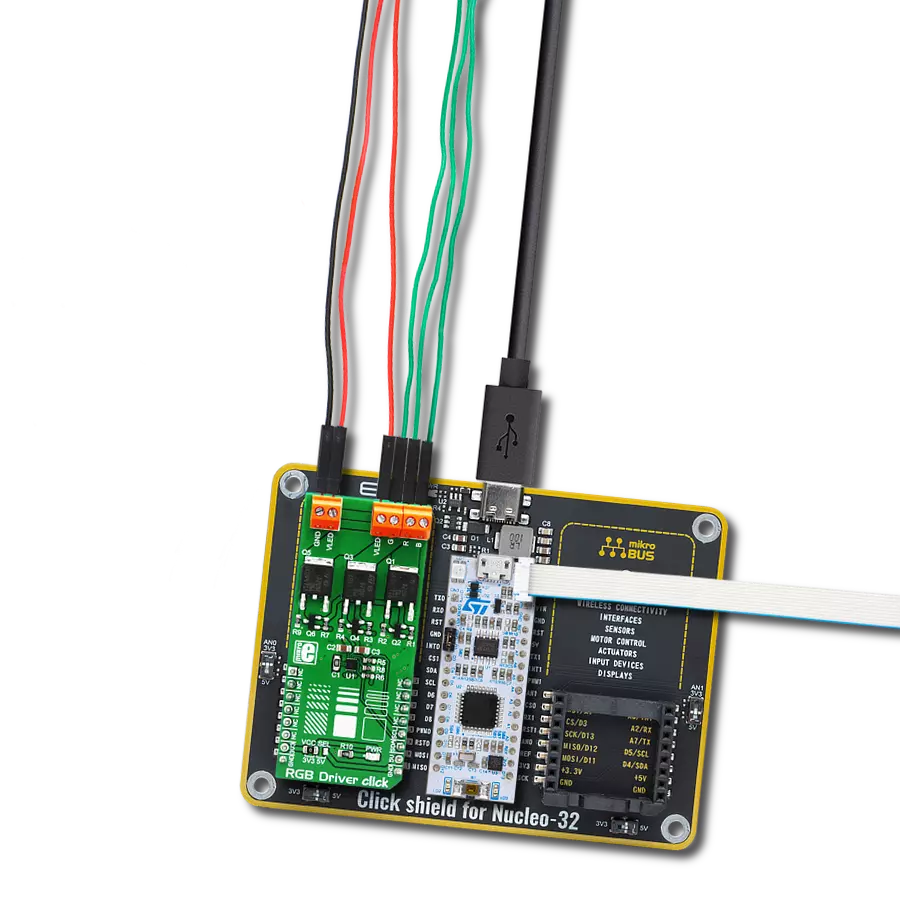
Empower your creativity by providing precise control over RGB LED strips, fixtures, and a wide range of RGB LED applications, allowing you to illuminate your world with captivating colors
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
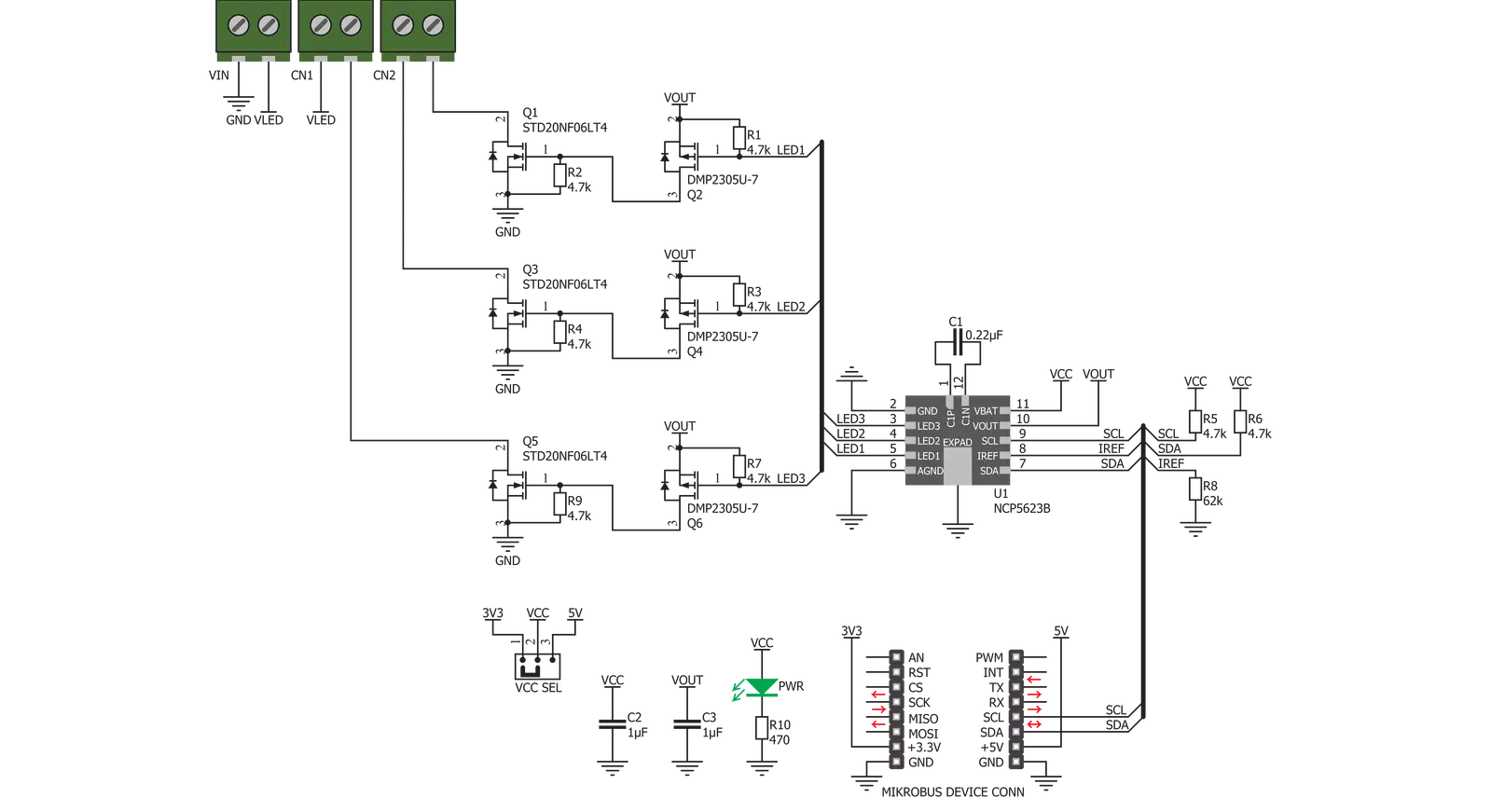
RGB Driver Click is based on the NCP5623B, a triple output RGB LED driver, controlled via the I2C interface, from ON Semiconductors. This IC is equipped with an internal DC/DC converter, that works as a high-efficiency charge pump, supplying all three LED segments. The current flow through each LED segment is regulated by an internal current mirror associated with each of the channels, and it is limited by an onboard resistor to about 20mA. To allow interfacing with LED strips and similar LED devices that require much higher voltages and currents than what NCP5623B is able to provide, the Click board™ utilizes additional power MOSFET elements. It uses STD20NF06LT4 N-Channel power MOSFETs, with very low RDSON of 0.03Ω, rated up to 60V. In practice, the maximum load will be determined by the power dissipation, but having in mind low RDSON value, these MOSFETs should withstand a reasonable amount of current, even with no additional heat sinks. The NCP5623B IC contains three integrated PWM structures, one for each channel. The PWM signal is used to modulate current from the DC/DC converter. The intensity of this current can be set
via I2C registers. Since there are MOSFETs instead of LEDs connected at the output stage of the IC, changing current will not affect the connected LED light intensity. Therefore, the only way to modify the intensity of the connected LEDs is to control the duty cycle of the internal PWM structures, for each LED channel. There are five bits used to control the duty cycle of the internal PWMs, resulting in 32 color steps per channel. Since the driver IC is constructed so its output drivers sink current from an internal charge pump DC/DC converter, additional P-channel low power MOSFETs are used to drive the gates of the N-channel Power MOSFETs. This allows current to sink from the external power supply source, connected load (LEDs), through the Power MOSFETs, and to the GND. This configuration allows for much higher voltage and current ratios than with the NCP5623B alone. The anodes of the LED channels are connected to the positive rail of the external power supply (labeled as VLED), while the cathodes of the red, green, and blue channels are connected to the terminals labeled as R, G, and B, respectively. The voltage of the external power
supply is determined by the requirements of the LEDs. For example, if the connected LED strip requires 12V, the voltage of the connected external voltage supply should also be 12V. The external power supply voltage should stay below 60V, as it is the breakdown voltage of the output MOSFETs. SCL and SDA lines of the IC are routed to the mikroBUS™ and allow secure and simple connection with the host MCU. The Click board™ is capable of interfacing to both 3.3V and 5V MCUs. This can be done by switching the small SMD jumper labeled as VCC SEL to the required position, selecting the appropriate logic voltage level. Output screw terminals are used to securely connect the LED power supply, as well as the R, G, and B LED channels. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
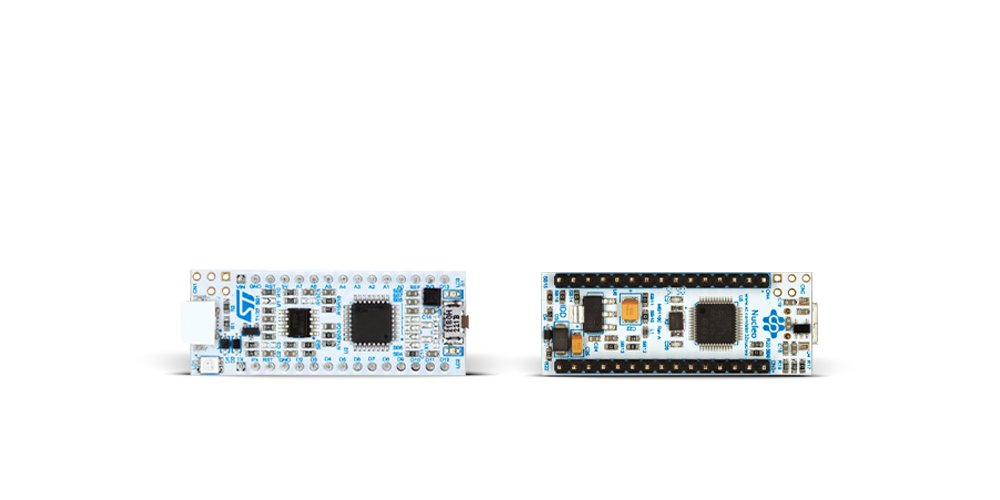
Development board
Nucleo 32 with STM32F031K6 MCU board provides an affordable and flexible platform for experimenting with STM32 microcontrollers in 32-pin packages. Featuring Arduino™ Nano connectivity, it allows easy expansion with specialized shields, while being mbed-enabled for seamless integration with online resources. The
board includes an on-board ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger/programmer, supporting USB reenumeration with three interfaces: Virtual Com port, mass storage, and debug port. It offers a flexible power supply through either USB VBUS or an external source. Additionally, it includes three LEDs (LD1 for USB communication, LD2 for power,
and LD3 as a user LED) and a reset push button. The STM32 Nucleo-32 board is supported by various Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) such as IAR™, Keil®, and GCC-based IDEs like AC6 SW4STM32, making it a versatile tool for developers.
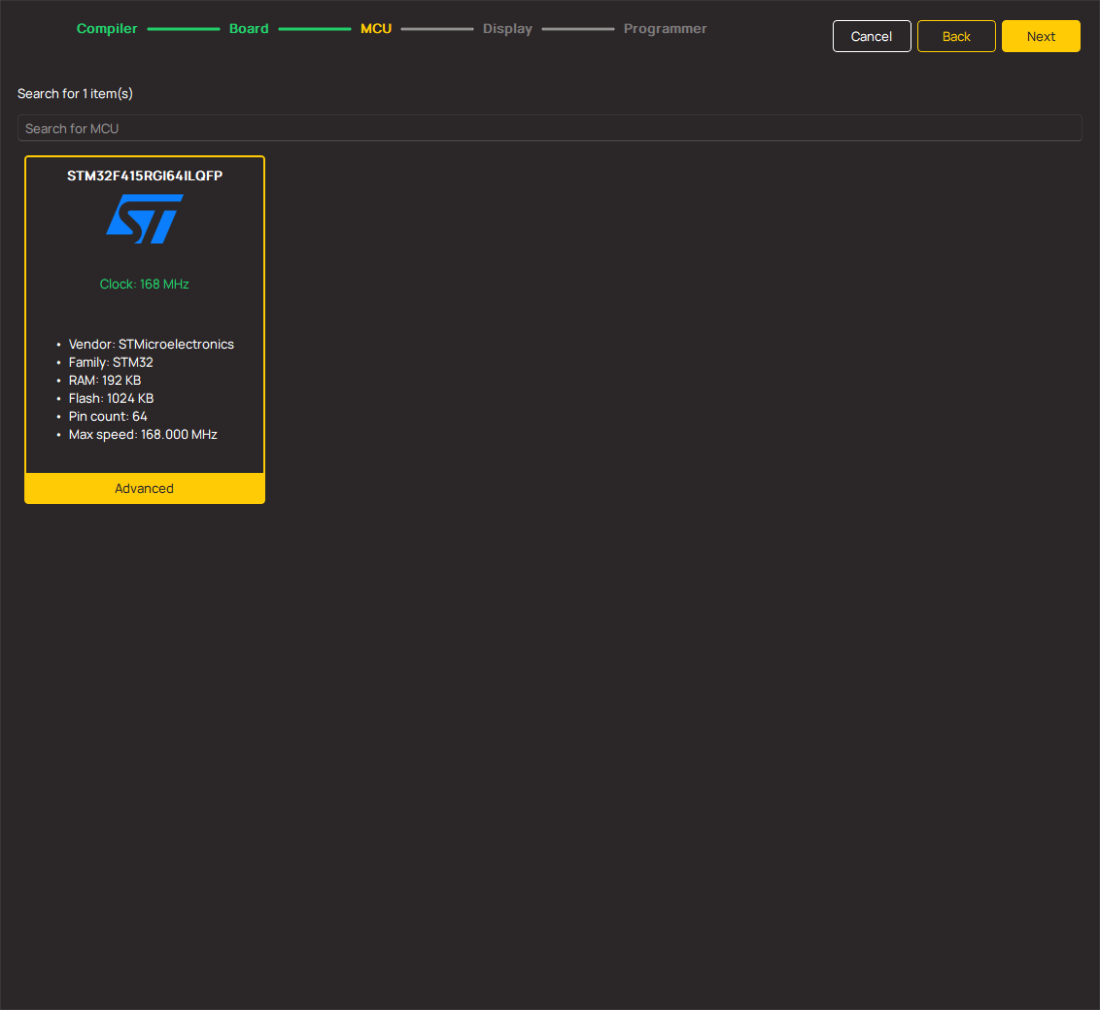
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M0
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
32
RAM (Bytes)
4096
You complete me!
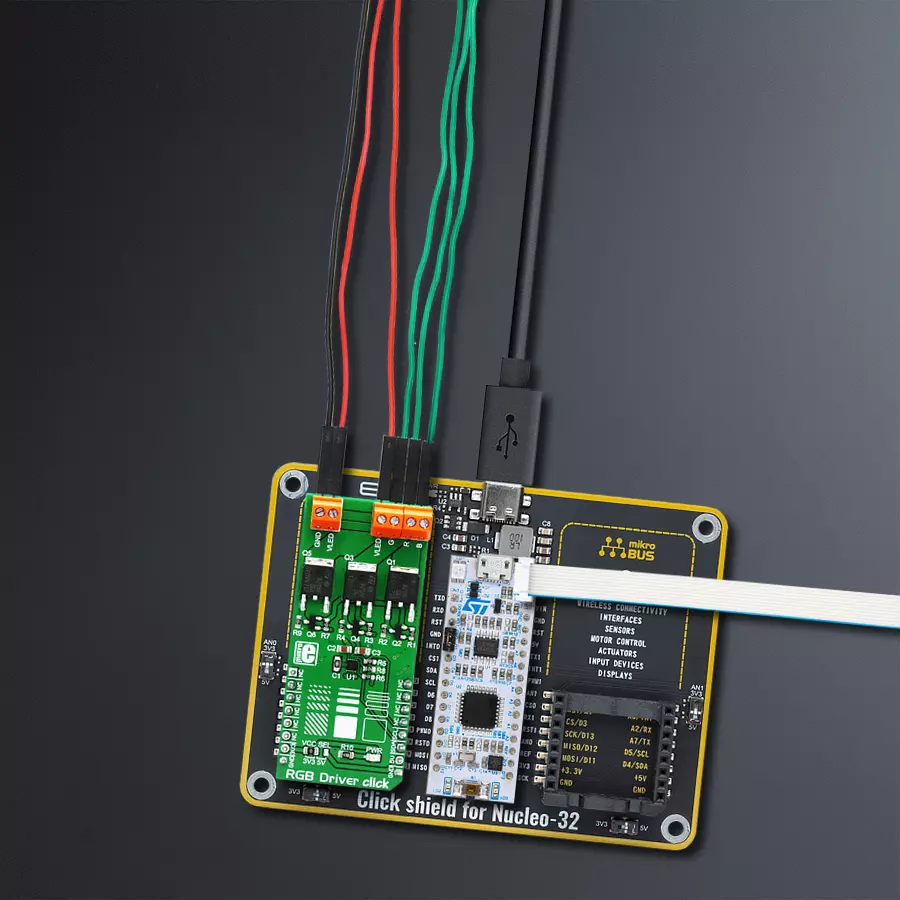
Accessories
Click Shield for Nucleo-32 is the perfect way to expand your development board's functionalities with STM32 Nucleo-32 pinout. The Click Shield for Nucleo-32 provides two mikroBUS™ sockets to add any functionality from our ever-growing range of Click boards™. We are fully stocked with everything, from sensors and WiFi transceivers to motor control and audio amplifiers. The Click Shield for Nucleo-32 is compatible with the STM32 Nucleo-32 board, providing an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new ideas and quickly create prototypes with any STM32 microcontrollers, choosing from the various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The STM32 Nucleo-32 boards do not require any separate probe as they integrate the ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger/programmer and come with the STM32 comprehensive software HAL library and various packaged software examples. This development platform provides users with an effortless and common way to combine the STM32 Nucleo-32 footprint compatible board with their favorite Click boards™ in their upcoming projects.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for RGB Driver Click driver.
Key functions:
rgbdriver_set_rgb_color- This function sets the color of the rgb LEDs through the parameters for red, green and bluergbdriver_set_color- This function sets the colorrgbdriver_shut_down- This function shut down device.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief RgbDriver Click example
*
* # Description
* This application sets the brightness over RGB value.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes driver and logger, and configures the Click board.
*
* ## Application Task
* Changes the color of RGB LED tape connected to the Click board every 2 seconds.
* The name of the selected color will be displayed on USB UART.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "rgbdriver.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static rgbdriver_t rgbdriver;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
rgbdriver_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
rgbdriver_cfg_setup( &cfg );
RGBDRIVER_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
rgbdriver_init( &rgbdriver, &cfg );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
rgbdriver_default_cfg( &rgbdriver );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
rgbdriver_set_color( &rgbdriver, RGBDRIVER_COLOR_RED_LOW_INTENSITY );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n--- RED ---\r\n" );
Delay_1sec( );
Delay_1sec( );
rgbdriver_set_color( &rgbdriver, RGBDRIVER_COLOR_ORANGE_LOW_INTENSITY );
log_printf( &logger, "--- ORANGE ---\r\n" );
Delay_1sec( );
Delay_1sec( );
rgbdriver_set_color( &rgbdriver, RGBDRIVER_COLOR_YELLOW_LOW_INTENSITY );
log_printf( &logger, "--- YELLOW ---\r\n" );
Delay_1sec( );
Delay_1sec( );
rgbdriver_set_color( &rgbdriver, RGBDRIVER_COLOR_GREEN_LOW_INTENSITY );
log_printf( &logger, "--- GREEN ---\r\n" );
Delay_1sec( );
Delay_1sec( );
rgbdriver_set_color( &rgbdriver, RGBDRIVER_COLOR_BLUE_LOW_INTENSITY );
log_printf( &logger, "--- BLUE ---\r\n" );
Delay_1sec( );
Delay_1sec( );
rgbdriver_set_color( &rgbdriver, RGBDRIVER_COLOR_WHITE_LOW_INTENSITY );
log_printf( &logger, "--- WHITE ---\r\n" );
Delay_1sec( );
Delay_1sec( );
rgbdriver_set_color( &rgbdriver, RGBDRIVER_COLOR_PURPLE_LOW_INTENSITY );
log_printf( &logger, "--- PURPLE ---\r\n" );
Delay_1sec( );
Delay_1sec( );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:LED Segment