
angle5_cfg_setup( &cfg );
ANGLE5_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
angle5_init( &angle5, &cfg );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
float new_angle = 0;
new_angle = angle5_read_angle_deg( &angle5 );
log_printf( &logger, "Angle: %.2f\r\n", new_angle );
Delay_ms( 100 );
}
void main ( void )
{
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END




































