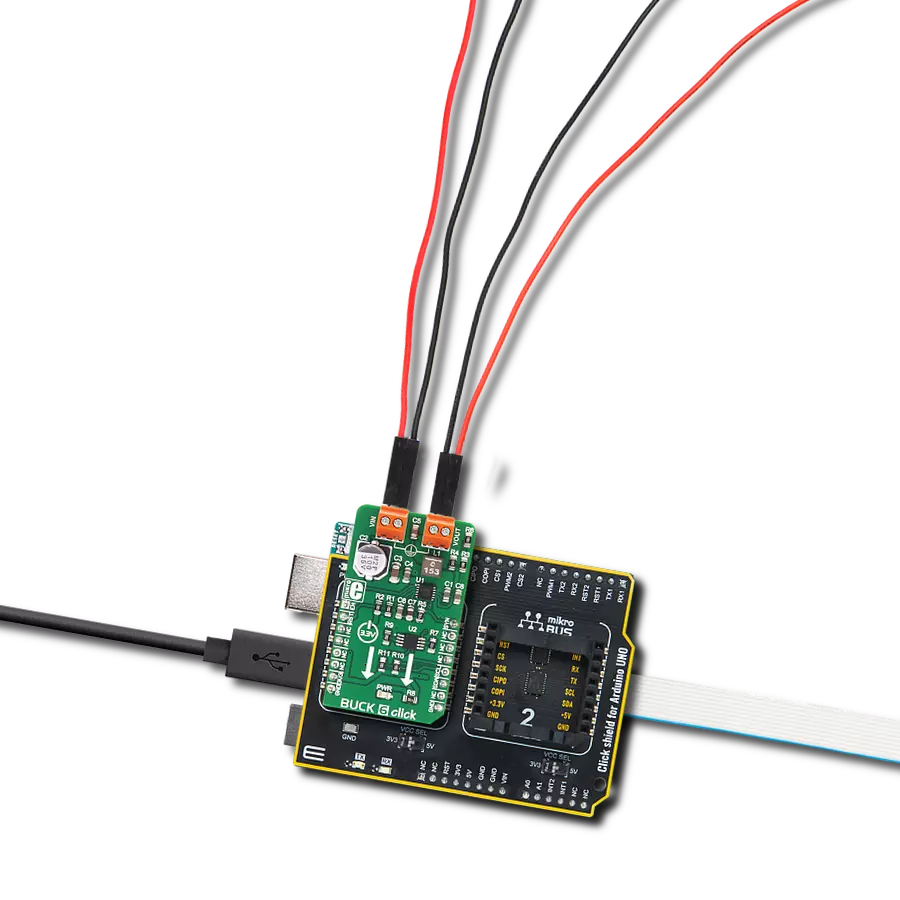
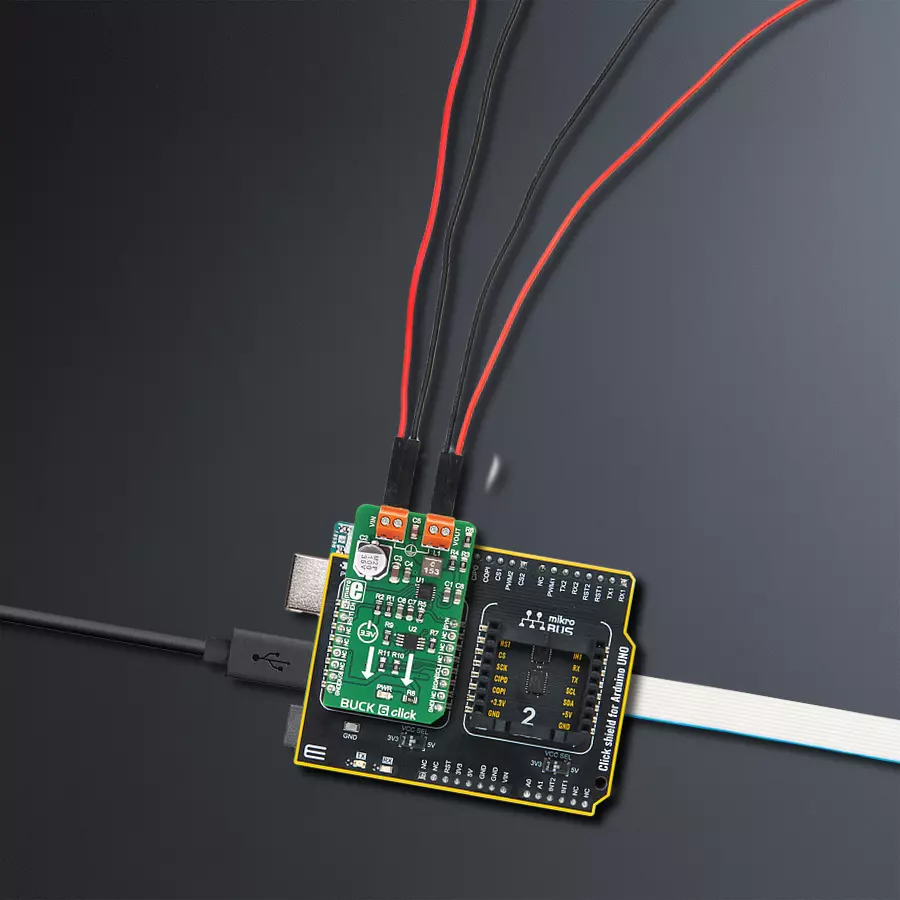
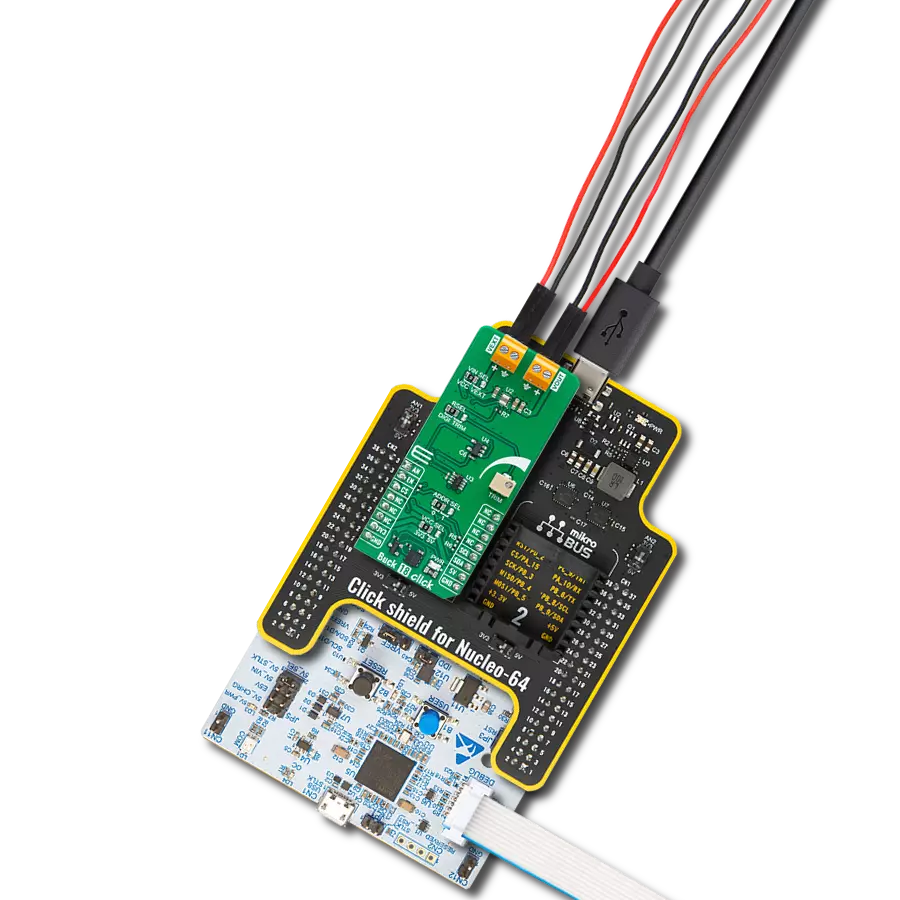
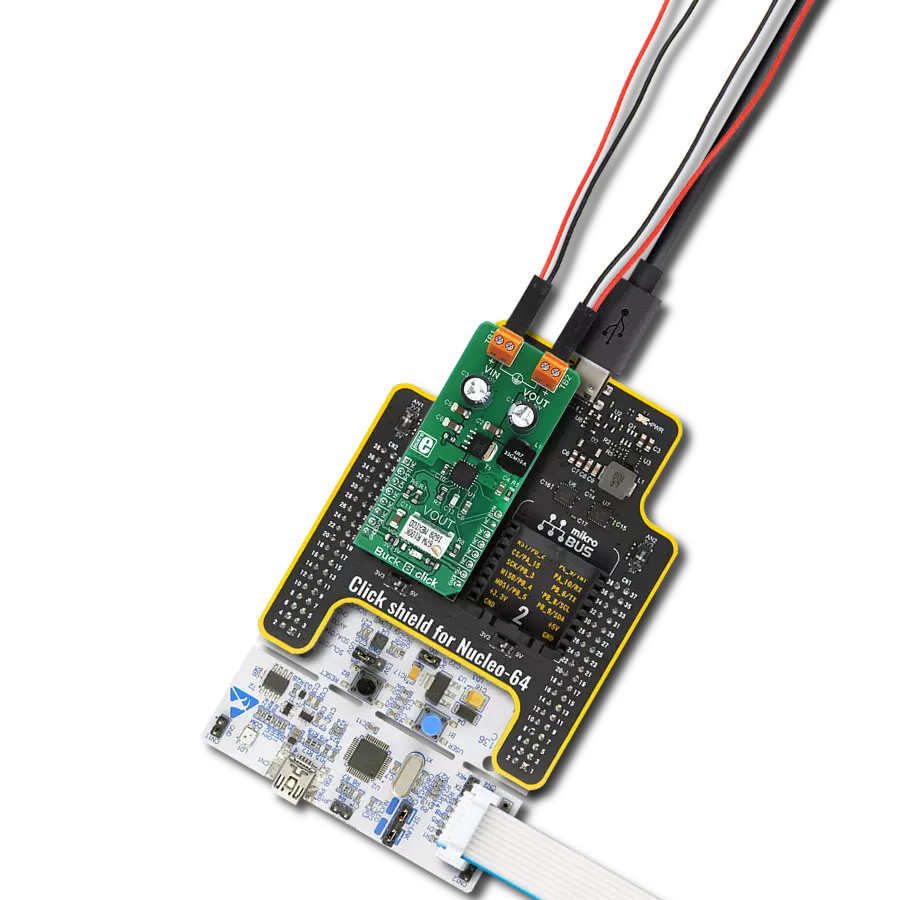
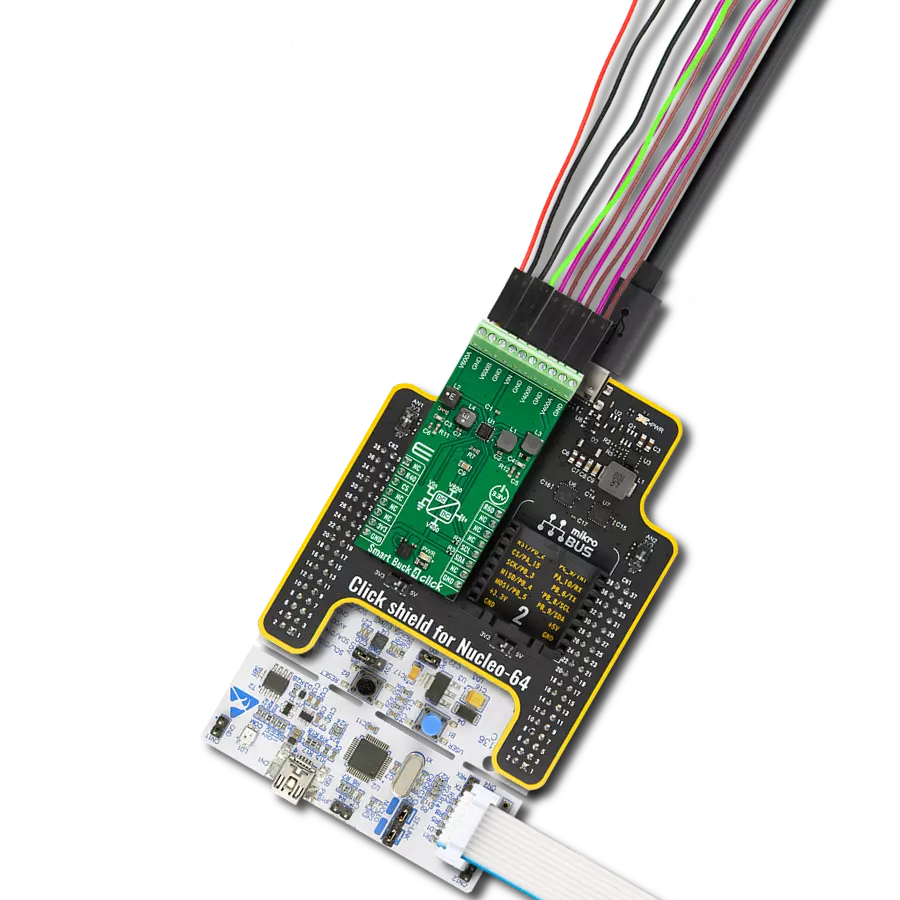
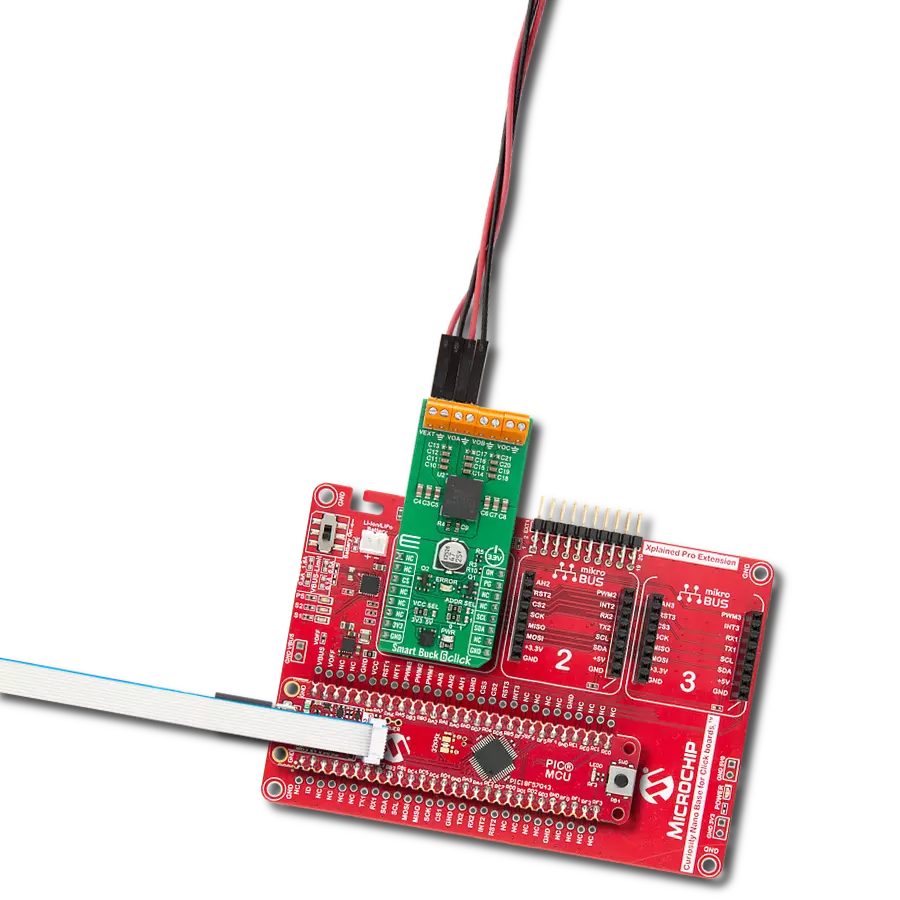
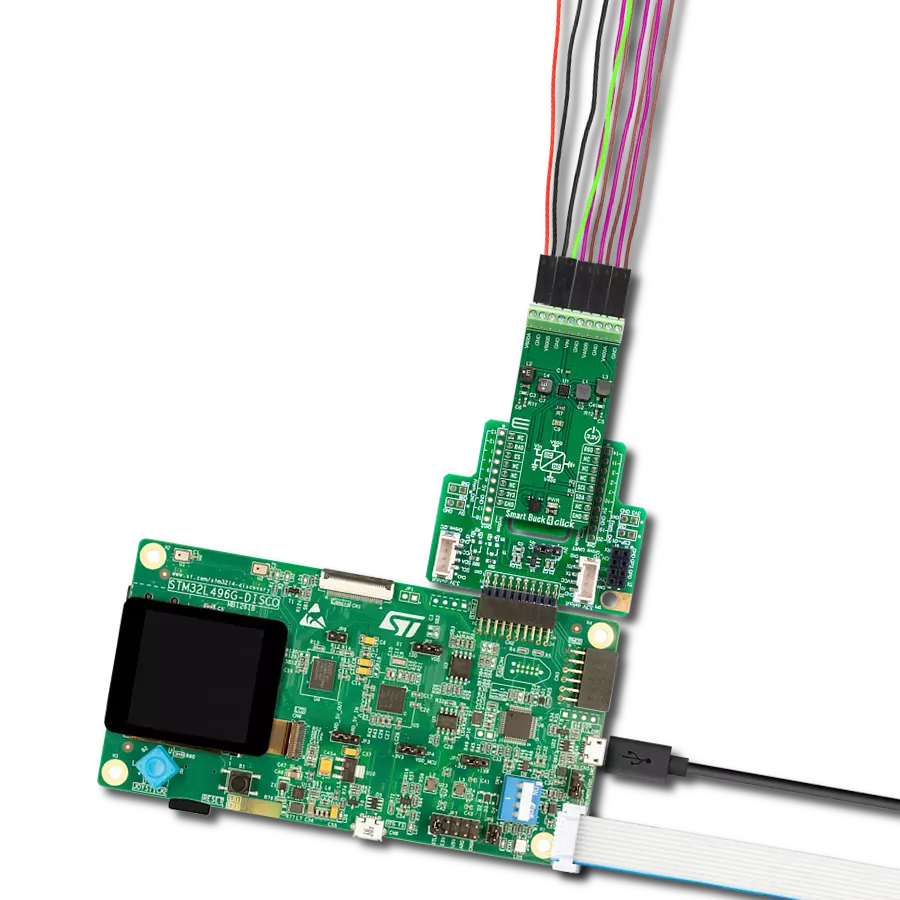
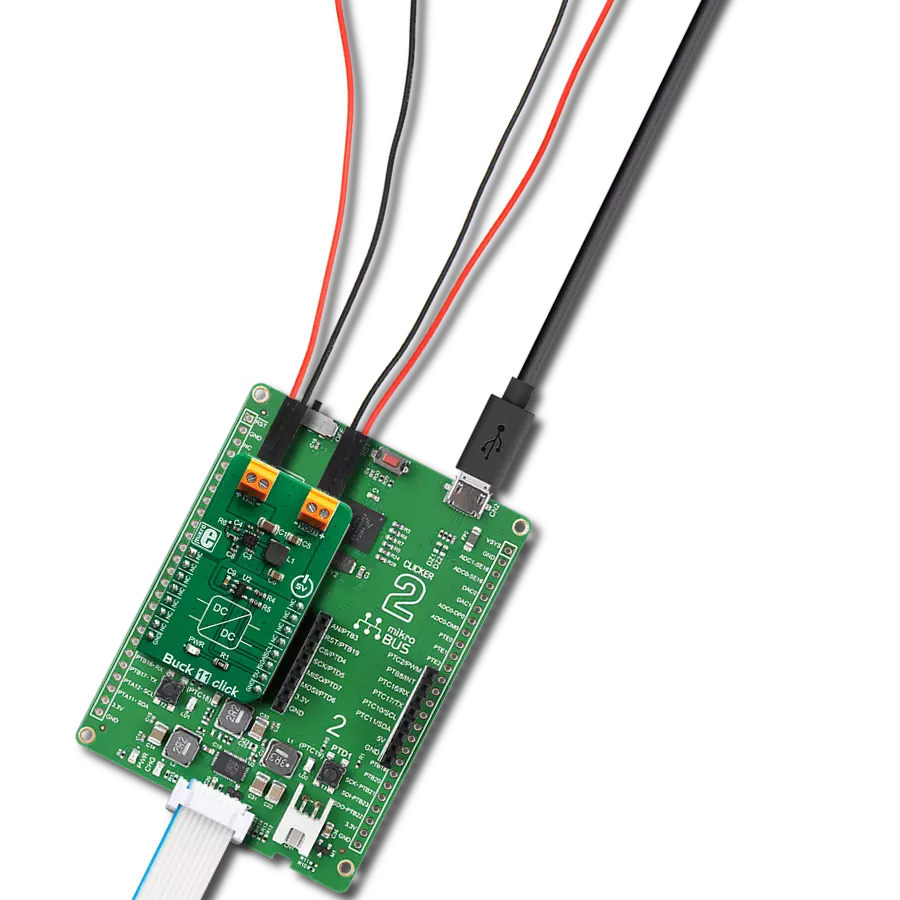
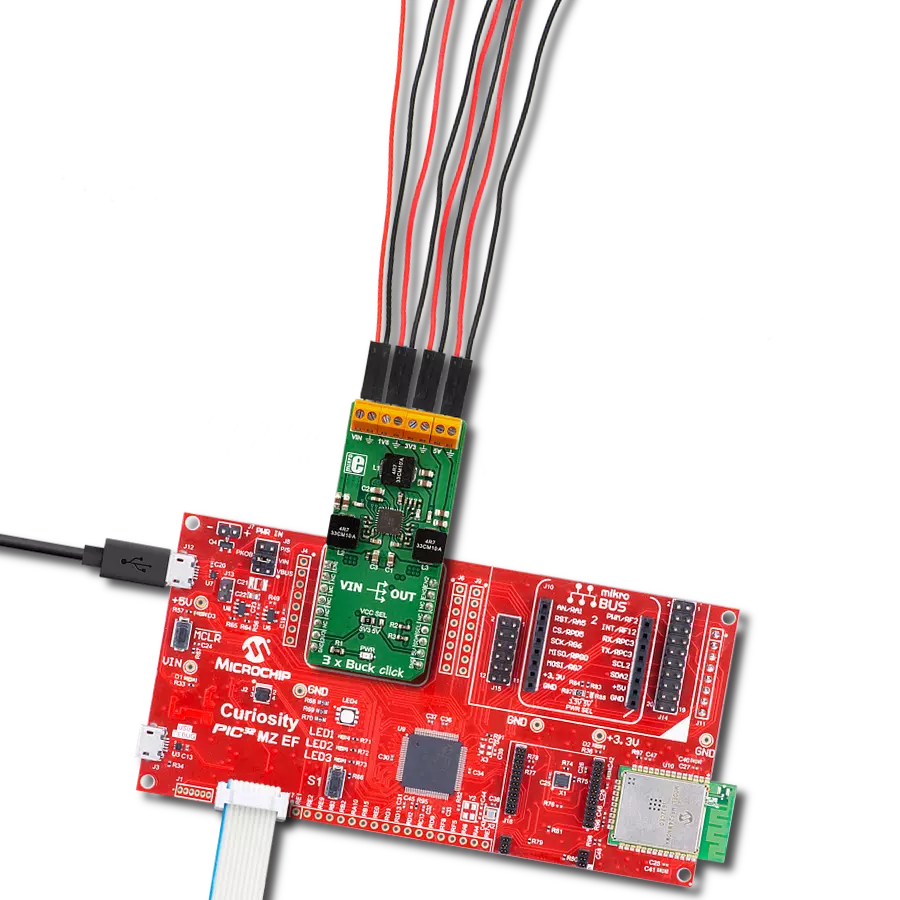
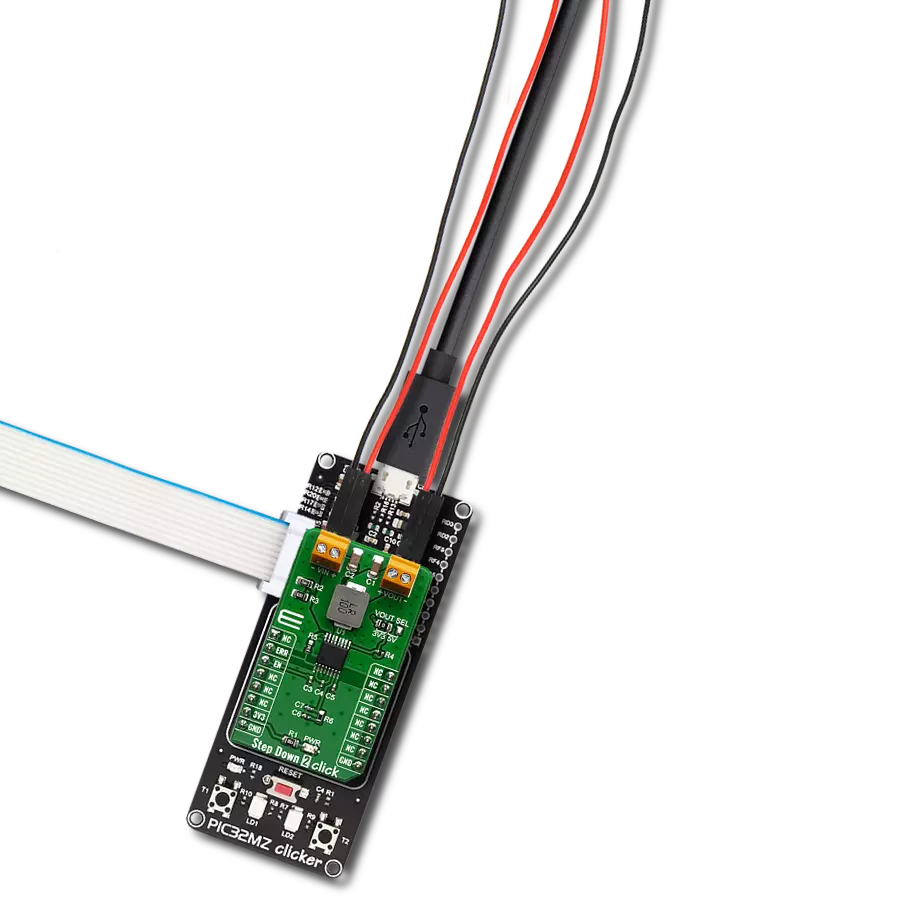
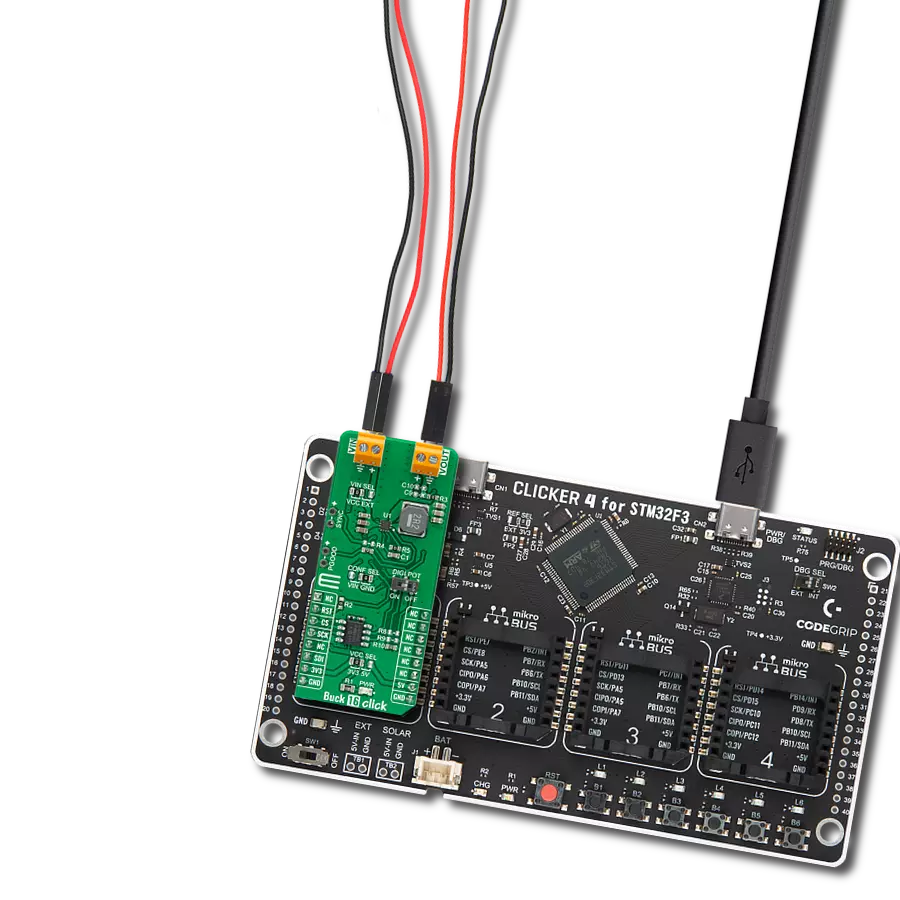
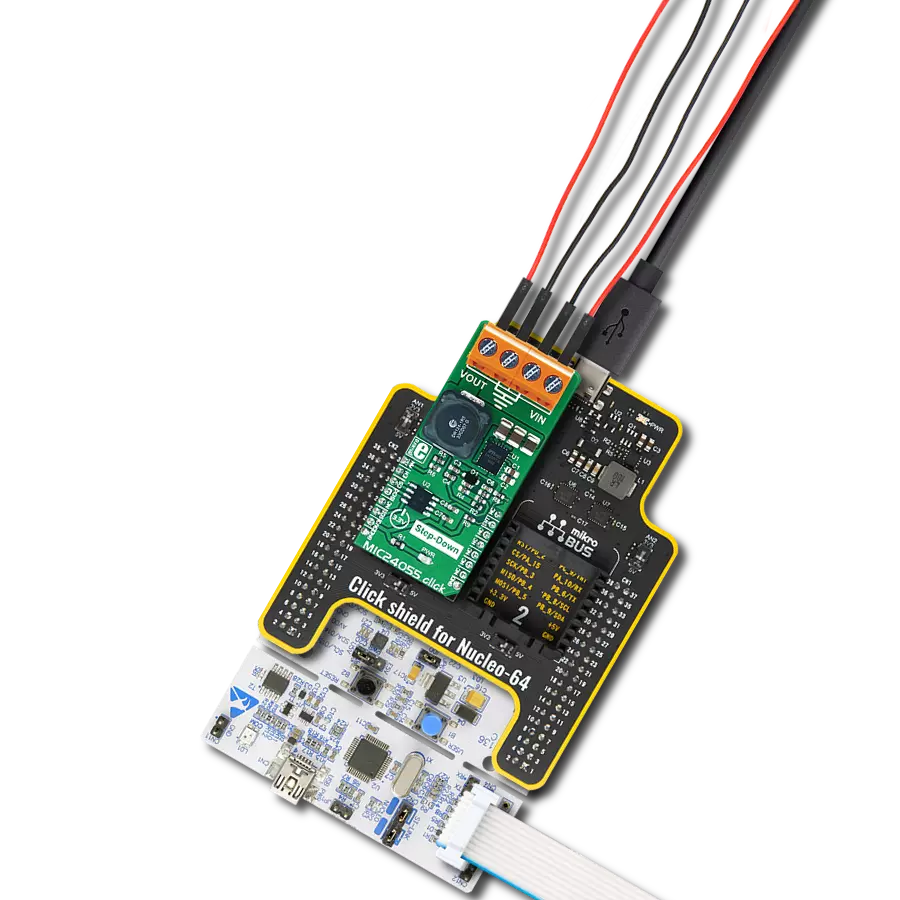
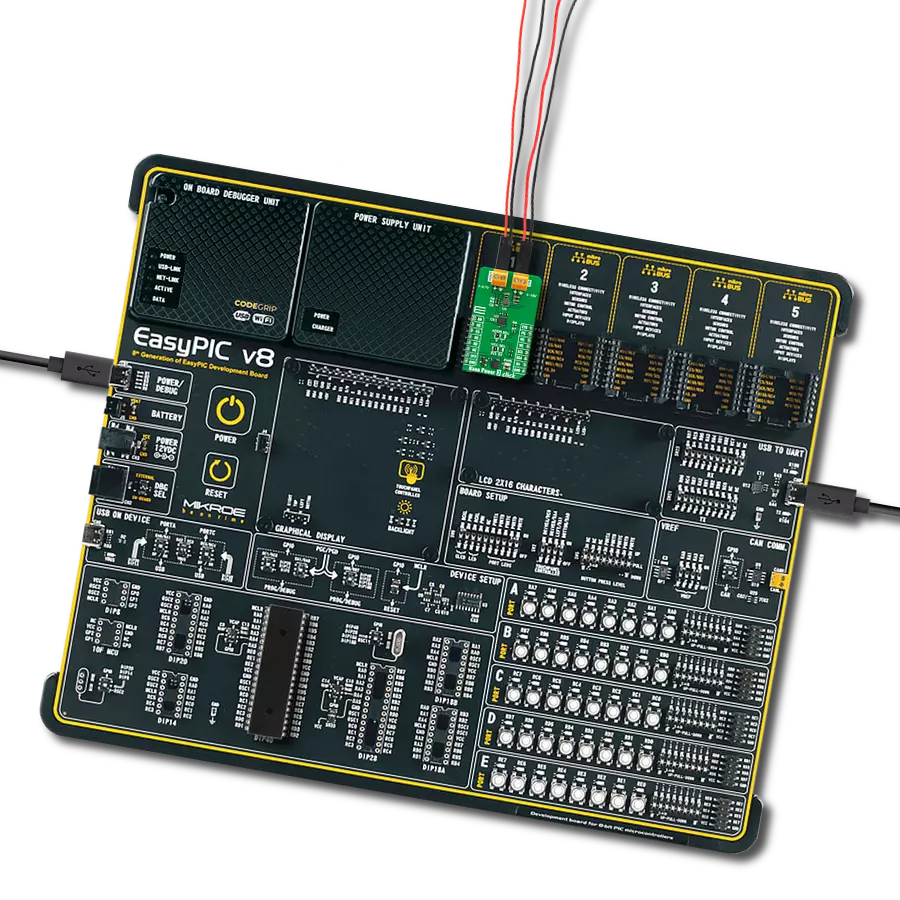
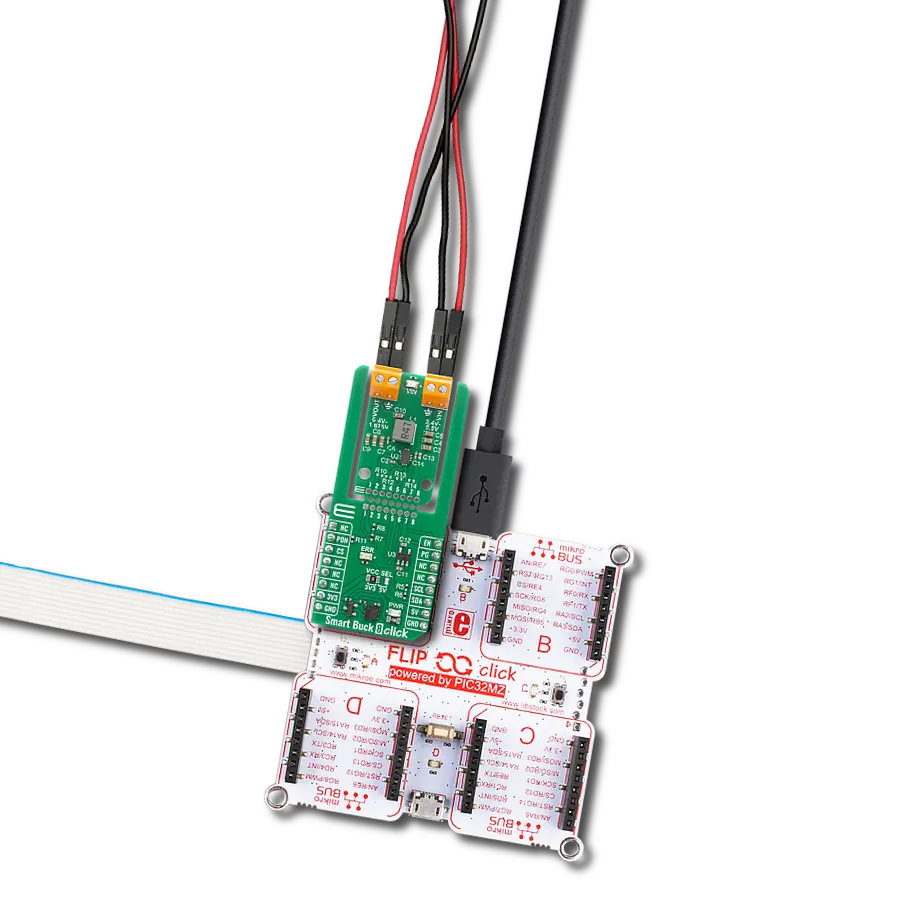
With its voltage regulation capabilities, this step-down buck solution ensures your electronic circuits' stable and reliable operation
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
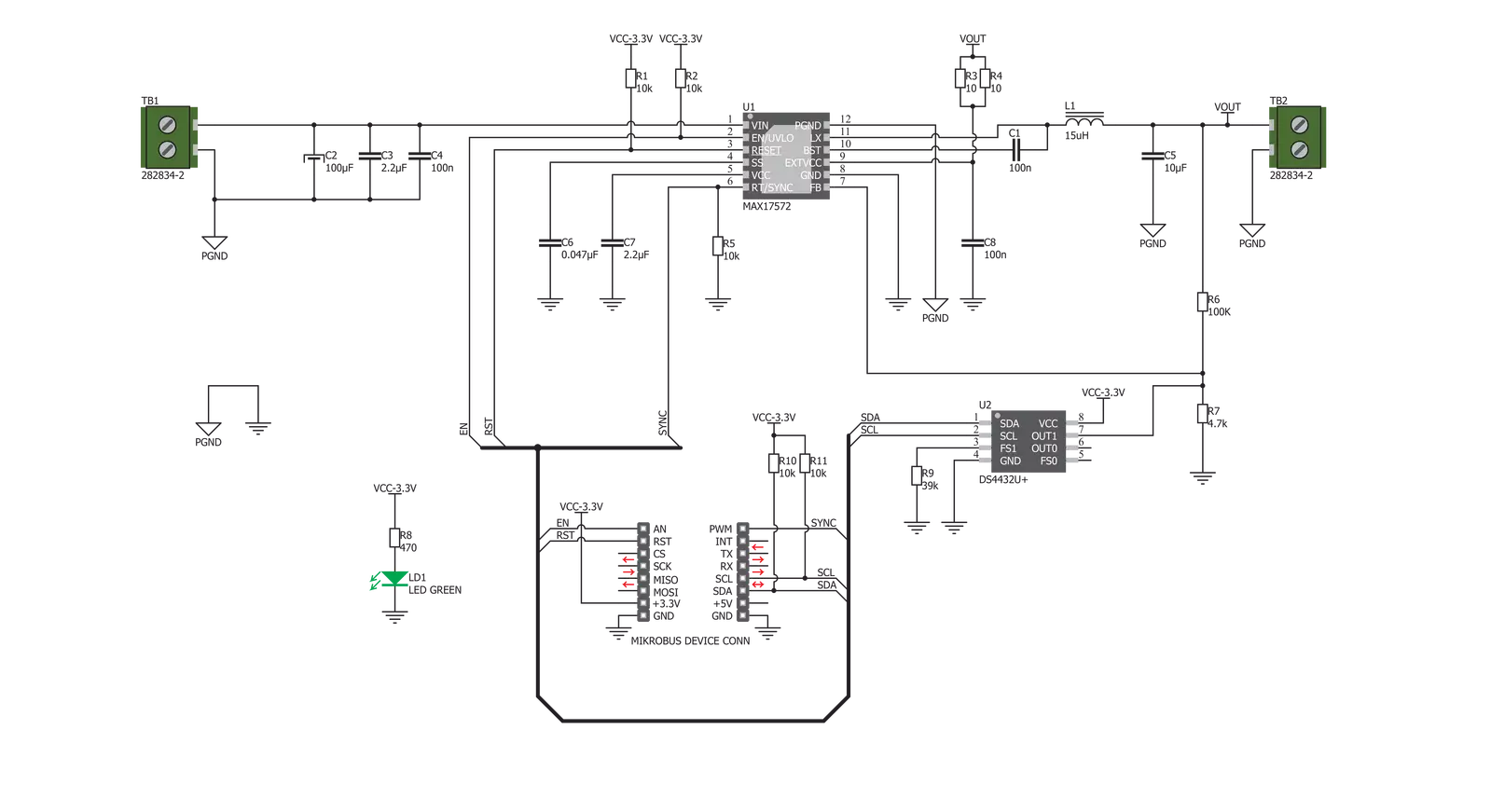
Buck 6 Click is based on the MAX17572, a step-down (buck) DC-DC converter from Analog Devices. This IC is the primary voltage regulation component, used in conjunction with the DS4432U, a dual channel, 7-Bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) with the I2C interface, also from Analog Devices. The DAC is connected to the FB pin of the MAX17572, affecting its internal PWM duty cycle and changing the output voltage that way. The MAX17572 requires very few components allowing the clean and simple design of the final application, considering all its features. The MAX17572 features robust overload and short-circuit protection. When the internally set current limit of 1.7A is exceeded, the high-side MOSFET is turned off, and the hiccup mode is triggered. This mode suspends the operation for 32,768 duty cycles, after which the soft start sequence is reattempted. If the fault condition is still present and the feedback voltage remains under 0.58V, the switching frequency will be halved to avoid overheating during the restart sequence. The output voltage regulation ranges from 0.9V up to 20V, with the input voltage up to 30V and greater than 5V. It should be noted that the input voltage must always be greater than the desired output
voltage. The voltage can be set via the I2C interface of the DS4432U DAC. The DAC is powered by the 3.3V rail of the mikroBUS™. This DAC requires very few components, such as the full-scale selection resistor. Since only one channel of the DAC is used, even fewer components are required for DAC itself. The DAC can both source and sink the current, so it must be properly set to get the desired effect on the output voltage. The included click board™ library contains a function that sets all the required initialization parameters and functions used to set up the output voltage. The soft start feature prevents the inrush current. The soft start capacitor determines this feature. The soft start is set to about 10ms on the BUCK 6 click. The EN pin of the MAX17572 is routed to the AN pin of the mikroBUS™. This pin is used to enable the buck converter but can also be used to set the undervoltage lockout threshold. If the input voltage falls under this threshold, the internal low drop output regulators (LDOs) will not power on the internal logic, and the buck converter will stay disabled. The onboard resistor pulls the EN pin up to the 3.3V mikroBUS™ power rail. The #RESET pin of the MAX17572 is an open drain output, and it is pulled to a HIGH logic level
by the onboard resistor. This pin is routed to the RST pin of the mikroBUS™ and can be used as the power good indication. When the output voltage drops below 92% of the nominal regulated output voltage, this pin is asserted and driven to a LOW logic level. One of the distinctive features of this buck converter is the ability to synchronize the switching clock frequency with an external clock signal. It is possible to synchronize the switching frequency within a range of about 0% to 10% lower than the value set by the onboard resistor, which is about 1.8MHz. For synchronizing purposes, the SYNC pin is routed to the PWM pin of the mikroBUS™. This feature primarily synchronizes switching frequencies when more than a single buck converter is used. The Click board™ is equipped with two screw terminals for an easy and secure connection. The input terminal is used to connect the input power source, while the output terminal is used to connect the load up to 1A. The click board is supplied with the auxiliary power for the DAC and other logic sections of the click board from the mikroBUS™ 3.3V power rail.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino UNO is a versatile microcontroller board built around the ATmega328P chip. It offers extensive connectivity options for various projects, featuring 14 digital input/output pins, six of which are PWM-capable, along with six analog inputs. Its core components include a 16MHz ceramic resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an
ICSP header, and a reset button, providing everything necessary to power and program the board. The Uno is ready to go, whether connected to a computer via USB or powered by an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. As the first USB Arduino board, it serves as the benchmark for the Arduino platform, with "Uno" symbolizing its status as the
first in a series. This name choice, meaning "one" in Italian, commemorates the launch of Arduino Software (IDE) 1.0. Initially introduced alongside version 1.0 of the Arduino Software (IDE), the Uno has since become the foundational model for subsequent Arduino releases, embodying the platform's evolution.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
32
RAM (Bytes)
2048
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino UNO has two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino UNO board without effort. The Arduino Uno, a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P, provides an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts and build prototypes with the ATmega328P microcontroller from various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (of which six can be used as PWM outputs), six analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator (CSTCE16M0V53-R0), a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and reset button. Most of the ATmega328P microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino UNO board with our Click Shield for Arduino UNO, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Buck 6 Click driver.
Key functions:
buck6_get_rst- Gets resetbuck6_set_mode- Set modebuck6_set_max_voltage- Set maximum voltage
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief BUCK6 Click example
*
* # Description
* BUCK 6 Click is an advanced synchronous DC-DC step down (buck) converter,
* with a very wide input voltage range and reasonably high output current.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization Driver init and settings chip on ACTIVE mode and setting the maximum range to 5V.
*
* ## Application Task
* Sets the different ranges of the maximum voltage.
*
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "buck6.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static buck6_t buck6;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
buck6_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
buck6_cfg_setup( &cfg );
BUCK6_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
buck6_init( &buck6, &cfg );
buck6_set_mode( &buck6, BUCK6_ACTIVE_MODE );
buck6_set_max_voltage( &buck6, BUCK6_MAX_RANGE_5000mV );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
buck6_set_max_voltage( &buck6, BUCK6_MAX_RANGE_2500mV );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
buck6_set_max_voltage( &buck6, BUCK6_MAX_RANGE_5000mV );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
buck6_set_max_voltage( &buck6, BUCK6_MAX_RANGE_7500mV );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
buck6_set_max_voltage( &buck6, BUCK6_MAX_RANGE_10000mV );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
buck6_set_max_voltage( &buck6, BUCK6_MAX_RANGE_7500mV );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
buck6_set_max_voltage( &buck6, BUCK6_MAX_RANGE_5000mV );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Buck