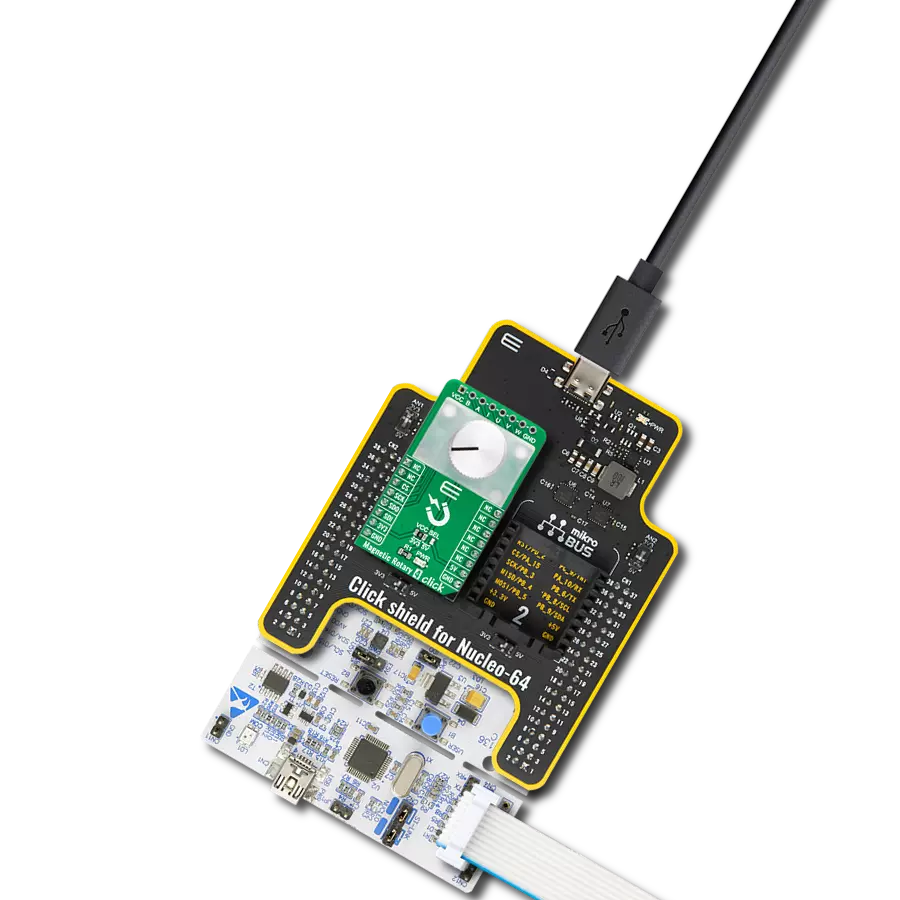
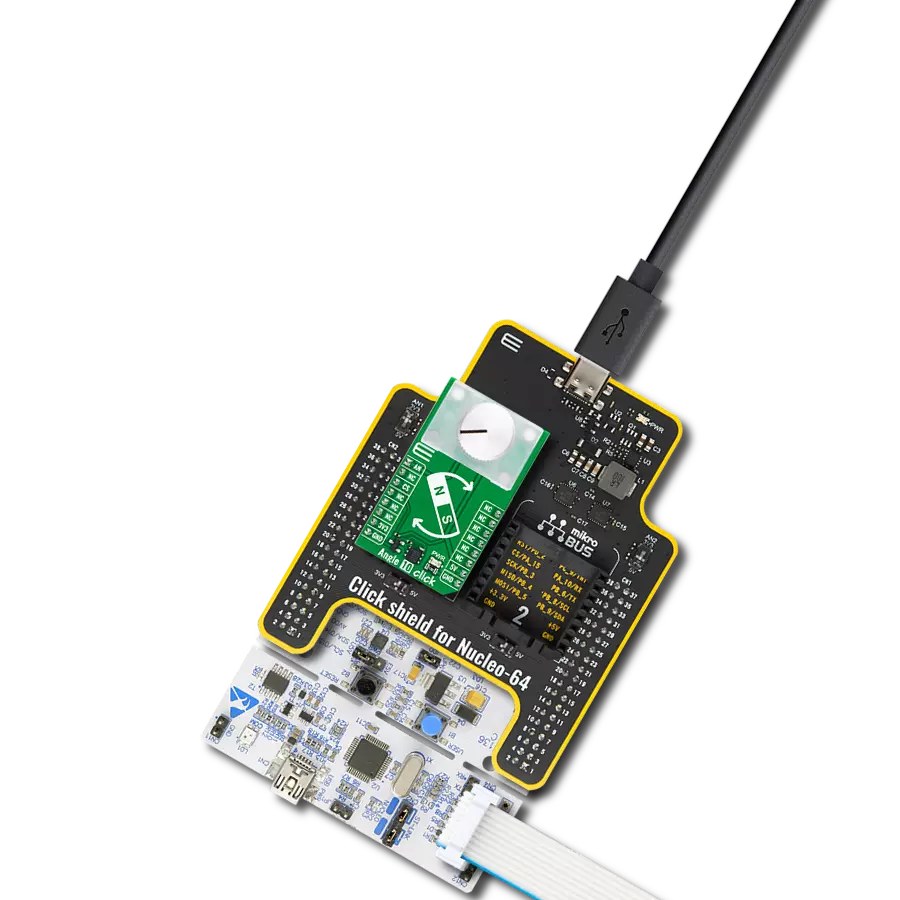
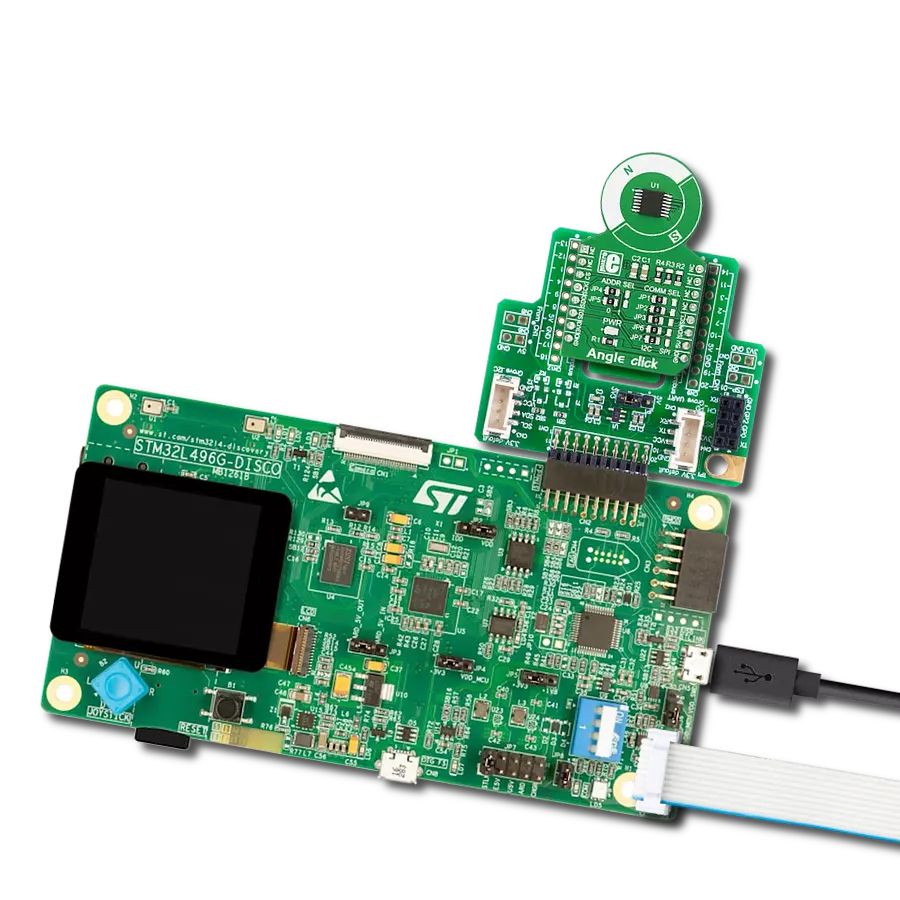
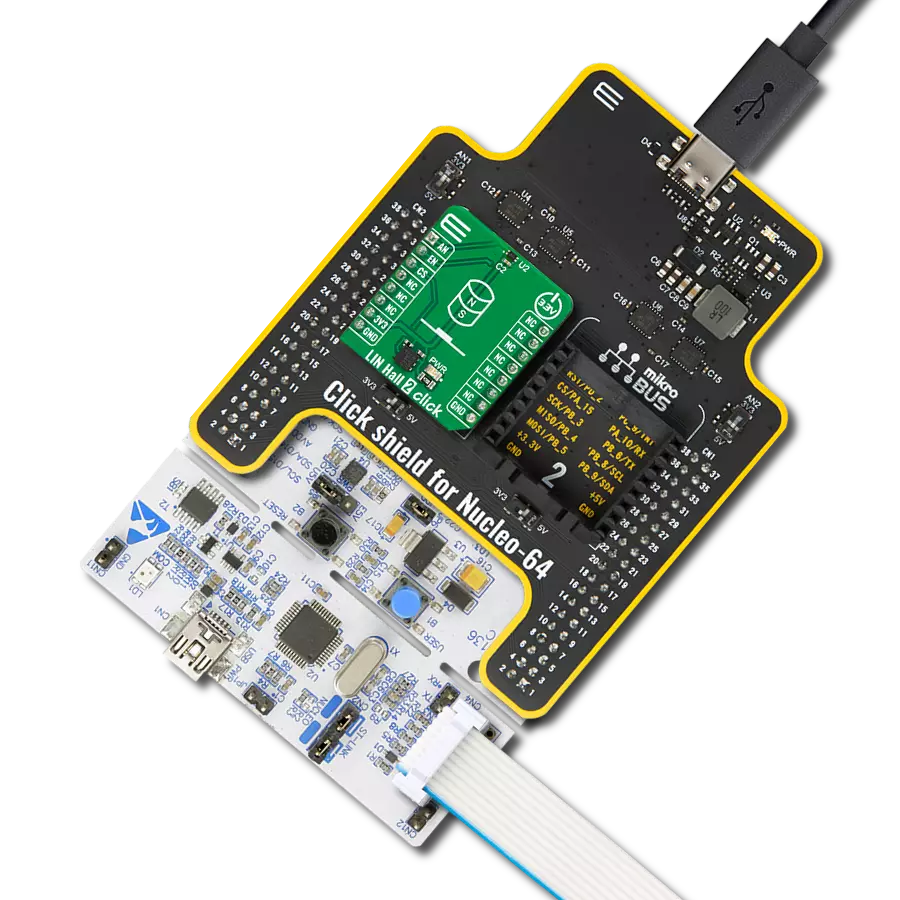
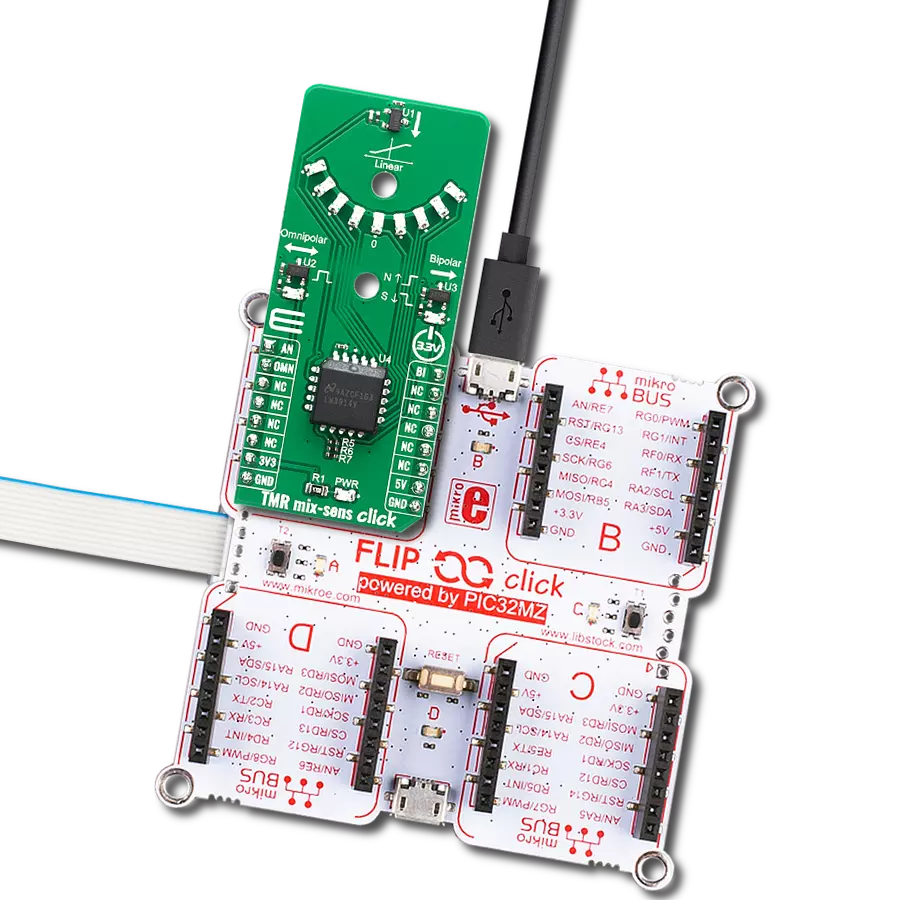
Our angular magnetic rotary sensor sets a new standard for accuracy, providing seamless and precise angular measurements over a full 360 degrees of magnet rotation
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
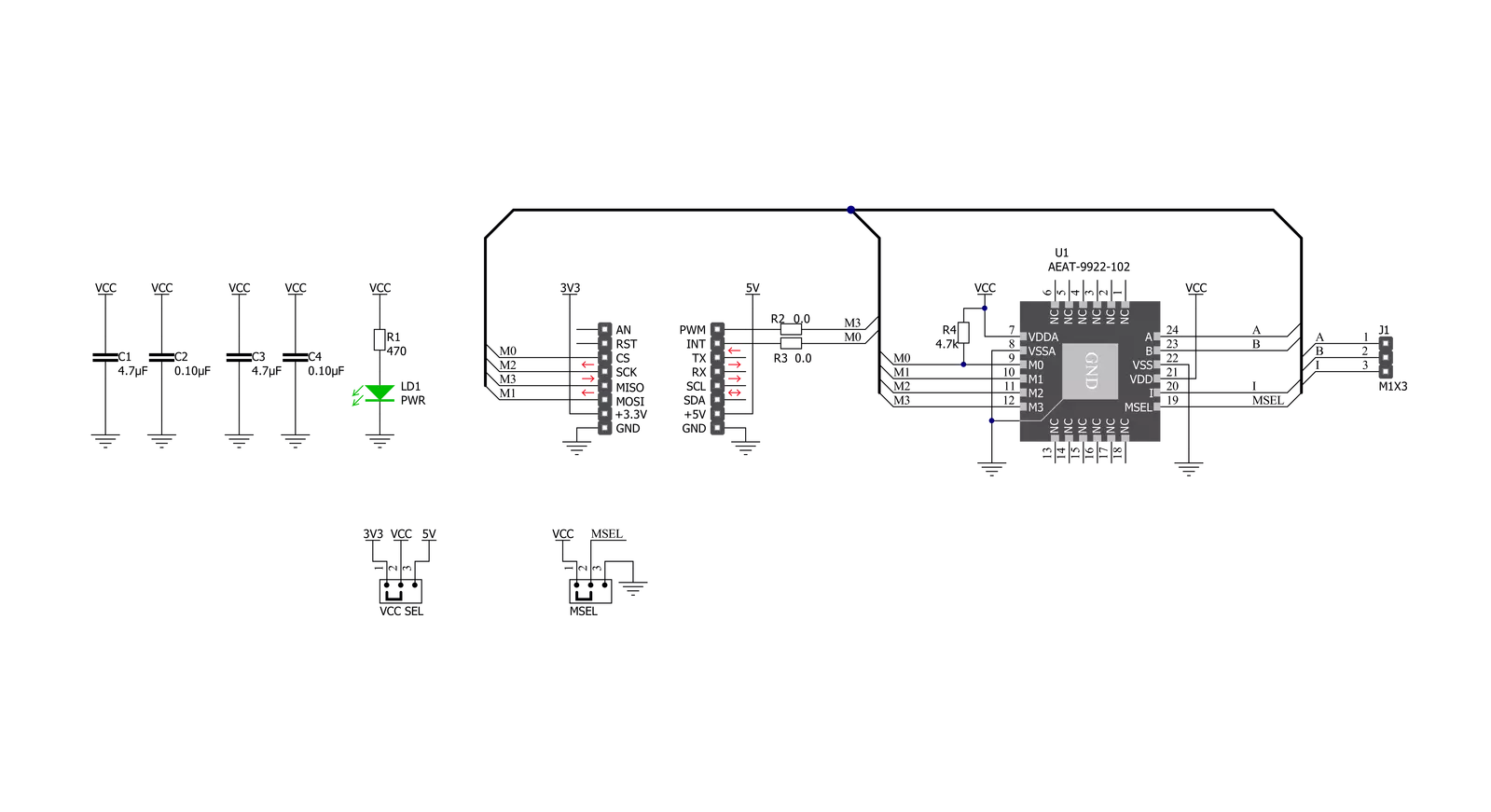
Magnetic Rotary 2 Click is based on the AEAT-9922, an angular magnetic rotary sensor manufactured with a CMOS standard process providing accurate angular measurement over a full 360 degrees of rotation from Broadcom Limited. It can accurately measure a magnet's rotational angle when aligned and perpendicular to the device by using its integrated Hall sensors to detect its magnetic field. The detected magnetic signals are then taken as input signals to be properly conditioned to negate their non-idealities before inputting them into the analog amplifiers for strength amplification and filtering. After which, the amplified analog signals are fed into the internal analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to be converted into digital signals for the final digital processing stage. A simple two-pole magnet generates the necessary magnetic field by rotating it perpendicularly. Wide magnetic field sensor configurations allow On-Axis (end of shaft) or Off-Axis (side of the shaft) modes in application. The used magnet should have sufficient
magnetic field strength (mT) to generate the magnetic field for signal generation. The device provides digital information of magnetic field strength high and magnetic field strength low to indicate whether the magnets are too close or far away from our device's surface. Magnetic Rotary 2 Click communicates with MCU through a standard SPI interface supporting the common SPI mode, SPI Mode 1. Digital processing provides a digitized output of the absolute and incremental signals. Each output is configurable via CS pin, MSEL (Mode Selection for desirable protocol) jumper, and AEAT-9922 internal PSEL registers configurable through memory. In addition, an absolute angular representation can also be selected using a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal by populating an onboard R2 resistor, which provides an instant indication of the magnet's angular position with a selectable and one-time programmable resolution from 10 to 18 bits. Alongside this feature, the communication error signal labeled as ERR and routed on the INT pin of
the mikroBUS™ socket can be activated by populating the onboard R3 resistor. The incremental outputs are available from digital outputs of their respective A, B, and I pins, the same for the U, V, and W commutation signals routed to the upper-right side onboard header. The incremental positions are indicated on ABI and UVW signals with a comprehensive user-configurable resolution from 1CPR, up to 10,000CPR of ABI signals, and pole pairs from 1 to 32 pole pairs (from 2 to 64 poles) for UVW commutation signals. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Fusion for STM32 v8 is a development board specially designed for the needs of rapid development of embedded applications. It supports a wide range of microcontrollers, such as different 32-bit ARM® Cortex®-M based MCUs from STMicroelectronics, regardless of their number of pins, and a broad set of unique functions, such as the first-ever embedded debugger/programmer over WiFi. The development board is well organized and designed so that the end-user has all the necessary elements, such as switches, buttons, indicators, connectors, and others, in one place. Thanks to innovative manufacturing technology, Fusion for STM32 v8 provides a fluid and immersive working experience, allowing
access anywhere and under any circumstances at any time. Each part of the Fusion for STM32 v8 development board contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. An advanced integrated CODEGRIP programmer/debugger module offers many valuable programming/debugging options, including support for JTAG, SWD, and SWO Trace (Single Wire Output)), and seamless integration with the Mikroe software environment. Besides, it also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development board. It can use a wide range of external power sources, including a battery, an external 12V power supply, and a power source via the USB Type-C (USB-C) connector.
Communication options such as USB-UART, USB HOST/DEVICE, CAN (on the MCU card, if supported), and Ethernet is also included. In addition, it also has the well-established mikroBUS™ standard, a standardized socket for the MCU card (SiBRAIN standard), and two display options for the TFT board line of products and character-based LCD. Fusion for STM32 v8 is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem for rapid development. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping and development thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU
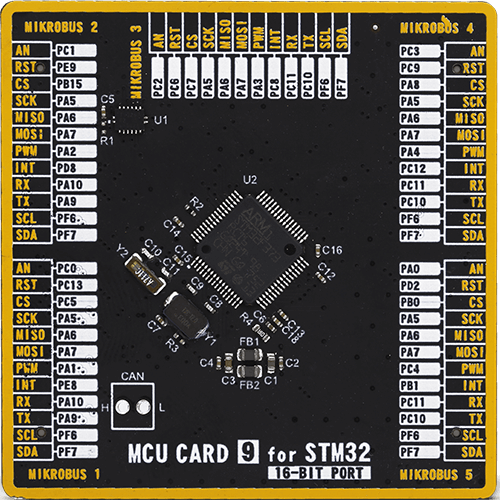
Type
8th Generation
Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
256
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
64
RAM (Bytes)
32768
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Magnetic Rotary 2 Click driver.
Key functions:
magneticrotary2_write_register- This function writes a data byte to the selected register by using SPI serial interfacemagneticrotary2_read_register- This function reads a data byte from the selected register by using SPI serial interfacemagneticrotary2_get_angle- This function reads the absolute position raw data and converts it to degrees (Angle)
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief MagneticRotary2 Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of Magnetic Rotary 2 Click board by reading and displaying
* the magnet's angular position in degrees.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and performs the Click default configuration.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads the magnet's angular position in degrees every 100ms and displays the results on the USB UART.
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "magneticrotary2.h"
static magneticrotary2_t magneticrotary2;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
magneticrotary2_cfg_t magneticrotary2_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
magneticrotary2_cfg_setup( &magneticrotary2_cfg );
MAGNETICROTARY2_MAP_MIKROBUS( magneticrotary2_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( SPI_MASTER_ERROR == magneticrotary2_init( &magneticrotary2, &magneticrotary2_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
if ( MAGNETICROTARY2_ERROR == magneticrotary2_default_cfg ( &magneticrotary2 ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Default configuration." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
float angle = 0;
if ( MAGNETICROTARY2_OK == magneticrotary2_get_angle ( &magneticrotary2, &angle ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Angle: %.2f degrees\r\n\n", angle );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END