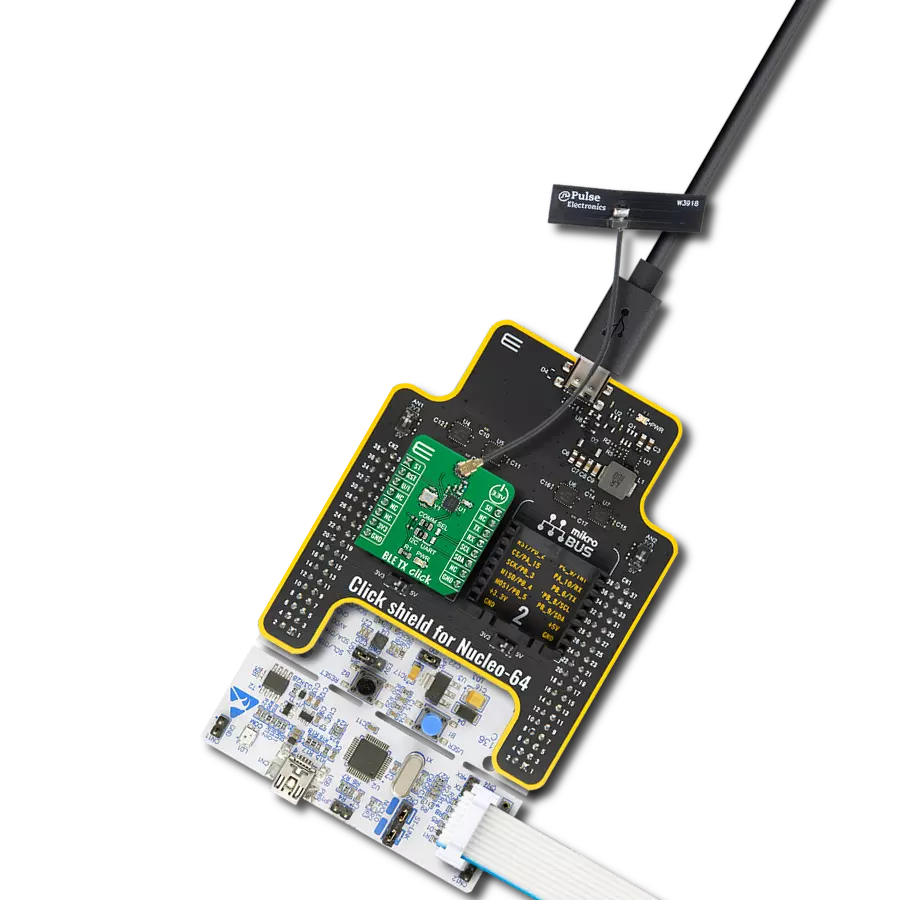
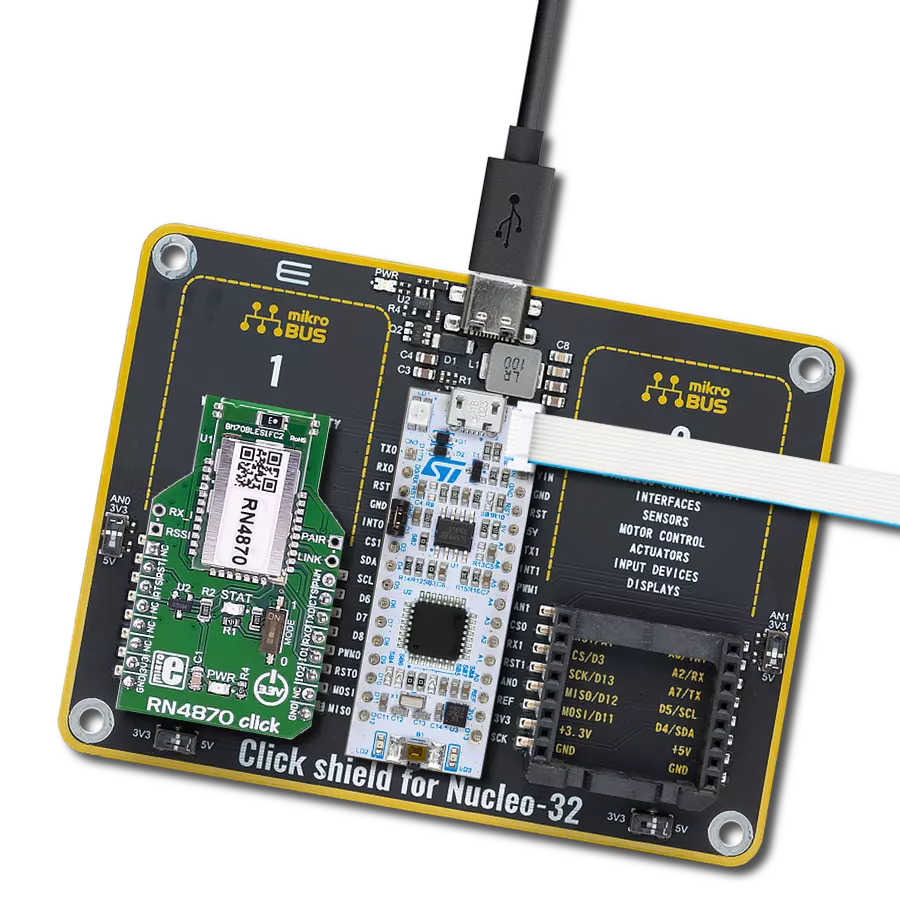
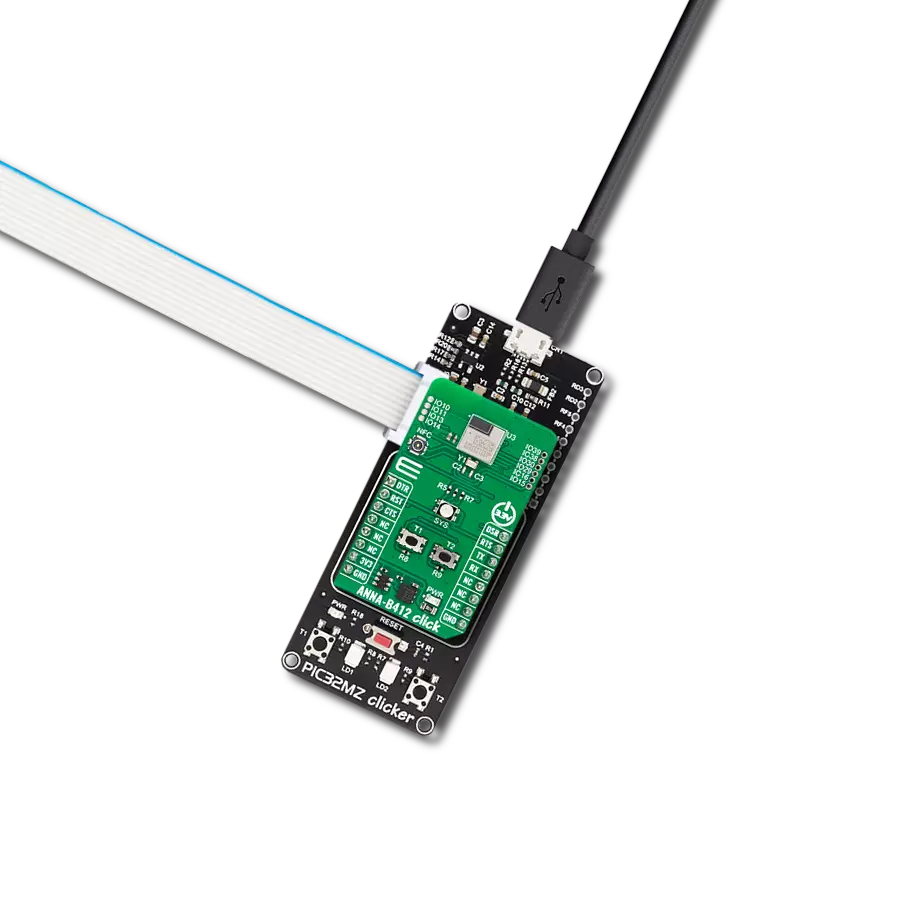
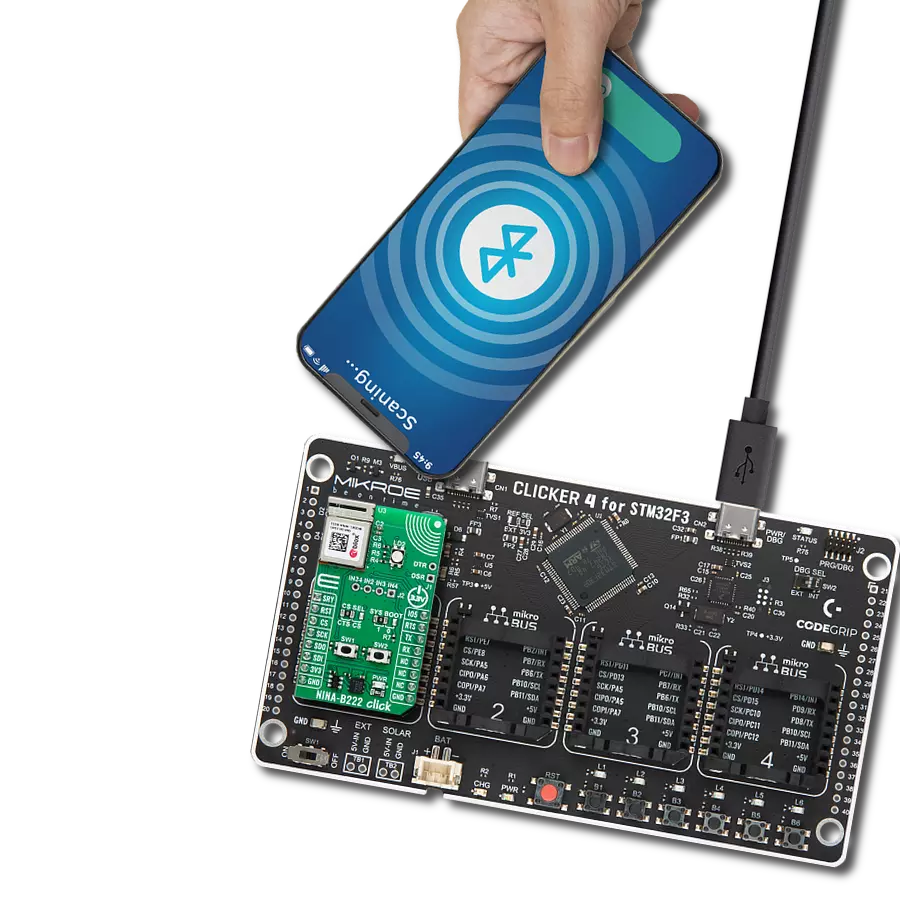
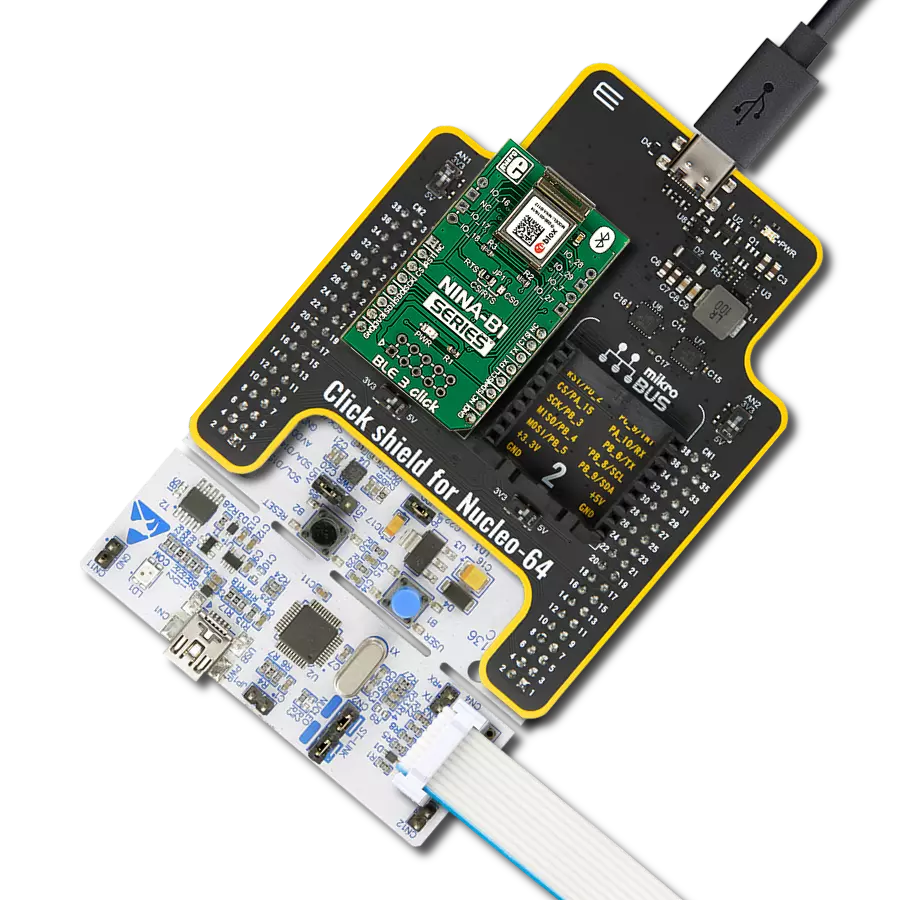
Whether you're on the go or at home, our Bluetooth solution ensures you're always connected, providing uninterrupted access to your favorite devices.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
BLE 6 Click is based on the BlueNRG-M2, a Bluetooth low energy application processor module from STMicroelectronics compliant with Bluetooth® v5.0. The BlueNRG-M2 module has been designed around the ST BlueNRG-2 SoC where its Cortex-M0 core can execute both Bluetooth protocols and customer application. Optimized memory architecture includes 256 kB of Flash memory and 24 kB of ultra-low-leakage RAM (with full data retention). The BLUENRG-M2 module has both 32 MHz and 32 kHz crystal oscillators implemented. It has been designed to leverage the BlueNRG-2 integrated DC-DC step-down converter in order to achieve the best power consumption in active mode. It also embeds a high-efficiency chip antenna. It can be configured
to support both application processor (host-less) and network processor (hosted) modes. The BlueNRG-M2 module provides a complete RF application platform in a tiny form factor (11.5 x 13.5 x 2.0 mm) and being a certified solution optimizes the time to market of the final applications. The BlueNRG-M2 module allows applications to meet the tight advisable peak current requirements imposed with the use of standard coin cell batteries. There are two possible software architectures: Host-less mode (application processor - customer application runs on the BlueNRG-M2 module) and Hosted mode (network processor - the module is configured as network module controlled by an external host connected via SPI or UART). The module comes with a
pre-programmed UART bootloader. The BlueNRG-M2 embeds the ARM serial wire debug (SWD) port routed to the SWD header connector. It is two pin (clock and single bi-directional data) debug interface, providing all the debug functionality plus real-time access to system memory without halting the processor or requiring any target resident code. Since the SPI peripheral can be used either as master or slave, the onboard SMD jumpers labeled as MODE SEL allow switching between the two. This Click Board™ is designed to be operated only with a 3.3V logic level. A proper logic voltage level conversion should be performed before the Click board™ is used with MCUs with logic levels of 5V.
Features overview
Development board
Nucleo-64 with STM32F091RC MCU offers a cost-effective and adaptable platform for developers to explore new ideas and prototype their designs. This board harnesses the versatility of the STM32 microcontroller, enabling users to select the optimal balance of performance and power consumption for their projects. It accommodates the STM32 microcontroller in the LQFP64 package and includes essential components such as a user LED, which doubles as an ARDUINO® signal, alongside user and reset push-buttons, and a 32.768kHz crystal oscillator for precise timing operations. Designed with expansion and flexibility in mind, the Nucleo-64 board features an ARDUINO® Uno V3 expansion connector and ST morpho extension pin
headers, granting complete access to the STM32's I/Os for comprehensive project integration. Power supply options are adaptable, supporting ST-LINK USB VBUS or external power sources, ensuring adaptability in various development environments. The board also has an on-board ST-LINK debugger/programmer with USB re-enumeration capability, simplifying the programming and debugging process. Moreover, the board is designed to simplify advanced development with its external SMPS for efficient Vcore logic supply, support for USB Device full speed or USB SNK/UFP full speed, and built-in cryptographic features, enhancing both the power efficiency and security of projects. Additional connectivity is
provided through dedicated connectors for external SMPS experimentation, a USB connector for the ST-LINK, and a MIPI® debug connector, expanding the possibilities for hardware interfacing and experimentation. Developers will find extensive support through comprehensive free software libraries and examples, courtesy of the STM32Cube MCU Package. This, combined with compatibility with a wide array of Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), including IAR Embedded Workbench®, MDK-ARM, and STM32CubeIDE, ensures a smooth and efficient development experience, allowing users to fully leverage the capabilities of the Nucleo-64 board in their projects.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M0
MCU Memory (KB)
256
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
64
RAM (Bytes)
32768
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Nucleo-64 comes equipped with two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the STM32 Nucleo-64 board with no effort. This way, Mikroe allows its users to add any functionality from our ever-growing range of Click boards™, such as WiFi, GSM, GPS, Bluetooth, ZigBee, environmental sensors, LEDs, speech recognition, motor control, movement sensors, and many more. More than 1537 Click boards™, which can be stacked and integrated, are at your disposal. The STM32 Nucleo-64 boards are based on the microcontrollers in 64-pin packages, a 32-bit MCU with an ARM Cortex M4 processor operating at 84MHz, 512Kb Flash, and 96KB SRAM, divided into two regions where the top section represents the ST-Link/V2 debugger and programmer while the bottom section of the board is an actual development board. These boards are controlled and powered conveniently through a USB connection to program and efficiently debug the Nucleo-64 board out of the box, with an additional USB cable connected to the USB mini port on the board. Most of the STM32 microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the STM32 Nucleo-64 board with our Click Shield for Nucleo-64, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for BLE 6 Click driver.
Key functions:
ble6_set_response_handler- Set response handlers function.ble6_set_handlers- Set handlers function.ble6_parser_rsp- Response parser function.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief BLE 6 Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example reads and processes data from BLE 6 Clicks.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization driver enables - UART, sets handlers initialize and enable UART interrupt, reset
* and configures BLE module, initialize BLE Server Profile ( Services and Characteristics ).
*
* ## Application Task
* The app starts by checking the system ready flag
* and returns the Bluetooth device address. After that,
* the chain of commands creates Primary Server Profiles:
* Device Information, Generic Access and Custom Service to Start Advertising.
* For transmit messages, we use Generic Access Primary Service
* with Write permissions of the characteristic Element.
* In this example, transmitting message is limited to a maximum of 11 characters.
* Results are being sent to the Usart Terminal where you can track their changes.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - void ble6_module_init ( void );
* - void ble6_event_handler ( void );
* - void ble6_display_log ( void );
* - void ble6_aci_gap_init ( void );
* - void ble6_le_meta_event ( void );
* - void ble6_handler ( void );
* - void ble6_response_handler ( void );
* - void ble6_local_version_info ( void );
*
* @note
* For communication with BLE 6 Click use the android application on the link:
* https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.macdom.ble.blescanner
*
* @author Stefan Ilic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "ble6.h"
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 256
static ble6_t ble6;
static log_t logger;
static ble6_rsp_t rsp_data;
static ble6_le_meta_event_t le_meta_event_data;
static ble6_rx_rsp_t ble6_rx_rsp;
uint8_t app_buf [ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ];
uint8_t rx_response [ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ];
uint8_t device_connected_flag = 0;
uint8_t hci_le_meta_event_connect [ 5 ] = { 0x04, 0x3E, 0x13, 0x01, 0x00 };
uint8_t hci_le_serverwrite_event [ 1 ] = { 0x04 };
uint8_t hci_read_local_version_information [ 4 ] = { 0x01, 0x01, 0x10, 0x00 };
uint8_t hci_info_confirm [ 4 ] = { 0xFF, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00 };
uint8_t aci_hal_get_fw_version [ 4 ] = { 0x01, 0x01, 0xFC, 0x00 };
uint8_t hci_reset [ 4 ] = { 0x01, 0x03, 0x0C, 0x00 };
uint8_t aci_hal_write_config_data [ 12 ] =
{
0x01, 0x0C, 0xFC, 0x08, 0x00, 0x06, 0x03, 0xEE, 0x00, 0xE1, 0x80, 0x02
};
uint8_t aci_hal_set_tx_power_level [ 6 ] = { 0x01, 0x0F, 0xFC, 0x02, 0x01, 0x04 };
uint8_t aci_gatt_init [ 4 ] = { 0x01, 0x01, 0xFD, 0x00 };
uint8_t aci_gap_init [ 7 ] = { 0x01, 0x8A, 0xFC, 0x03, 0x0F, 0x00, 0x0B };
uint8_t aci_gatt_update_value [ 21 ] =
{
0x01, 0x06, 0xFD, 0x11, 0x05, 0x00, 0x06, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0B,
'B', 'L', 'E', ' ', '6', ' ', 'c', 'l', 'i', 'c', 'k'
};
uint8_t hci_le_set_scan_response_data [ 36 ] =
{
0x01, 0x09, 0x20, 0x20, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00
};
uint8_t aci_gap_set_discoverable [ 30 ] =
{
0x01, 0x83, 0xFC, 0x19, 0x00, 0x00, 0x08, 0x00, 0x09, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0C, 0x09,
'B', 'L', 'E', ' ', '6', ' ', 'c', 'l', 'i', 'c', 'k', 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00
};
/**
* @brief BLE 6 module initialisation.
* @details This function is used for initialisation of BLE 6 Click.
*/
void ble6_module_init ( void );
/**
* @brief BLE 6 event handler.
* @details This function is used for checking conncection of BLE 6 Click.
*/
void ble6_event_handler ( void );
/**
* @brief BLE 6 display log.
* @details This function is used for displaying log of BLE 6 Click.
*/
void ble6_display_log ( void );
/**
* @brief BLE 6 aci gap initialisation.
* @details This function is used for aci gap initialisation of BLE 6 Click.
*/
void ble6_aci_gap_init ( void );
/**
* @brief BLE 6 le meta event.
* @details This function is used for low energy events of BLE 6 Click.
*/
void ble6_le_meta_event ( void );
/**
* @brief BLE 6 handler.
* @details This function is used for getting data of BLE 6 Click.
*/
void ble6_handler ( void );
/**
* @brief BLE 6 response handler.
* @details This function is used for displaying data response of BLE 6 Click.
*/
void ble6_response_handler ( void );
/**
* @brief BLE 6 local version info.
* @details This function is used for displaying local version info of BLE 6 Click.
*/
void ble6_local_version_info ( void );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
ble6_cfg_t ble6_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
ble6_cfg_setup( &ble6_cfg );
BLE6_MAP_MIKROBUS( ble6_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
err_t init_flag = ble6_init( &ble6, &ble6_cfg );
if ( UART_ERROR == init_flag )
{
log_error( &logger, " Application Init Error. " );
log_info( &logger, " Please, run program again... " );
for ( ; ; );
}
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
ble6_power_on( &ble6, BLE6_MODULE_POWER_ON );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
ble6_module_init( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "-> Local Version Information: \r\n" );
ble6_send_command( &ble6, &hci_read_local_version_information[ 0 ], 4 );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
ble6_handler( );
ble6_display_log( );
ble6_local_version_info( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "-> ACI GAP Update Value: \r\n" );
ble6_send_command( &ble6, &aci_gatt_update_value[ 0 ], 21 );
Delay_ms ( 10 );
ble6_handler( );
ble6_display_log( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "-> HCI Set Scan. Response Data: \r\n" );
ble6_send_command( &ble6, &hci_le_set_scan_response_data[ 0 ], 36 );
Delay_ms ( 10 );
ble6_handler( );
ble6_display_log( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "-> ACI GAP Set Discoverable: \r\n" );
ble6_send_command( &ble6, &aci_gap_set_discoverable[ 0 ], 30 );
Delay_ms ( 10 );
ble6_handler( );
ble6_display_log( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
ble6_event_handler( );
while ( device_connected_flag )
{
int32_t cnt = ble6_generic_read( &ble6, rx_response, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
if ( ( ble6_strncmp( rx_response, hci_le_serverwrite_event, 1 ) == 0 ) && ( cnt > 13 ) )
{
ble6_response_handler( );
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
void ble6_handler ( void )
{
uint16_t tmp;
uint8_t cnt;
ble6_generic_read( &ble6, rx_response, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
tmp = rx_response[ 5 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rx_response[ 4 ];
rsp_data.event_code = rx_response[ 1 ];
rsp_data.length = rx_response[ 2 ];
rsp_data.cmd_opcode = tmp;
rsp_data.status = rx_response[ 6 ];
for ( cnt = 0; cnt < rsp_data.length - 4; cnt++ )
{
rsp_data.payload[ cnt ] = rx_response[ cnt + 7 ];
}
memset( &rx_response[ 0 ], 0, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
}
void ble6_connect_handler ( void )
{
uint8_t cr_len;
uint16_t tmp;
uint8_t cnt;
ble6_generic_read( &ble6, rx_response, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
cr_len = 0;
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
le_meta_event_data.le_event_code = rx_response[ 1 ];
le_meta_event_data.le_length = rx_response[ 2 ];
le_meta_event_data.le_subevent_code = rx_response[ 3 ];
le_meta_event_data.le_status = rx_response[ 4 ];
tmp = rx_response[ 6 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rx_response[ 5 ];
if ( le_meta_event_data.le_subevent_code == 0x01 )
{
cr_len = 8;
}
le_meta_event_data.le_conn_hdl = tmp;
le_meta_event_data.le_role = rx_response[ 7 ];
le_meta_event_data.le_peer_addr_type = rx_response[ 8 ];
for ( cnt = 0; cnt < 6; cnt++ )
{
le_meta_event_data.le_peer_addr[ cnt ] = rx_response[ cnt + 9 ];
}
tmp = rx_response[ 16 - cr_len ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rx_response[ 15 - cr_len ];
le_meta_event_data.le_conn_interval = tmp;
tmp = rx_response[ 18 - cr_len ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rx_response[ 17 - cr_len ];
le_meta_event_data.le_conn_latency = tmp;
tmp = rx_response[ 20 - cr_len ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rx_response[ 19 - cr_len ];
le_meta_event_data.le_sup_timeout = tmp;
le_meta_event_data.le_master_clk_accuracy = rx_response[ 21 ];
memset( rx_response, 0, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
}
void ble6_response_handler ( void )
{
uint16_t attr_pos;
uint16_t tmp;
ble6_rx_rsp.event_code = rx_response[ 1 ];
log_printf( &logger, " Event Code : 0x%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) ble6_rx_rsp.event_code );
ble6_rx_rsp.length = rx_response[ 2 ];
log_printf( &logger, " Length : 0x%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) ble6_rx_rsp.length );
tmp = rx_response[ 4 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rx_response[ 3 ];
ble6_rx_rsp.e_code = tmp;
log_printf( &logger, " Ecode : 0x%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) ble6_rx_rsp.e_code );
tmp = rx_response[ 6 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rx_response[ 5 ];
ble6_rx_rsp.conn_hdl = tmp;
log_printf( &logger, " Connection Handle : 0x%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) ble6_rx_rsp.conn_hdl );
tmp = rx_response[ 8 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rx_response[ 7 ];
ble6_rx_rsp.attr_hdl = tmp;
log_printf( &logger, " Attr. Handle : 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) ble6_rx_rsp.attr_hdl );
tmp = rx_response[ 10 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rx_response[ 9 ];
ble6_rx_rsp.offset = tmp;
log_printf( &logger, " Offset : 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) ble6_rx_rsp.offset );
tmp = rx_response[ 12 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rx_response[ 11 ];
ble6_rx_rsp.attr_data_len = tmp;
log_printf( &logger, " Attr. Data Length : 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) ble6_rx_rsp.attr_data_len );
for ( attr_pos = 0; attr_pos < ble6_rx_rsp.attr_data_len; attr_pos++ )
{
ble6_rx_rsp.attr_data[ attr_pos ] = rx_response[ attr_pos + 13 ];
app_buf[ attr_pos ] = ble6_rx_rsp.attr_data[ attr_pos ];
}
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " <--- RX DATA : %s \r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
memset( app_buf, 0, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
memset( rx_response, 0, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
memset( ble6_rx_rsp.attr_data, 0, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
}
void ble6_local_version_info ( void )
{
uint16_t tmp;
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Local Version Information \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " HCI Version : 0x%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) rsp_data.payload[ 0 ] );
tmp = rsp_data.payload[ 2 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rsp_data.payload[ 1 ];
log_printf( &logger, " HCI Revision : 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) tmp );
log_printf( &logger, " LMP/PAL Version : 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) rsp_data.payload[ 3 ] );
tmp = rsp_data.payload[ 5 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rsp_data.payload[ 4 ];
log_printf( &logger, " Manufacture Name: 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) tmp );
tmp = rsp_data.payload[ 7 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rsp_data.payload[ 6 ];
log_printf( &logger, " LMP/PAL Sub Ver : 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) tmp );
memset( rsp_data.payload, 0, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
}
void ble6_le_meta_event ( void )
{
uint8_t cnt;
log_printf( &logger, " CONNECT LE META EVENT \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Event Code : 0x%.4X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) le_meta_event_data.le_event_code );
log_printf( &logger, " Length : 0x%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) le_meta_event_data.le_length );
log_printf( &logger, " Subevent Code : 0x%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) le_meta_event_data.le_subevent_code );
log_printf( &logger, " Status : " );
if ( le_meta_event_data.le_status == 0x00 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "OK\r\n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, "ERROR 0x%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) le_meta_event_data.le_status );
}
log_printf( &logger, " Connection Handle : 0x%.4X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) le_meta_event_data.le_conn_hdl );
if ( le_meta_event_data.le_subevent_code == 0x01 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Role : " );
if ( le_meta_event_data.le_role == 0x00 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Master\r\n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, "Slave\r\n" );
}
log_printf( &logger, " Peer Address Type : " );
if ( le_meta_event_data.le_role == 0x00 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "Specific\r\n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, "Random\r\n" );
}
log_printf( &logger, " Peer Address : " );
for ( cnt = 0; cnt < 5; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X:", ( uint16_t ) le_meta_event_data.le_peer_addr[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) le_meta_event_data.le_peer_addr[ 5 ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, " Connection Interval : 0x%.4X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) le_meta_event_data.le_conn_interval );
log_printf( &logger, " Connection Latency : 0x%.4X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) le_meta_event_data.le_conn_latency );
log_printf( &logger, " Supervision Timeout : 0x%.4X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) le_meta_event_data.le_sup_timeout );
if ( le_meta_event_data.le_subevent_code == 0x01 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Master Clock Accurancy: 0x%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) le_meta_event_data.le_master_clk_accuracy );
}
}
void ble6_aci_gap_init ( void )
{
uint16_t tmp;
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " ACI GAP Initialization \r\n" );
tmp = rsp_data.payload[ 1 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rsp_data.payload[ 0 ];
log_printf( &logger, " Service Handle : 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) tmp );
tmp = rsp_data.payload[ 3 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rsp_data.payload[ 2 ];
log_printf( &logger, " Dev Name Char Hdl.: 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) tmp );
tmp = rsp_data.payload[ 5 ];
tmp <<= 8;
tmp |= rsp_data.payload[ 4 ];
log_printf( &logger, " Appearance Handle : 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) tmp );
memset( rsp_data.payload, 0, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
}
void ble6_display_log ( void )
{
log_printf( &logger, "<- New Response:\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Opcode: 0x%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) rsp_data.cmd_opcode );
log_printf( &logger, " Length: 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) rsp_data.length );
log_printf( &logger, " Status: " );
if ( rsp_data.status == 0x00 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "OK\r\n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, "0x%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) rsp_data.status );
}
}
void ble6_event_handler ( void )
{
ble6_generic_read( &ble6, rx_response, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
if ( ble6_strncmp( rx_response, hci_le_meta_event_connect, 5 )
== 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " *** Device connected *** \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
ble6_connect_handler( );
ble6_le_meta_event( );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
device_connected_flag = 1;
}
}
void ble6_module_init ( void )
{
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " *** SW Reset *** \r\n" );
ble6_send_command( &ble6, hci_info_confirm, 4 );
Delay_ms ( 10 );
memset( rx_response, 0, 255 );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
ble6_generic_read( &ble6, rx_response, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "-> Firmware Details: \r\n" );
ble6_send_command( &ble6, aci_hal_get_fw_version, 4 );
Delay_ms ( 10 );
ble6_handler( );
ble6_display_log( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "-> HCI Reset: \r\n" );
ble6_send_command( &ble6, hci_reset, 4 );
Delay_ms ( 10 );
ble6_handler( );
ble6_display_log( );
Delay_ms ( 10 );
ble6_handler( );
ble6_display_log( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "-> ACI HAL Write Configuration: \r\n" );
ble6_send_command( &ble6, aci_hal_write_config_data, 12 );
Delay_ms ( 10 );
ble6_handler( );
ble6_display_log( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "-> ACI Set Tx Power Level: \r\n" );
ble6_send_command( &ble6, aci_hal_set_tx_power_level, 6 );
Delay_ms ( 10 );
ble6_handler( );
ble6_display_log( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "-> ACI GATT Init.: \r\n" );
ble6_send_command( &ble6, aci_gatt_init, 4 );
Delay_ms ( 10 );
ble6_handler( );
ble6_display_log( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "-> ACI GAP Init.: \r\n" );
ble6_send_command( &ble6, aci_gap_init, 7 );
Delay_ms ( 10 );
ble6_handler( );
ble6_display_log ();
ble6_aci_gap_init( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:BT/BLE