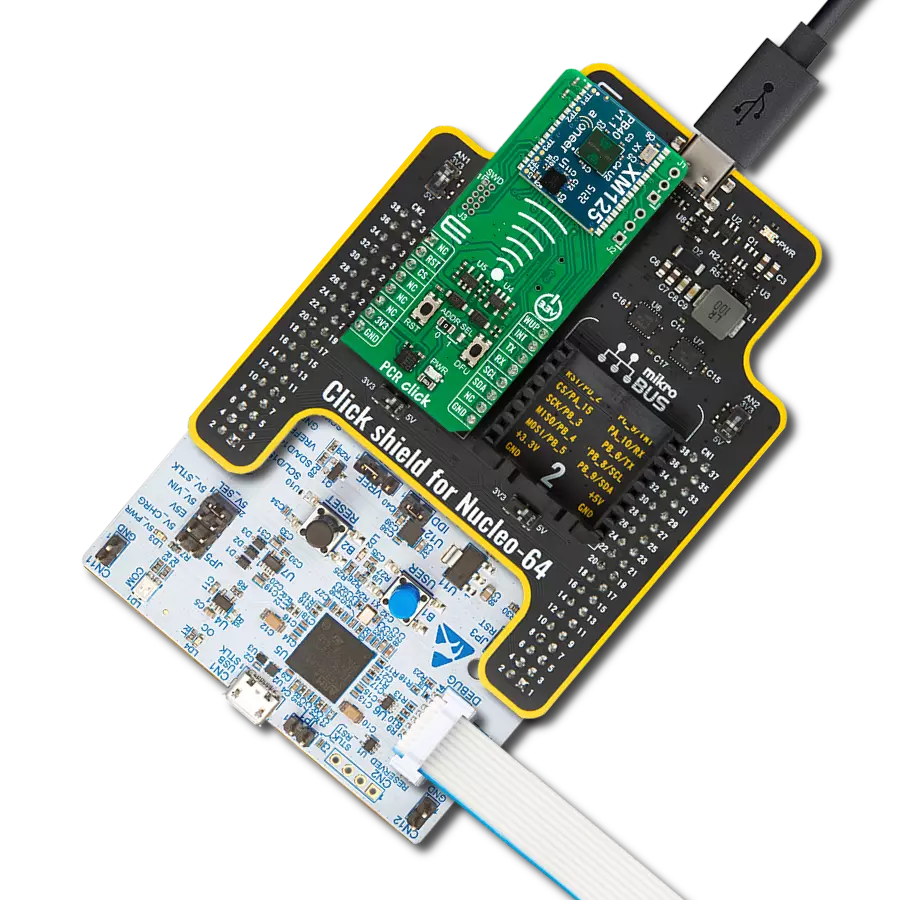
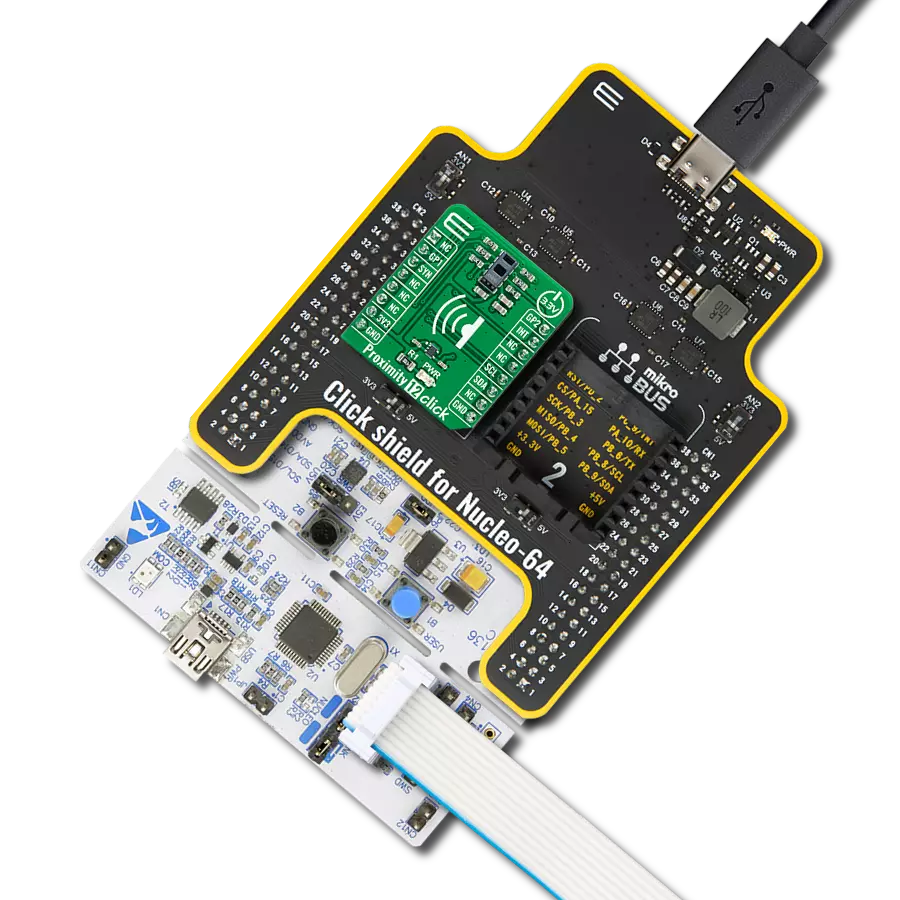
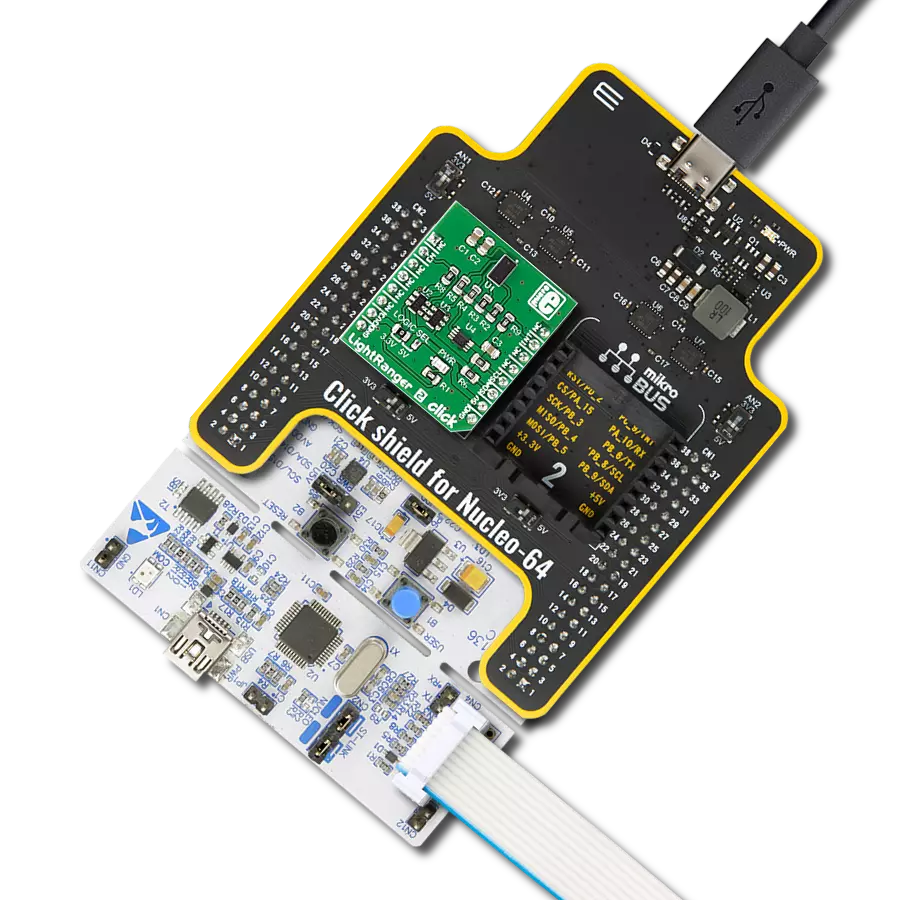
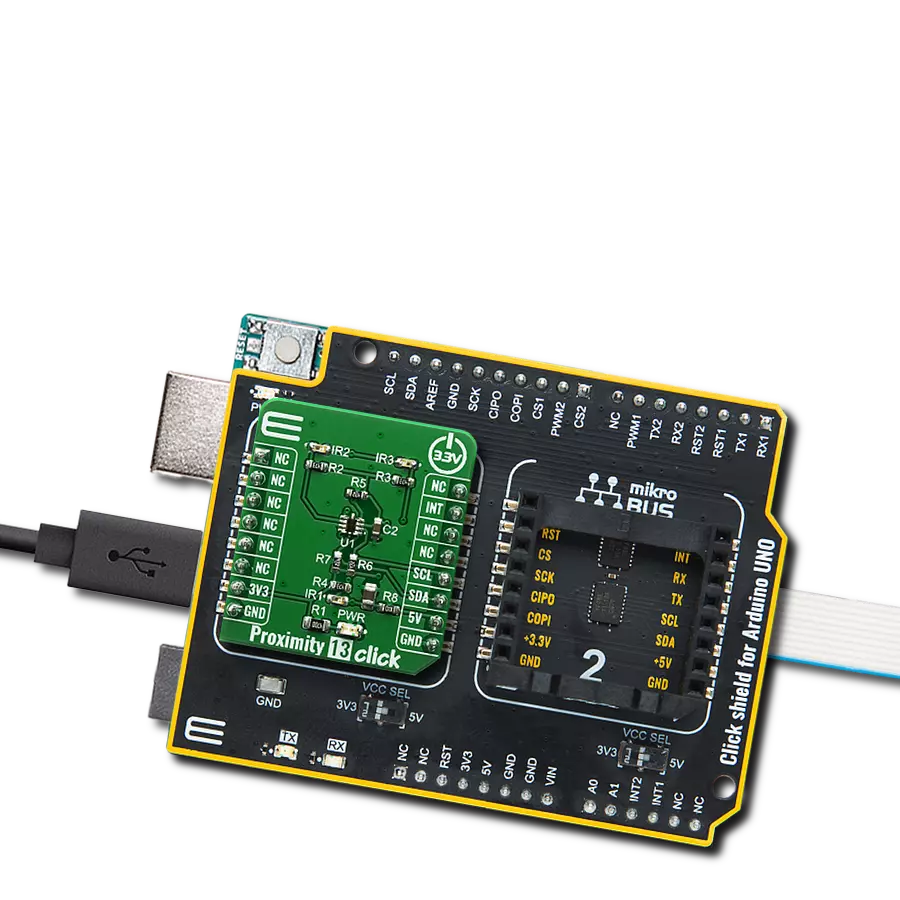
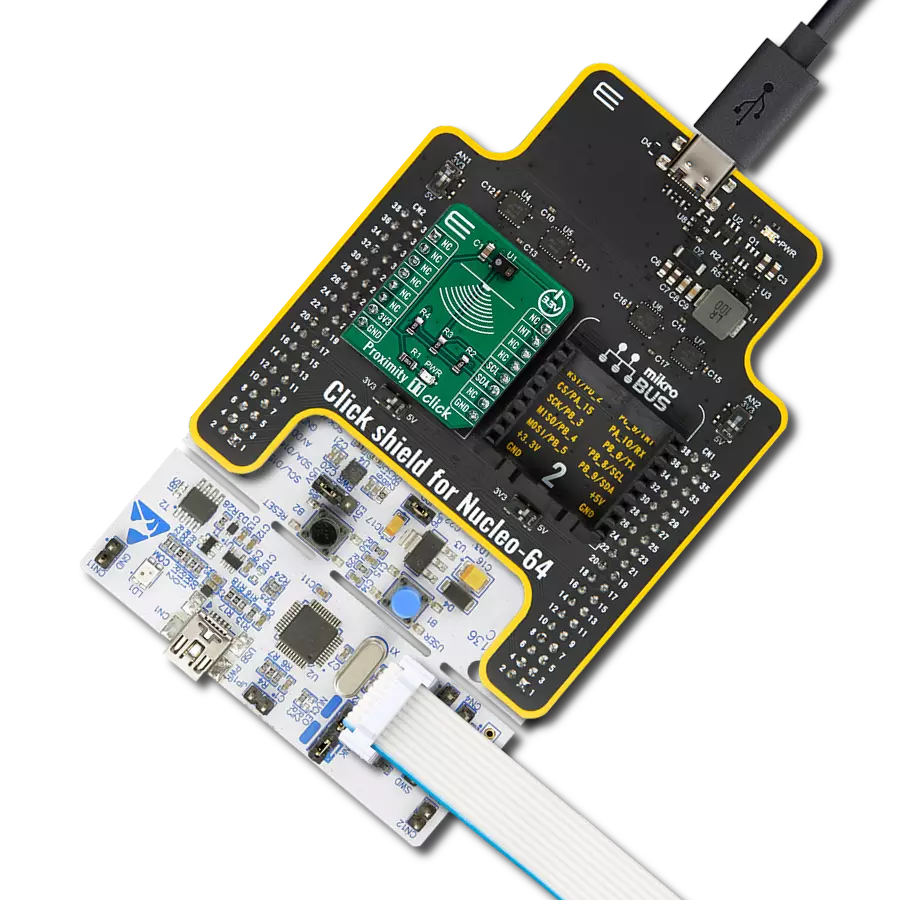
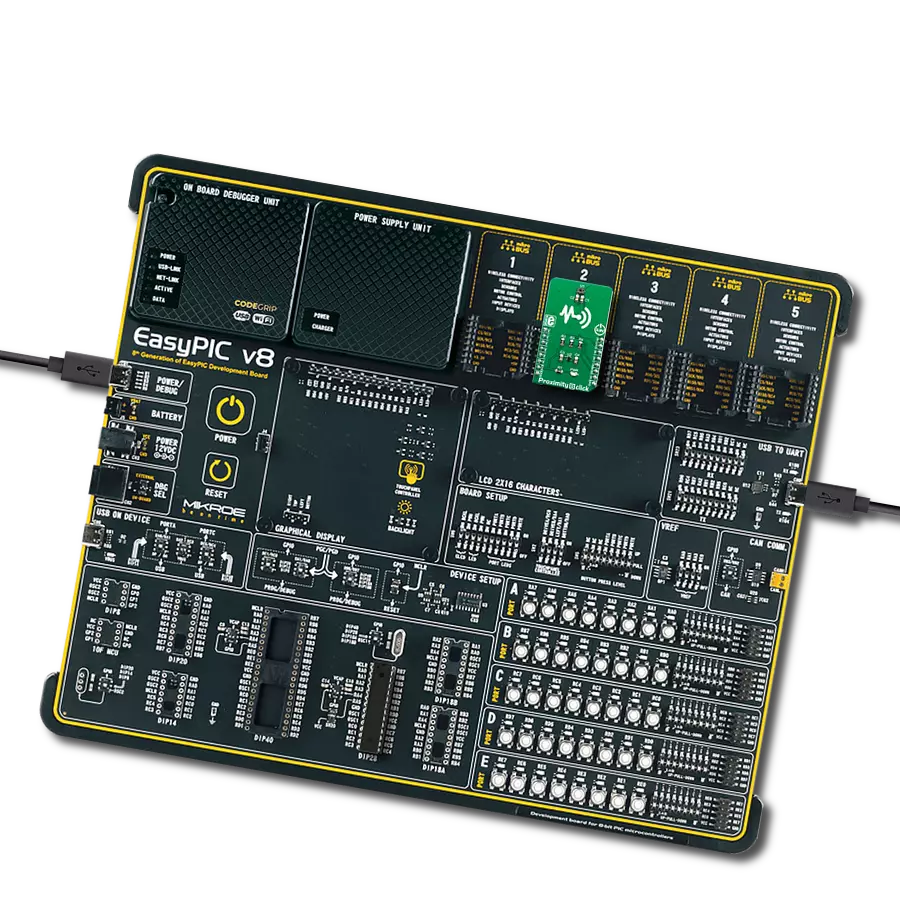
Enhance your projects with precise proximity sensing and reliable distance measurements, even in challenging ambient light conditions
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
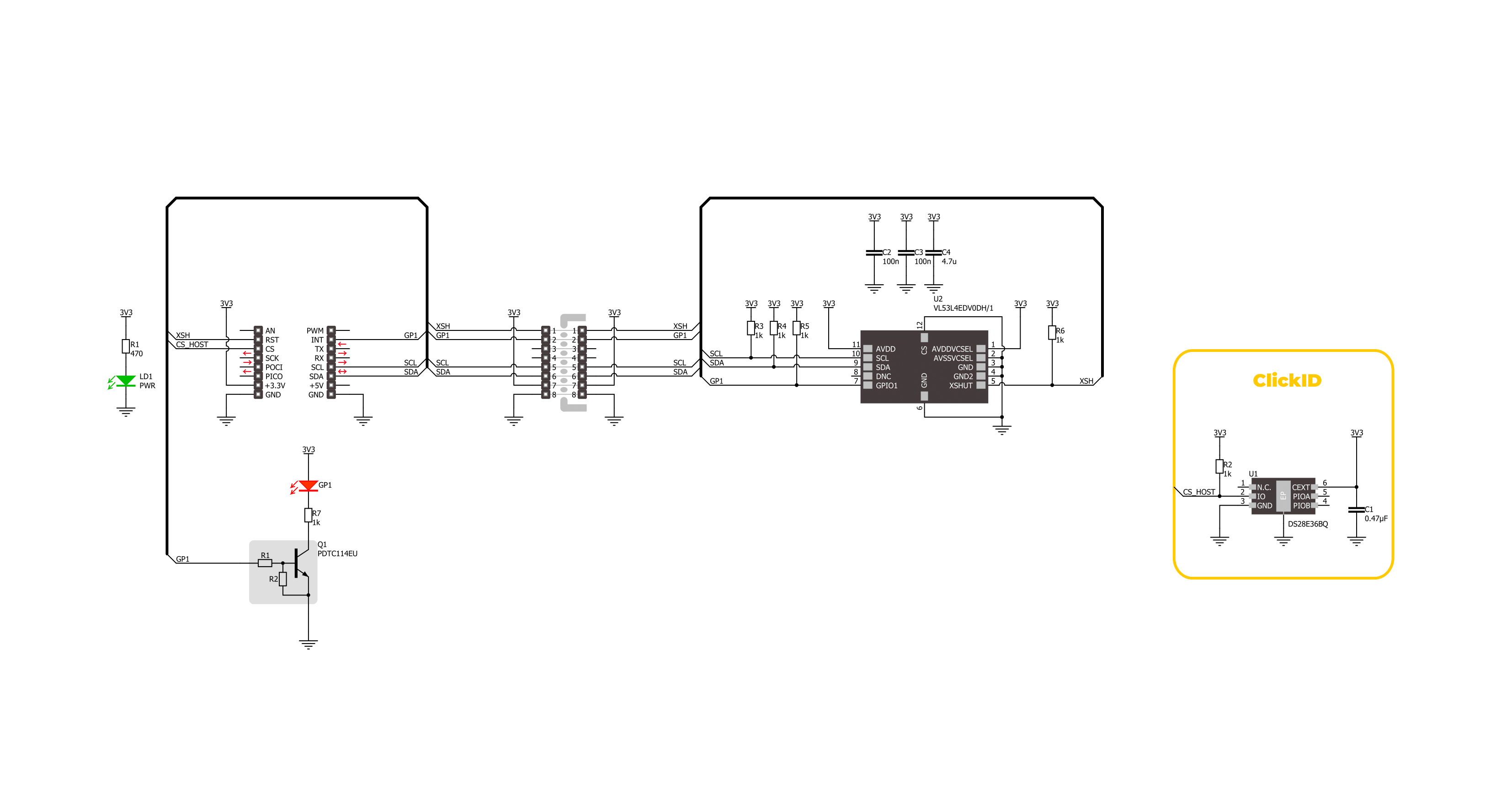
Proximity 21 Click is based on the VL53L4ED, a high-precision Time-of-Flight (ToF) proximity sensor from STMicroelectronics, known for its extended temperature capability. This sensor is made for accurate short-range measurements, offering a field of view (FoV) of 18° and measuring distances from 1mm up to 1300mm under standard conditions and up to 1150mm in extended temperature environments. The VL53L4ED operates effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 105°C, ensuring consistent performance even in harsh industrial settings. Additionally, it provides reliable distance measurements up to 800mm even in ambient light conditions of 5klx, making it ideal for applications requiring precise proximity sensing such as industrial automation, security systems, robotics, smart lighting, and biometric distance measurements. The VL53L4ED uses STMicroelectronics' FlightSense technology,
allowing it to measure absolute distances regardless of target color or reflectance. It includes a SPAD (single photon avalanche diode) array, enhancing its performance across ambient lighting conditions and various cover glass materials. Additionally, the sensor integrates a VCSEL (vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser) that emits an invisible 940nm IR light, certified as Class 1 eye-safe. Proximity 21 Click is designed in a unique format supporting the newly introduced MIKROE feature called "Click Snap." Unlike the standardized version of Click boards, this feature allows the main IC area to become movable by breaking the PCB, opening up many new possibilities for implementation. Thanks to the Snap feature, the VL53L4ED can operate autonomously by accessing its signals directly on the pins marked 1-8. Additionally, the Snap part includes a specified and fixed screw hole position, enabling users to secure
the Snap board in their desired location. This Click board™ uses a standard 2-wire I2C interface for communication with the host MCU, supporting Fast Mode Plus with a clock frequency of up to 1MHz. In addition to the interface pins, the sensor also uses the XSH shutdown pin from the mikroBUS™ socket for device power-up and boot sequence. The device can be fully powered down when not in use and then reactivated by the host MCU using the XSH pin. It also uses the GP1 pin from the mikroBUS™ socket as a hardware interrupt, along with a red GP1 LED indicator, to signal and visually indicate various conditions. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Clicker 2 for Kinetis is a compact starter development board that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It comes with an onboard 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4F microcontroller, the MK64FN1M0VDC12 from NXP Semiconductors, two mikroBUS™ sockets for Click board™ connectivity, a USB connector, LED indicators, buttons, a JTAG programmer connector, and two 26-pin headers for interfacing with external electronics. Its compact design with clear and easily recognizable silkscreen markings allows you to build gadgets with unique functionalities and
features quickly. Each part of the Clicker 2 for Kinetis development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the possibility of choosing the Clicker 2 for Kinetis programming method, using a USB HID mikroBootloader or an external mikroProg connector for Kinetis programmer, the Clicker 2 board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development kit. It provides two ways of board-powering; through the USB Micro-B cable, where onboard voltage regulators provide the appropriate voltage levels to each component on the board, or
using a Li-Polymer battery via an onboard battery connector. All communication methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board, including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, reset button, and several user-configurable buttons and LED indicators. Clicker 2 for Kinetis is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem, allowing you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
NXP
Pin count
121
RAM (Bytes)
262144
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Proximity 21 Click driver.
Key functions:
proximity21_get_gpio1_pin- This function returns the GPIO1 (interrupt) pin logic state.proximity21_get_result- This function gets the results reported by the sensor.proximity21_clear_interrupt- This function clears the data ready interrupt.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief Proximity 21 Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of Proximity 21 Click board by reading and displaying
* the target distance in millimeters on the USB UART.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and performs the Click default configuration.
*
* ## Application Task
* Waits for a data ready interrupt, then reads the measurement results and logs
* the target distance (millimeters) and signal quality (the higher the value the better
* the signal quality) to the USB UART.
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "proximity21.h"
static proximity21_t proximity21;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
proximity21_cfg_t proximity21_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
proximity21_cfg_setup( &proximity21_cfg );
PROXIMITY21_MAP_MIKROBUS( proximity21_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( I2C_MASTER_ERROR == proximity21_init( &proximity21, &proximity21_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
if ( PROXIMITY21_ERROR == proximity21_default_cfg ( &proximity21 ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Default configuration." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
proximity21_data_t results;
// Wait for a data ready interrupt
while ( proximity21_get_gpio1_pin ( &proximity21 ) );
if ( PROXIMITY21_OK == proximity21_get_result ( &proximity21, &results ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Distance [mm]: %u\r\n", results.distance_mm );
log_printf( &logger, " Signal [kcps/SPAD]: %u\r\n\n", results.signal_per_spad_kcps );
proximity21_clear_interrupt ( &proximity21 );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Proximity