Stay ahead of potential health risks with our temperature measurement technology, designed to provide early warnings of temperature fluctuations in critical environments.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
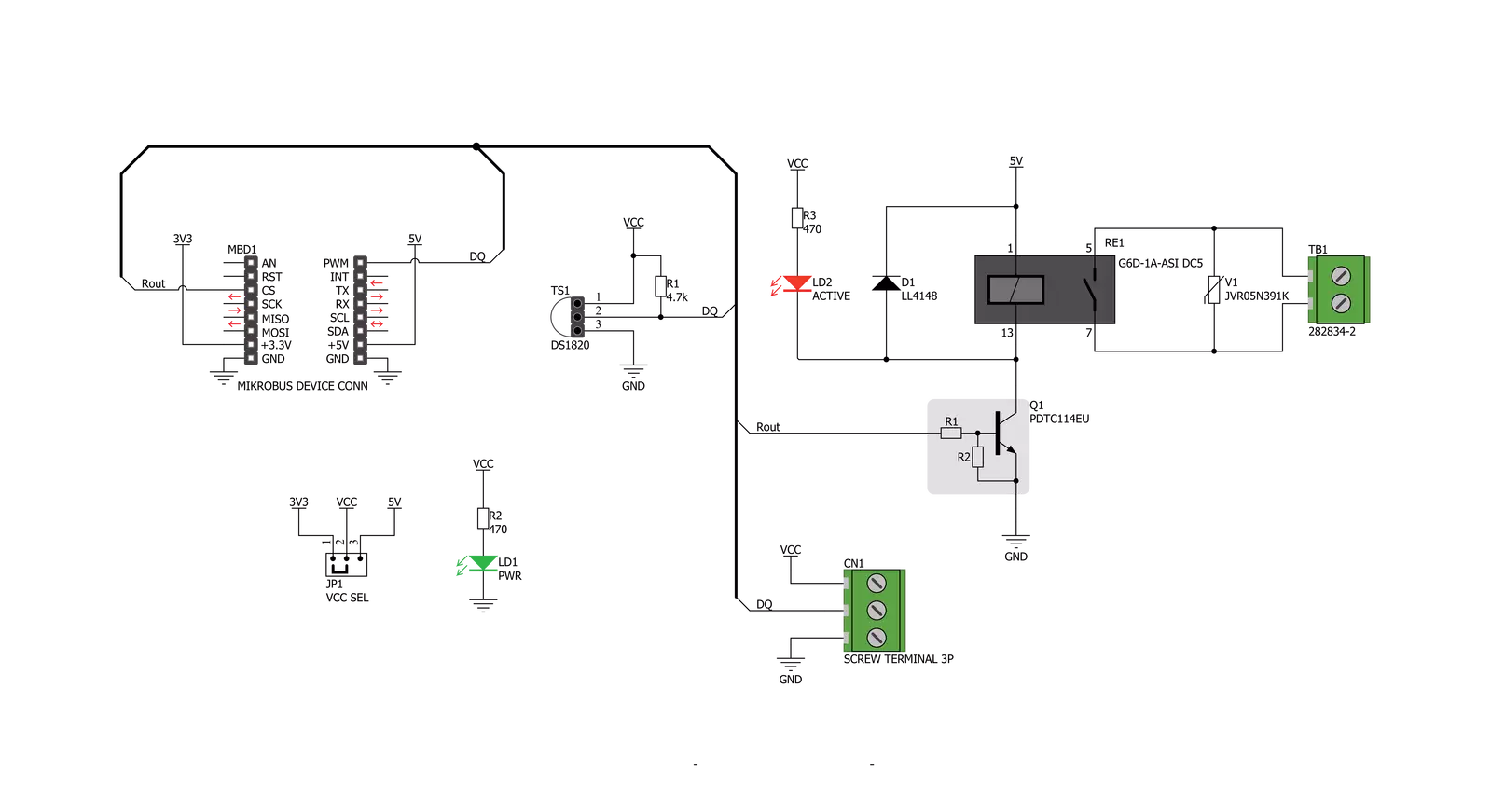
Thermostat 2 Click is designed without the main IC; it allows an externally connected thermal sensor to be used, instead. It can be interfaced with the DS1820 compatible sensor which uses 1-Wire® communication. The Click board™ is equipped with a 3-pin female socket, which can be used to install the DS1820 compatible sensor in TO-92 casing, onboard. There is also a 3-pole screw terminal, that can be used if the sensor needs to be installed on a remote location, i.e. onto a heating component. The screw-terminal shares its lines with the socket. The 1-Wire® communication with the host MCU is performed over the PWM pin of the mikroBUS™. Depending on the temperature information obtained over the 1-Wire® interface, the host MCU can take the necessary action: it can either open or close contacts of the relay. The Click board™ uses the G6D series PCB power relay, from Omron. This quality relay can withstand an amazingly large number of mechanical cycles, with no load connected. However, when there is a significant load connected at its output, micro-electric arcs cause the contacts to wear over time. With the maximum load current of 5A, it can sustain up to 70,000
cycles. Its contacts are made of silver alloy, yielding exceptional ON resistance of only 100mΩ (max). The relay is activated by a magnetic field, generated in a built-in coil on the low-voltage side. The coil is activated by the host MCU. The voltage for the coil activation is 5V, while the current through the coil is 40mA. The MCU is not able to drive the coil directly, therefore an NPN transistor had to be added. Its base is controlled by the host MCU, allowing the coil to drain enough current from the 5V mikroBUS™ power rail. The base of the transistor is routed to the CS pin of the Click board™. The transistor packs two biasing resistors in the same casing, so it can be directly used on the MCU pin, without external biasing resistors. A red color LED, labeled as ACTIVE is used to indicate that the transistor is in an open state and that the current is running through the relay coil. When the current through a coil (or any other inductor) is suddenly changed, the backEMF will be generated, opposing the changes of the current. This can sometimes lead to damage to the control circuit: in this case, the transistor will become inversely polarized. To prevent this from happening, a flyback diode is added
across the coil. During the normal operation, this diode does not conduct any current. However, when the coil is switched OFF, the inverse polarization will cause the current to pass through this diode with minimum resistance. This prevents inverse (flyback) voltage from building up, so the transistor remains safe. Contacts at the output may be connected to a higher voltage and larger current may run through. To prevent high voltage transients in this case, a flyback diode is not a viable option. Therefore, Thermostat 2 click uses a varistor (VDR). This component rapidly drops its resistance as the voltage rises above its rated clamping voltage. The excessive voltage transient will pass through the VDR since it will become a current path with the least resistance. During the normal operation, while the voltage stays below the rated clamping voltage, VDR has a very high resistance, so the current runs through the electrical circuit, instead. The operating voltage of the Click board™ can be selected by the VCC SEL jumper. This jumper allows selecting either 3.3V or 5V from the mikroBUS™. The selected voltage will be applied to the VCC pin of the connected DS1820 sensor.
Features overview
Development board
Clicker 2 for Kinetis is a compact starter development board that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It comes with an onboard 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4F microcontroller, the MK64FN1M0VDC12 from NXP Semiconductors, two mikroBUS™ sockets for Click board™ connectivity, a USB connector, LED indicators, buttons, a JTAG programmer connector, and two 26-pin headers for interfacing with external electronics. Its compact design with clear and easily recognizable silkscreen markings allows you to build gadgets with unique functionalities and
features quickly. Each part of the Clicker 2 for Kinetis development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the possibility of choosing the Clicker 2 for Kinetis programming method, using a USB HID mikroBootloader or an external mikroProg connector for Kinetis programmer, the Clicker 2 board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development kit. It provides two ways of board-powering; through the USB Micro-B cable, where onboard voltage regulators provide the appropriate voltage levels to each component on the board, or
using a Li-Polymer battery via an onboard battery connector. All communication methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board, including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, reset button, and several user-configurable buttons and LED indicators. Clicker 2 for Kinetis is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem, allowing you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
NXP
Pin count
121
RAM (Bytes)
262144
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Thermostat 2 Click driver.
Key functions:
thermostat2_read_temperature- This function reads the temperature value in Celsius.thermostat2_relay_state- This function turns the relay on/off.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief Thermostat 2 Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of Thermostat 2 Click board by reading
* and displaying the temperature in Celsius and turning the relay on/off
* depending on the temperature value.
* DS1820, DS18S20 and DS18B20 chips can be used in this example.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and performs the Click default configuration.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads and displays the temperature measured by the Click board on the UART Terminal.
* If the temperature goes beneath the THERMOSTAT2_TEMPERATURE_LIMIT,
* the relay will be turned off while otherwise it will be turned on.
* In both cases an appropriate message will be displayed on the terminal.
*
* @author Aleksandra Cvjetićanin
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "thermostat2.h"
static thermostat2_t thermostat2;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
thermostat2_cfg_t thermostat2_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
thermostat2_cfg_setup( &thermostat2_cfg );
THERMOSTAT2_MAP_MIKROBUS( thermostat2_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( ONE_WIRE_ERROR == thermostat2_init( &thermostat2, &thermostat2_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
if ( THERMOSTAT2_ERROR == thermostat2_default_cfg ( &thermostat2 ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Default config." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
static uint8_t relay_state = 0xFF;
float temperature;
if ( THERMOSTAT2_OK == thermostat2_read_temperature ( &thermostat2, &temperature ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Temperature: %.2f C\r\n\n ", temperature );
}
if ( temperature < THERMOSTAT2_TEMPERATURE_LIMIT )
{
if ( relay_state != THERMOSTAT2_RELAY_ON )
{
log_info( &logger, " Relay is ON.\r\n " );
thermostat2_relay_state ( &thermostat2, THERMOSTAT2_RELAY_ON );
relay_state = THERMOSTAT2_RELAY_ON;
}
}
else
{
if ( relay_state != THERMOSTAT2_RELAY_OFF )
{
log_info( &logger, " Relay is OFF.\r\n" );
thermostat2_relay_state ( &thermostat2, THERMOSTAT2_RELAY_OFF );
relay_state = THERMOSTAT2_RELAY_OFF;
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END

































