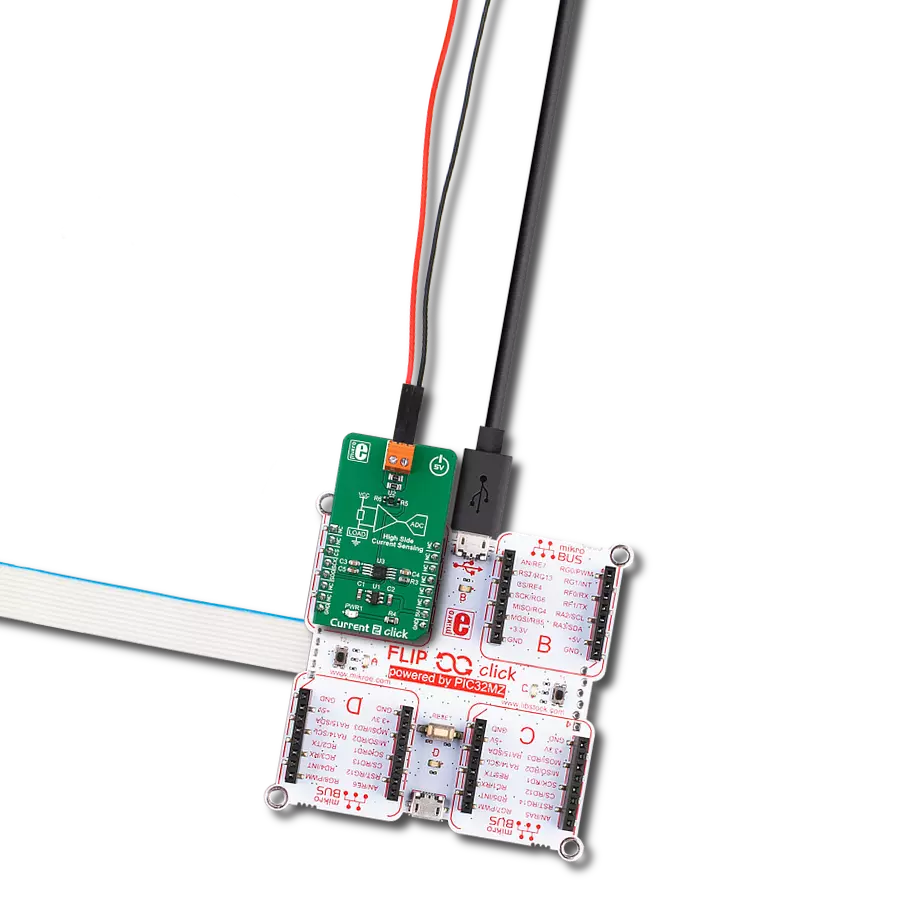
Unleash the potential of accurate bidirectional current sensing with our solution, engineered to go beyond simple measurements. Empower your systems with the ability to monitor, analyze, and optimize power usage in both directions for unprecedented control.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
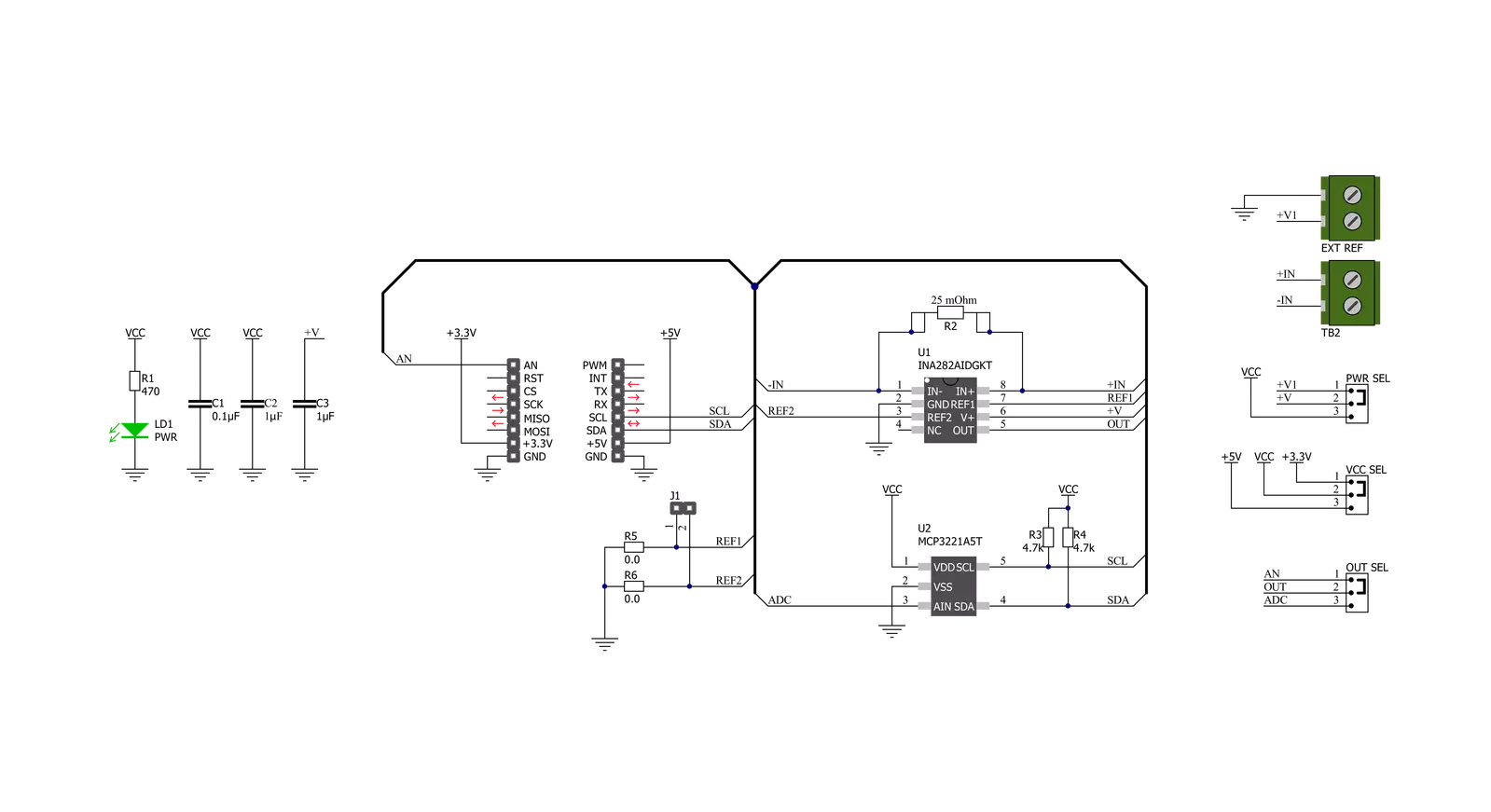
Current 7 Click is based on the INA381, a high-accuracy current-sensing amplifier from Texas Instruments. This voltage output current-sensing amplifier accurately measures voltages developed across the current-sensing resistor (also known as a current-shunt resistor) at a common-mode range that extends 14V below the negative supply rail as up to 80V, allowing for either low-side or high-side current sensing. The zero-drift topology enables high-precision measurements with maximum input offset voltages as low as 70μV over a wide temperature range. This Click board™ possesses two ways to communicate with the MCU. The analog output signal of the INA282 can be converted to a digital value using MCP3221, a successive approximation A/D converter with a 12-bit resolution from Microchip using a 2-wire I2C
compatible interface, or can be sent directly to an analog pin of the mikroBUS™ socket labeled as AN. The MCP3221 provides one single-ended input with low power consumption, a low maximum conversion current, and a Standby current of 250μA and 1μA, respectively. Data can be transferred at up to 100kbit/s in the Standard and 400kbit/s in the Fast Mode. Selection can be performed by onboard SMD jumper labeled as OUT SEL, setting it to an appropriate position marked as AN and ADC. The INA282 also allows a connection of external voltage signals on the onboard headers labeled REF1 and REF2 for the device’s reference voltage. This reference voltage determines how the output responds to certain input conditions. The configurable settings of the reference voltage control resistors, R5 and R6, allow the INA282 to
be used in unidirectional and bi-directional applications. More information about these operational modes can be found in the attached datasheet. This Click board™ can operate with both 3.3V and 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. It allows both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs to use the communication lines properly. Additionally, there is a possibility for the INA282 power supply selection via jumper labeled as PWR SEL to supply the INA282 from an external power supply terminal in the range from 2.7V to 18V or with mikroBUS™ power rails. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used, as a reference, for further development.

Features overview
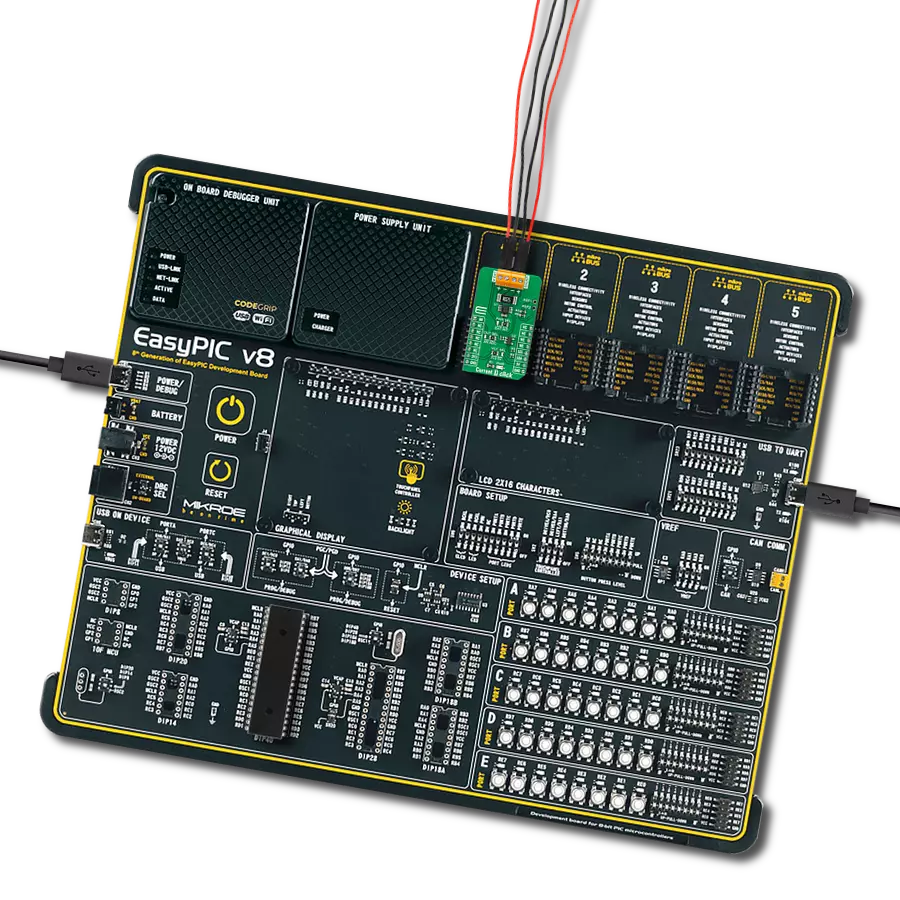
Development board
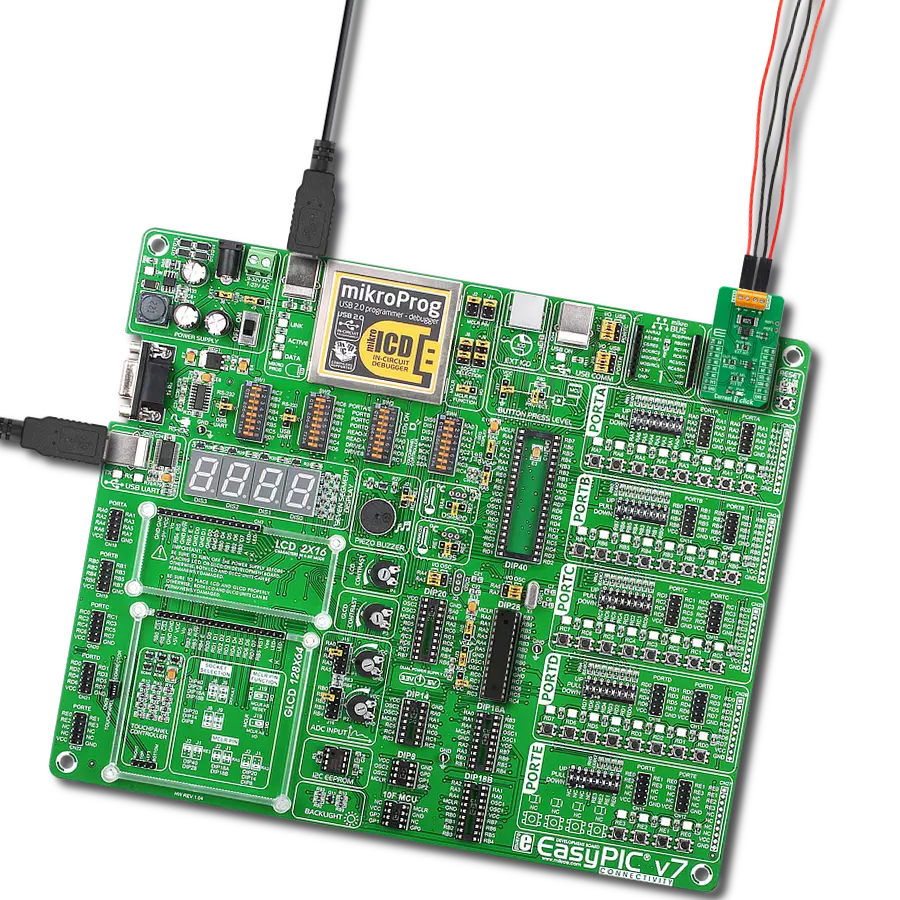
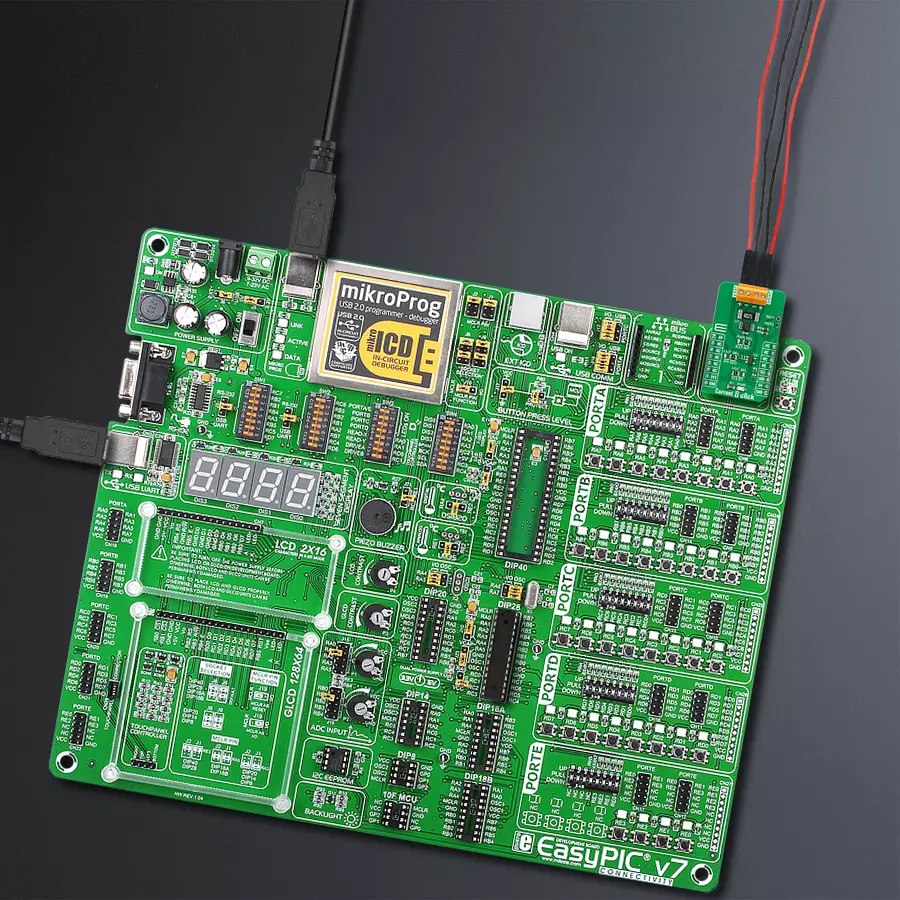
EasyPIC v7 is the seventh generation of PIC development boards specially designed to develop embedded applications rapidly. It supports a wide range of 8-bit PIC microcontrollers from Microchip and has a broad set of unique functions, such as a powerful onboard mikroProg programmer and In-Circuit debugger over USB-B. The development board is well organized and designed so that the end-user has all the necessary elements in one place, such as switches, buttons, indicators, connectors, and others. With four different connectors for each port, EasyPIC v7 allows you to connect accessory boards, sensors, and custom electronics more efficiently than ever. Each part of
the EasyPIC v7 development board contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. An integrated mikroProg, a fast USB 2.0 programmer with mikroICD hardware In-Circuit Debugger, offers many valuable programming/debugging options and seamless integration with the Mikroe software environment. Besides it also includes a clean and regulated power supply block for the development board. It can use various external power sources, including an external 12V power supply, 7-23V AC or 9-32V DC via DC connector/screw terminals, and a power source via the USB Type-B (USB-B) connector. Communication options such as
USB-UART and RS-232 are also included, alongside the well-established mikroBUS™ standard, three display options (7-segment, graphical, and character-based LCD), and several different DIP sockets. These sockets cover a wide range of 8-bit PIC MCUs, from PIC10F, PIC12F, PIC16F, PIC16Enh, PIC18F, PIC18FJ, and PIC18FK families. EasyPIC v7 is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem for rapid development. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping and development thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC
MCU Memory (KB)
64
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
28
RAM (Bytes)
3800
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Current 7 Click driver.
Key functions:
current7_read_voltage- This function reads raw ADC value and converts it to proportional voltage levelcurrent7_get_current- This function reads the input current level [A] based on CURRENT7_NUM_CONVERSIONS of voltage measurementscurrent7_set_vref- This function sets the voltage reference for Current 7 Click driver
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief Current7 Click example
*
* # Description
* This library contains API for Current 7 Click driver.
* The demo application reads current ( A ).
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes I2C or AN driver and log UART.
*
* ## Application Task
* This is an example that demonstrates the use of the Current 7 Click board™.
* In this example, we read and display the current ( A ) data.
* Results are being sent to the Usart Terminal where you can track their changes.
*
* @author Nenad Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "current7.h"
static current7_t current7;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
current7_cfg_t current7_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
current7_cfg_setup( ¤t7_cfg );
CURRENT7_MAP_MIKROBUS( current7_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( I2C_MASTER_ERROR == current7_init( ¤t7, ¤t7_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
float current = 0;
current7_get_current( ¤t7, ¤t );
log_printf( &logger, " Current : %.3f A\r\n", current );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END