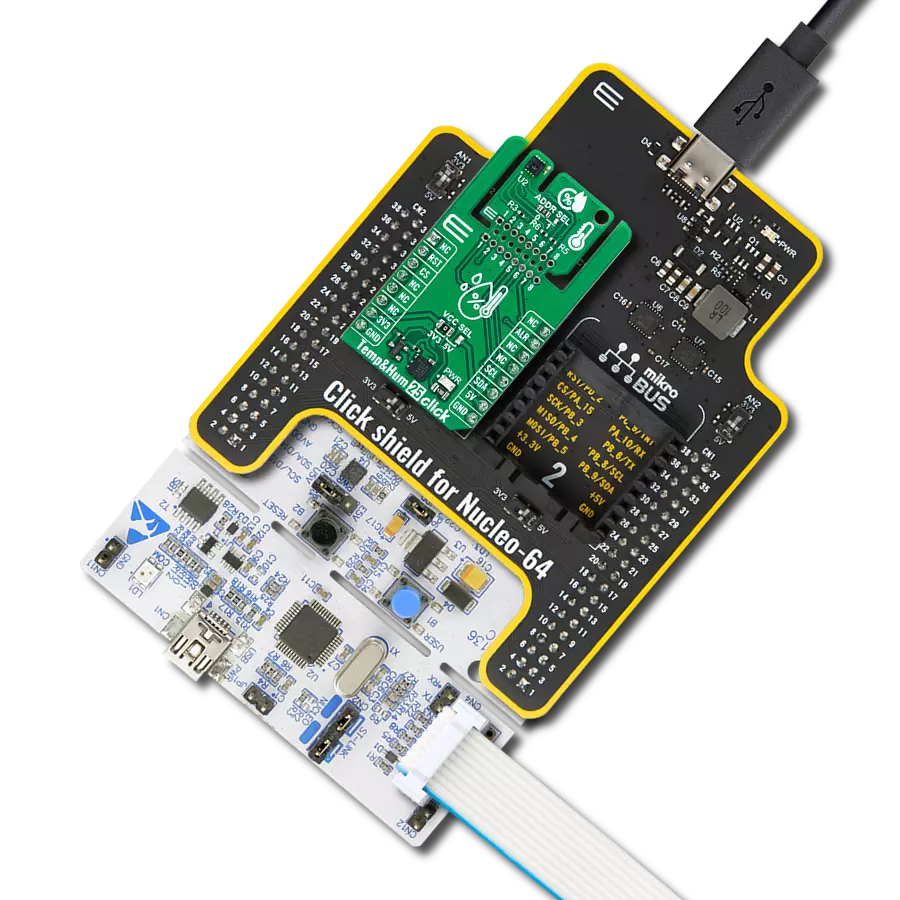
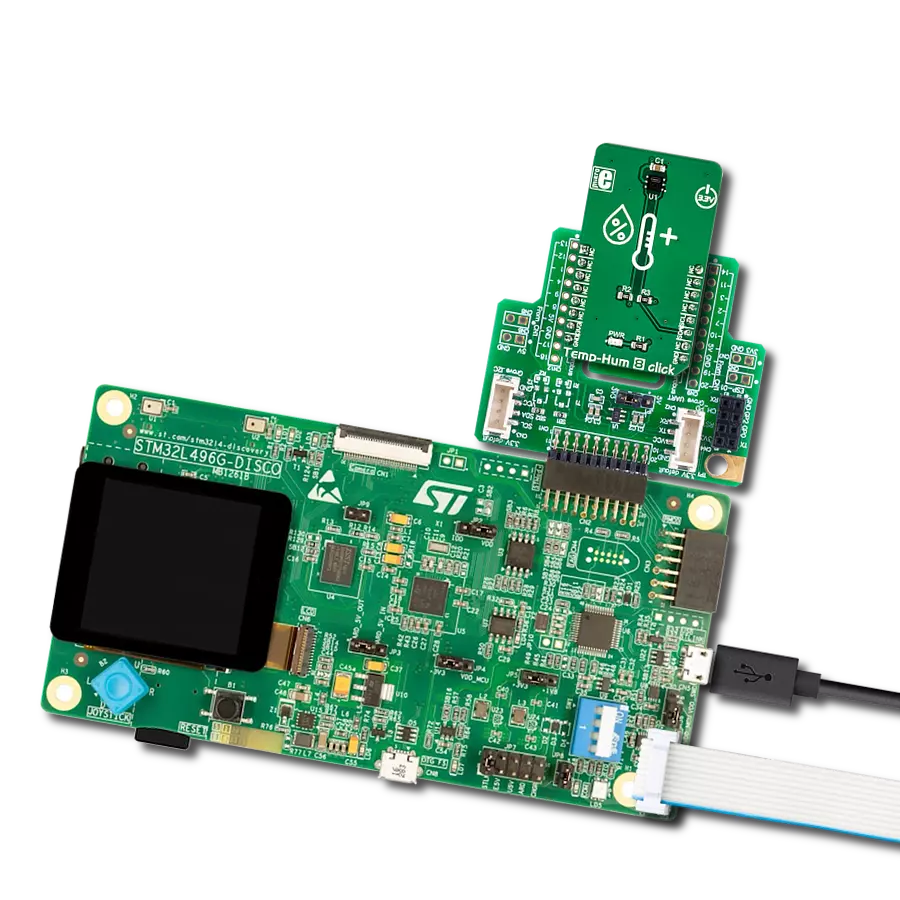
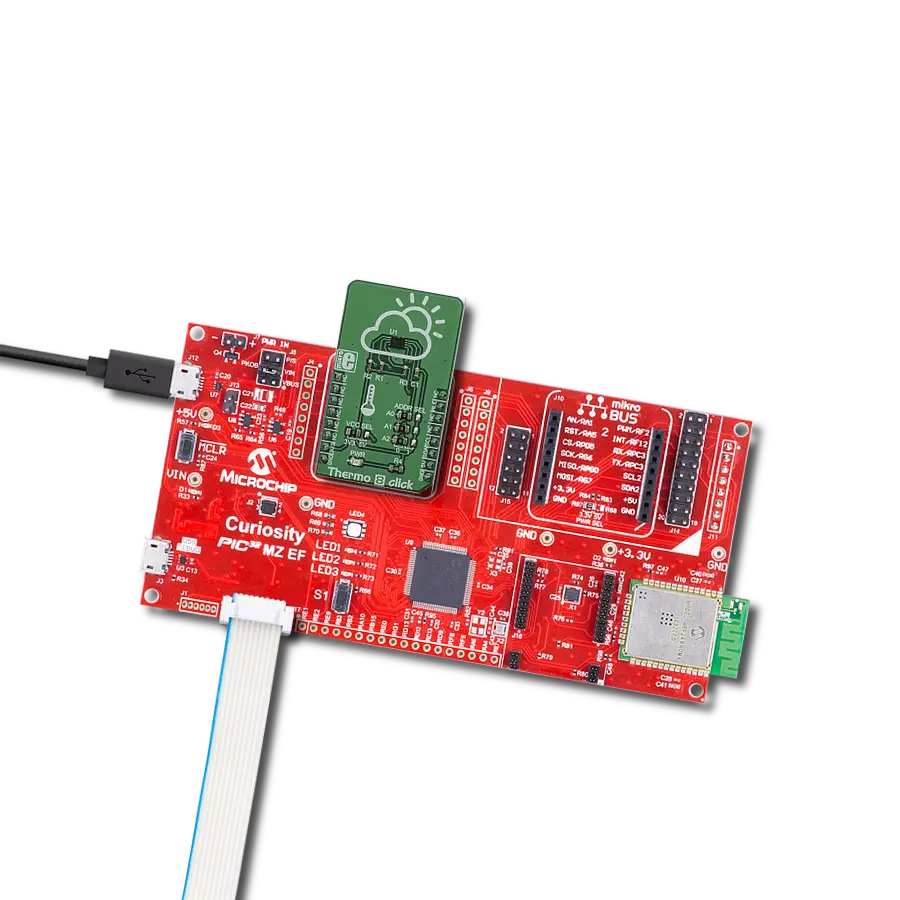
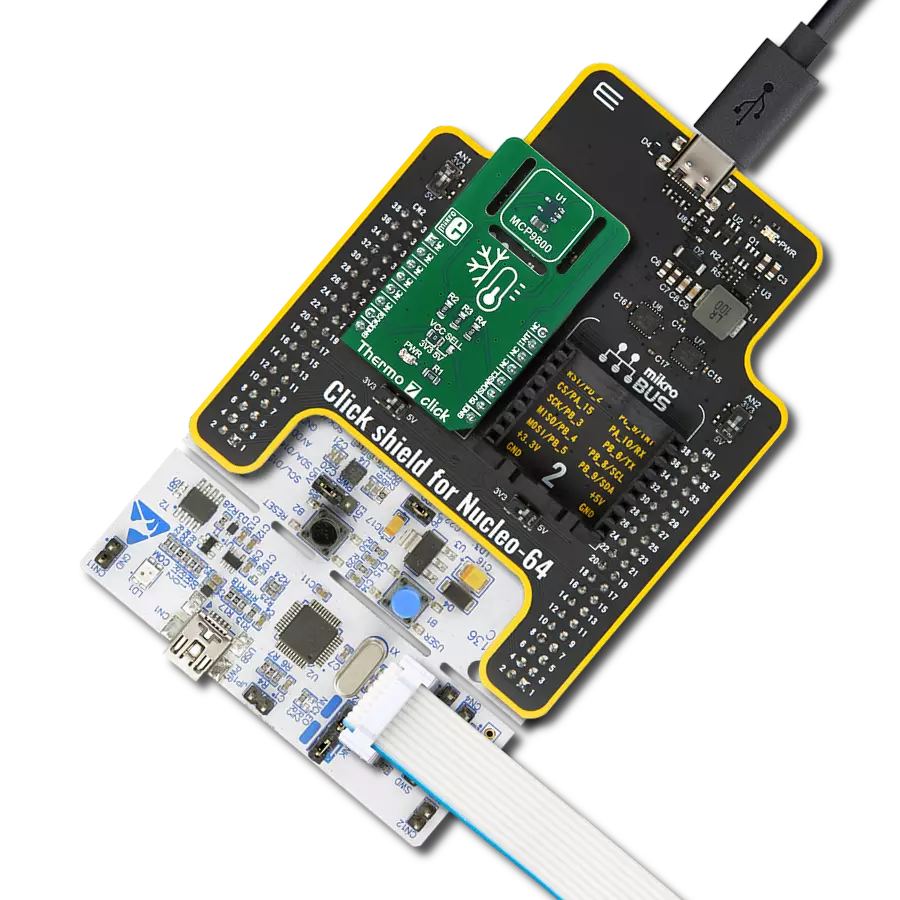
Undoubtedly the best choice for highly accurate temperature measurements
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
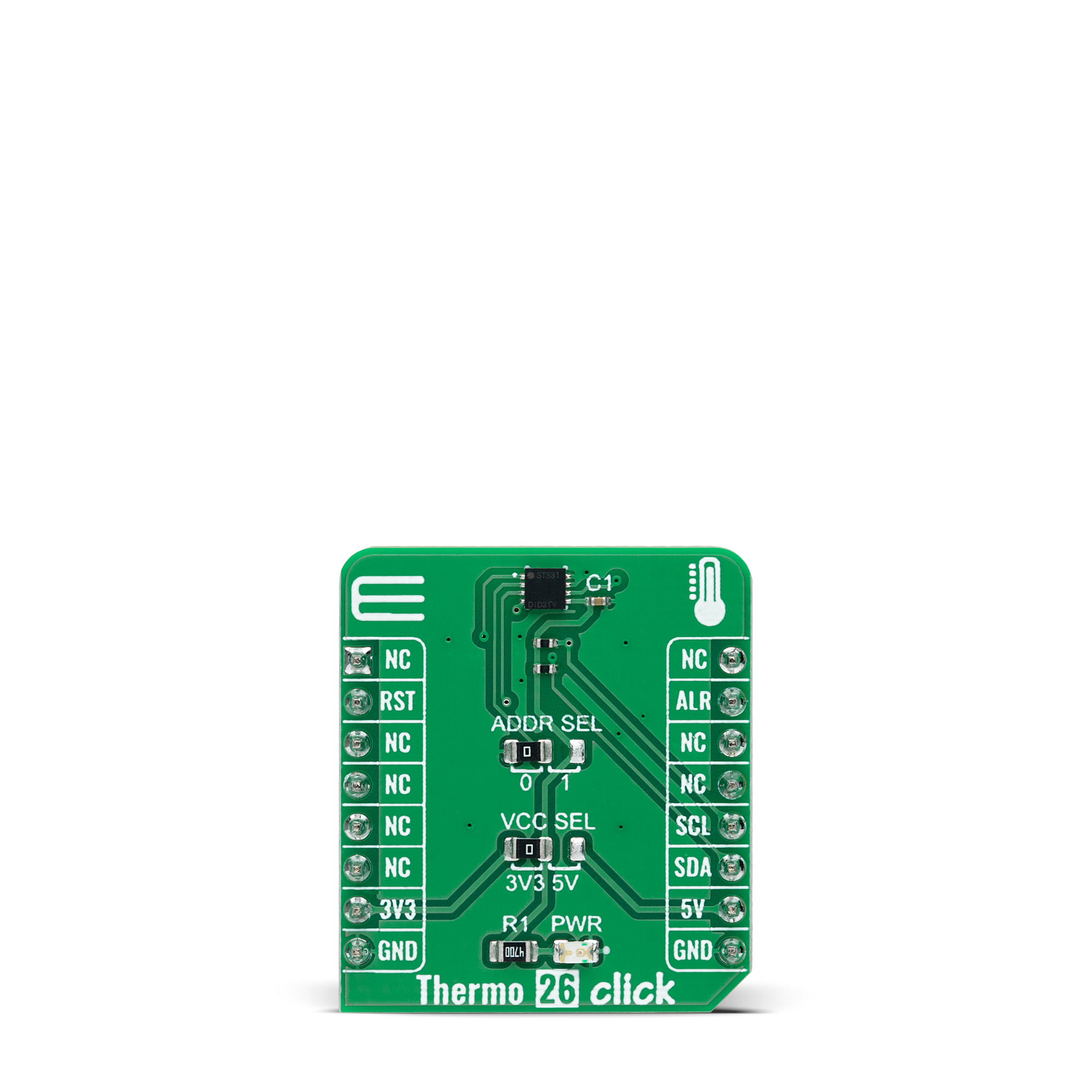
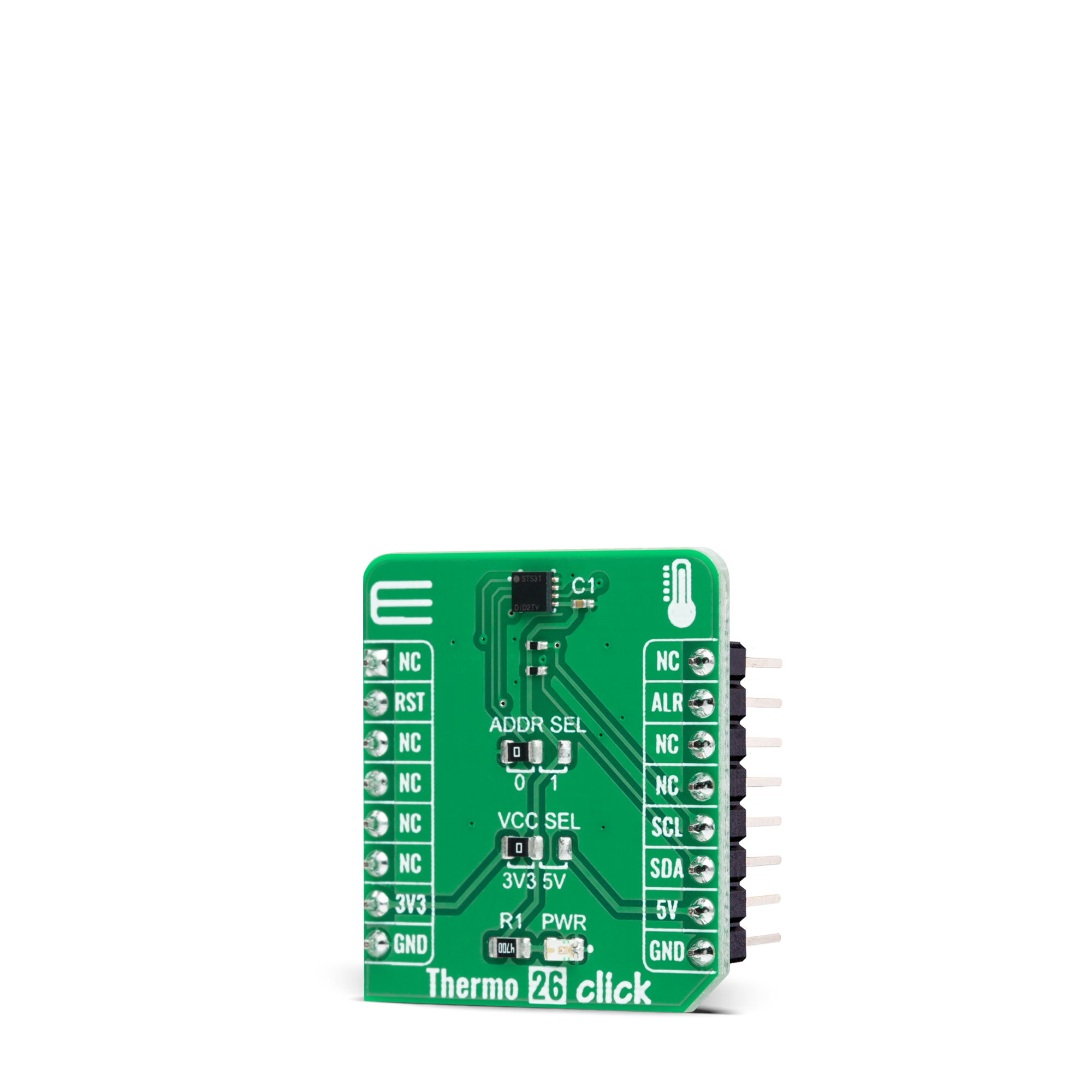
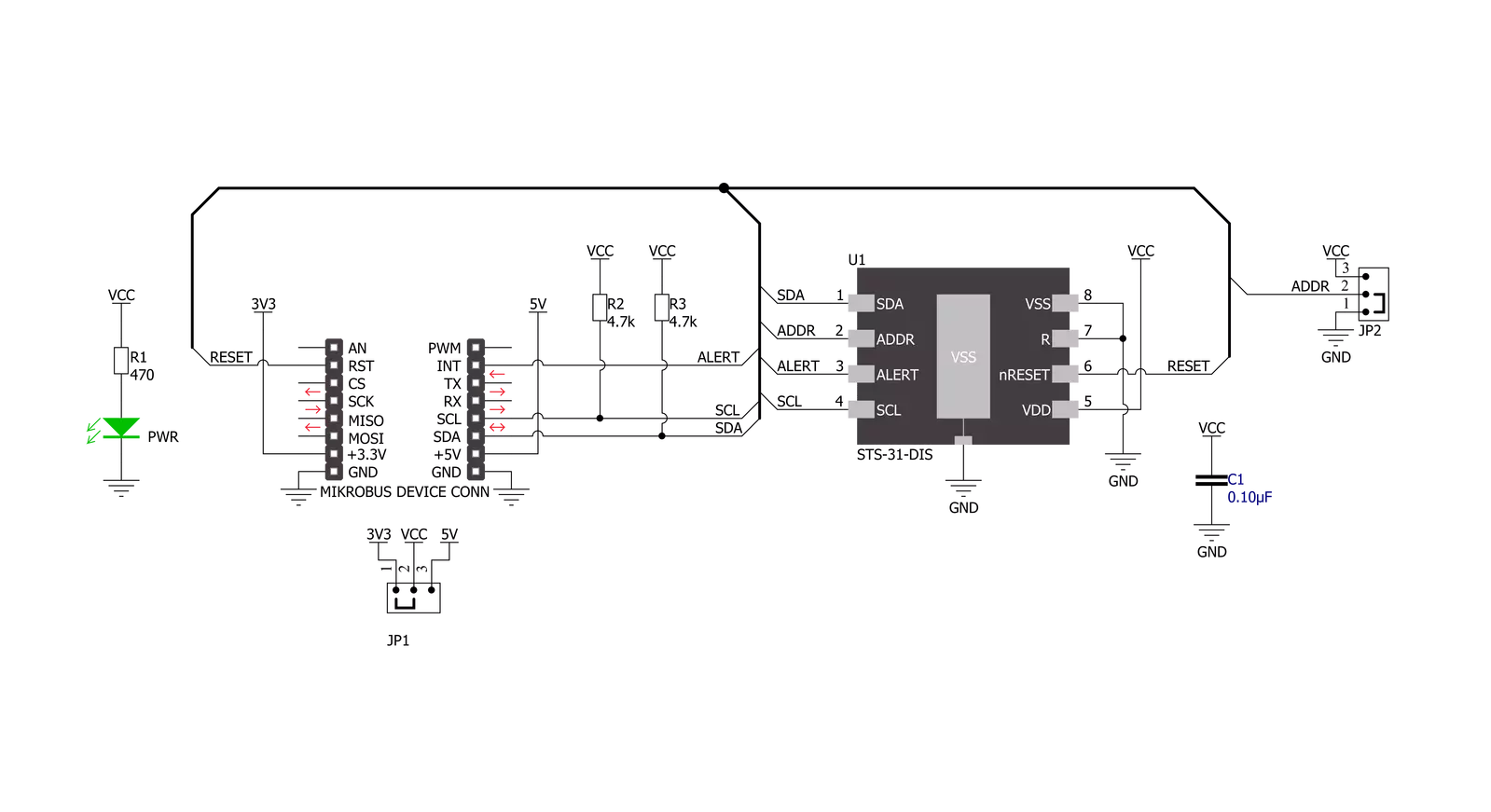
Thermo 26 Click is based on the STS31-DIS, a digital temperature sensor from Sensirion with increased intelligence, reliability, NIST traceability, and improved accuracy specifications utilizing the industry-proven CMOSens® Technology. It integrates a digital temperature sensor with a 16-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC), a data processing circuit, and serial interface logic functions in one package. The voltage is digitized and converted to a 16-bit temperature result in degrees Celsius, with a resolution of 0.01°C. The STS31-DIS temperature sensor gives a fully calibrated, linearized, and supply-voltage-
compensated digital output with outstanding accuracy of up to ±0.2°C typical over a temperature range of 0°C to 90°C. Thermo 26 Click communicates with an MCU using the standard I2C 2-Wire interface to read data and configure settings, supporting Fast Mode Plus up to 1MHz. Also, the STS31-DIS allows choosing the least significant bit (LSB) of its I2C slave address using the SMD jumper labeled ADDR SEL. It also possesses an additional interrupt alert signal, routed on the INT pin of the mikroBUS™ socket labeled as ALT. The ALT pin indicates when a specific
interrupt event occurs, depending on the temperature reading value relative to programmable limits. The general reset function is routed on the RST pin of the mikroBUS™ socket. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used, as a reference, for further development.

Features overview
Development board
PICPLC16 v7a is the seventh generation of PIC development boards, providing an environment for experimenting with industrial devices. It comes with an onboard 8-bit PIC microcontroller, the PIC18F97J60 from Microchip, and a broad set of unique functions, such as the first-ever embedded debugger/programmer over USB-C. The development board also consists of 16 opto-inputs and 16 relays for currents up to 16A. It is well organized and designed so that the end-user has all the necessary elements, such as switches, buttons, indicators, and connectors, in one place. With eight connectors for each port, PICPLC16 v7a
allows you to develop PIC-based industrial, home, or office automation applications more efficiently than ever. Each part of the PICPLC16 v7a development board contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the advanced integrated CODEGRIP programmer/debugger module, which offers many valuable programming/debugging options and seamless integration with the Mikroe software environment, the board also includes a clean and regulated power supply block for the development board. It can use a wide range of external power sources, including an external 12V
power supply, 7-23V AC or 9-32V DC via DC connector/screw terminals, and a power source via the USB Type-C (USB-C) connector. Communication options such as LIN and Ethernet are also included, alongside the well-established mikroBUS™ standard. PICPLC16 v7a is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem for rapid industrial development. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping and development thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC
MCU Memory (KB)
128
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
3808
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Thermo 26 Click driver.
Key functions:
thermo26_read_serial_numThis function reads the 32-bit unique serial number.thermo26_start_measurementThis function starts the measurements by sending the specified command.thermo26_read_temperatureThis function reads the temperature raw data measurements and converts them to degrees Celsius.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief Thermo 26 Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of Thermo 26 Click board by reading and displaying
* the temperature measurements.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and resets the device, and after that reads the serial number and
* starts the periodic measurements at 2 mps with high repeatability.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads the temperature measurement in degrees Celsius and displays the results on the USB UART
* approximately once per second.
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "thermo26.h"
static thermo26_t thermo26;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
thermo26_cfg_t thermo26_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
thermo26_cfg_setup( &thermo26_cfg );
THERMO26_MAP_MIKROBUS( thermo26_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( I2C_MASTER_ERROR == thermo26_init( &thermo26, &thermo26_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
thermo26_reset_device ( &thermo26 );
uint32_t serial_num;
if ( THERMO26_ERROR == thermo26_read_serial_num ( &thermo26, &serial_num ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Read serial number." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_printf ( &logger, " Serial number: 0x%.8LX\r\n", serial_num );
if ( THERMO26_ERROR == thermo26_start_measurement ( &thermo26, THERMO26_CMD_PERIODIC_2_MPS_REP_HIGH ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Start measurement." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
float temperature;
if ( THERMO26_OK == thermo26_read_temperature ( &thermo26, &temperature ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Temperature: %.2f\r\n\n", temperature );
}
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Temperature & humidity